Private 5G networks are cutting-edge wireless telecommunications technologies exclusively owned and operated by a single entity or organization. Unlike public 5G networks, managed by a telecommunications provider and serving a wide range of users, private 5G networks are customized to meet the unique security and reliability requirements of the owner or organization that manages them.
By leveraging private 5G networks, businesses can enjoy unprecedented flexibility when designing their network platform and services. The enhanced privacy and security offered by private 5G networks ensure that sensitive data and communications are protected from unauthorized access. Moreover, the scalability of these networks allows businesses to quickly adapt and expand their network capabilities as their needs evolve.
In addition to privacy, cybersecurity, and scalability advantages, private 5G networks offer significant cost savings compared to public 5G networks. Businesses can optimize resource allocation and minimize unnecessary expenses by having full control over their network platform.
Private 5G networks empower organizations with a comprehensive and tailored solution that addresses their specific requirements, enabling them to benefit from advanced connectivity and unlock new opportunities for innovation and growth.
The State of Private 5G Networks
As the adoption of private 5G networks continues to accelerate, enterprises must understand the security landscape surrounding these networks. Omdia interviewed 150 enterprises and 150 service providers to gain insights into the current state of enterprise private 5G network security. The study encompassed various industries across multiple countries.
The study revealed that 58% of enterprises had already deployed private 5G networks, while the remaining 42% planned to do so within the following year. Among the deployed networks, only 35% were in production, with 65% in the proof-of-concept stage. However, a significant portion (46%) is expected to transition from proof of concept to show within the coming year. Organizations primarily deployed private 5G networks to improve operational efficiency, expand connectivity, and lower operating costs.
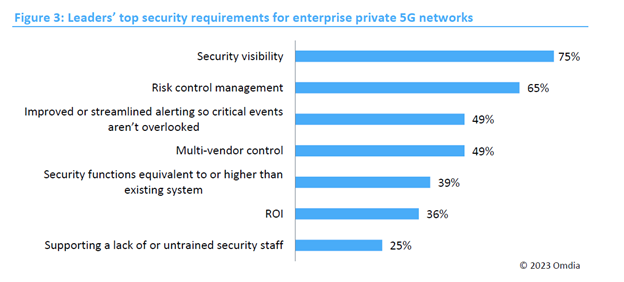
Despite expecting cost savings, 60% of enterprises acknowledged the need for new security measures to integrate private 5G network security with their existing platform. Leaders within organizations prioritized security visibility, risk control management, streamlined alerting, multi-vendor control, and equivalent or enhanced security functions compared to their current systems. On the other hand, the overall view focused more on authentication and access control.
Most enterprises anticipated managing the planning, deployment, and operation of the private 5G network core, IoT endpoints, and data network. However, they relied on service providers or suppliers to plan, deploy, and operate the radio access network (RAN) and multi-access edge computing (MEC).
This shared-responsibility model necessitates a collaborative approach to security, with enterprises securing their on-premises elements and service providers connecting the RAN and the enterprise edge. Enterprises planned to allocate 5-10% of their IT budgets to 5G private network security.
Enterprises preferred security-specific vendors when acquiring security solutions for private 5G networks. However, only some enterprises were familiar with the 5G security supplier solutions, suggesting a potential gap in awareness and knowledge.
Future Challenges and Solutions
Adopting private 5G networks brings about several challenges that organizations need to address. Let's delve deeper into some of these challenges and potential solutions:
Many organizations already have established security platform to protect their networks. Integrating private 5G networks with this platform seamlessly can be challenging, especially since 5G introduces new architectural elements and protocols.
Organizations should invest in security solutions that can be easily integrated with their existing platform to overcome this challenge.
The 3GPP standards for private 5G networks are still evolving, and security protocols and best practices may have gaps. This lack of standardized guidelines can lead to inconsistencies in security implementations across different private 5G networks.
Organizations should actively participate in industry standardization efforts to shape the security guidelines for private 5G networks. In the interim, they can collaborate with security vendors and experts to develop best practices tailored to their specific network requirements.
Private 5G networks often involve shared responsibility between the network operator and the enterprise deploying the network. Determining the exact responsibilities of each party and ensuring a consistent and robust cyber security posture can be complex.
Clearly defining the roles and responsibilities of all stakeholders involved in the private 5G network is essential. Organizations should establish Service Level Agreements (SLAs) that outline cyber security requirements, incident response procedures, and accountability measures for both the network operator and the enterprise.
As private 5G networks become critical for mission-critical applications and handle sensitive data, they become prime targets for cyber-attacks. Threat actors may exploit vulnerabilities in the 5G infrastructure or use advanced attack techniques to gain unauthorized access.
Organizations should adopt a multi-layered security approach to mitigate cyber security risks. This includes using next-generation firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, encryption, and regular security audits to identify and remediate vulnerabilities promptly. Continuous monitoring and threat intelligence can also help detect and respond to potential threats in real time.
Private 5G networks offer tremendous opportunities for enterprises but require careful consideration of security challenges. By integrating new security measures, actively participating in standardization efforts, clarifying responsibilities, and adopting a multi-layered security approach, organizations can harness the potential of private 5G networks while safeguarding their operations and sensitive data. Investing in cyber security-specific vendors and service providers will also ensure a robust security posture in this dynamic and evolving environment.
To read a full copy of the report with Omdia and Trend Micro,CTOne, please visit: https://resources.trendmicro.com/IoT_Beyond-Secure-Omdia-Report.html

