Phobos Emerges as a Formidable Threat in Q1 2024, LockBit Stays in the Top Spot: Ransomware in Q1 2024
Updated to add new data and insights on May 23, 2024
LockBit stays as most active group, with dark horse Phobos and 8Base coming in second
Trend threat intelligence revealed that ransomware groups started relatively slow this year, with 2,661,519 ransomware threats detected and blocked by Trend Micro across email, URL, and file layers. This is less than half of the detected and blocked ransomware threats recorded in the first half of 2023, which racked up 6.7 million total detections.
Despite recent setbacks and an observed decline, LockBit takes the top spot with 1,360 detections, making up 3.1% of the total ransomware families in terms of file detection in the first quarter of this year, topping the list across all three months. However, the high number of detections could be attributed to various ransomware groups using the leaked LockBit 3.0 ransomware builder; this includes groups affiliated with LockBit, as well as those unaffiliated with the gang, such as DragonForce and Bl00dy. Prior to its takedown, we came into possession of a sample that we believe to be LockBit’s latest version, an in-development version of a platform-agnostic malware-in-testing we are tracking as LockBit-NG-Dev. We believe this would have formed the basis of a LockBit 4.0 that the group can be assumed to have been working on.
LockBit is known to exploit the CVE-2018-13379 vulnerability, which entered the top twenty CVEs detected by our Home Network Security for the month of March with 249,600 digital vaccine hits.
Our analysis of ransomware-as-a-service groups’ leak site and open-source intelligence (OSINT) research reveal that 8Base ransomware is making bold strides in its extortion, coming after LockBit in most active RaaS groups. 8Base ties with notorious BlackBasta at 69 declared victims for the first quarter of 2024, while LockBit continues to hold the top spot with 217 declared victims.
Data from leak sites, on which ransomware operators publish successful attacks showed there were 1,023 total victims of the 48 active ransomware groups in the first quarter of 2024, 22.6% of last year’s total victim count of 4,523.
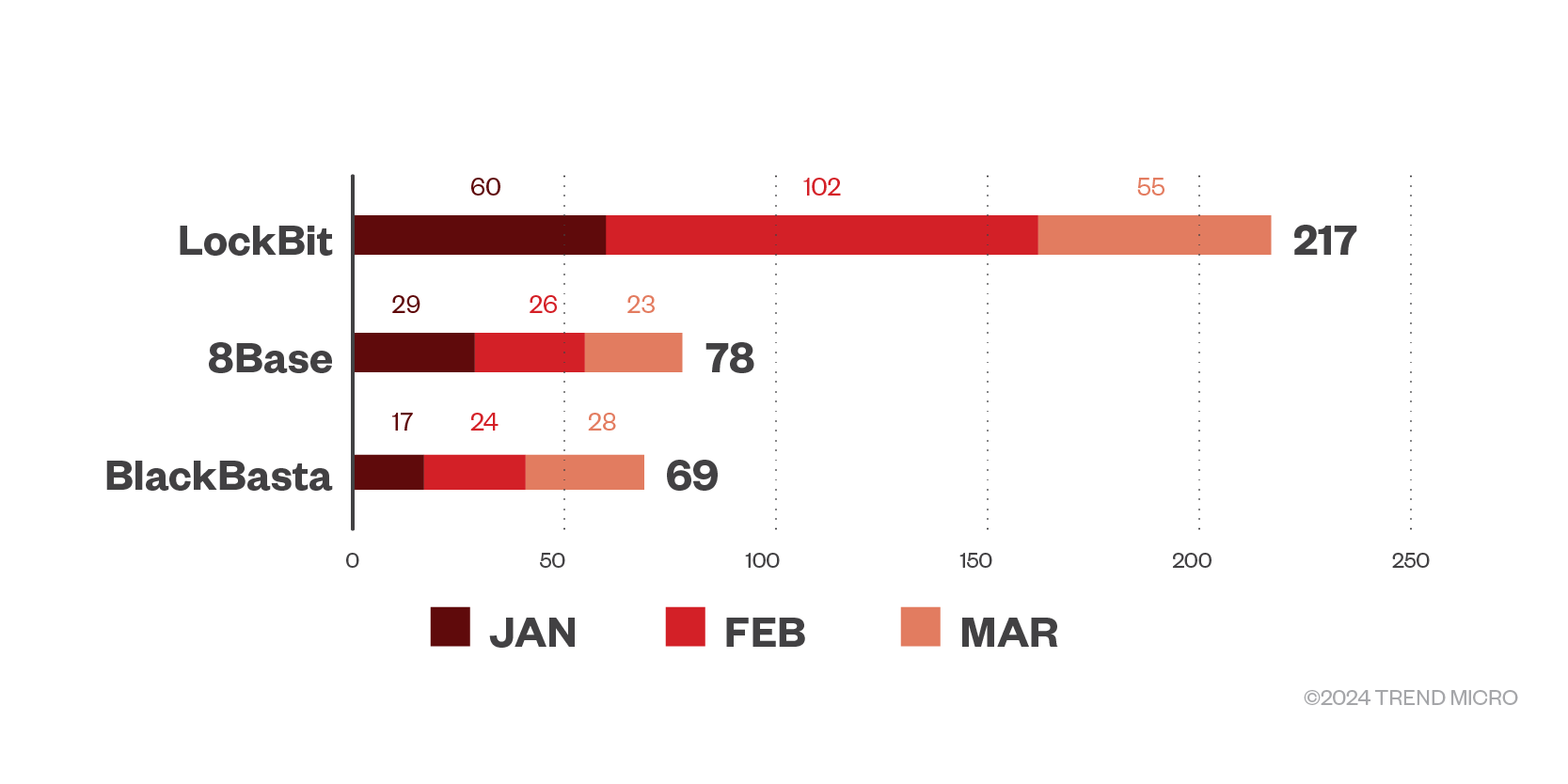
Figure 1. The number of victims declared by the top three RaaS groups per month in the first quarter of 2024.
Source: RaaS and extortion groups’ leak sites and Trend’s OSINT research
The 8Base ransomware positions itself as “penetration testers” and adopts a name-and-shame tactic, claiming in its leak site to exclusively target organizations that “have neglected the privacy and importance of the data of their employees and customers.” In October 2023, it targeted healthcare and public health sector organizations in the United States, where the Health Sector Cybersecurity Coordination Center (HC3) published an analyst note about the group.
Our investigation of 8Base ransomware reveals that the group has been observed to use Phobos ransomware version 2.9.1. This version uses SmokeLoader for initial obfuscation for ingress, unpacking, and loading of the payload.
Interestingly, our customer telemetry reveals that Phobos ransomware also follows LockBit in terms of detections, making up 1.5% of detections in the first quarter. Phobos ransomware detections peaked in March alongside LockBit; the former had 240 detections, almost half of the latter’s 576 detections. This rise in detection from Phobos could be attributed to the 8Base gang’s RaaS activity and their use of the former’s variant.
Phobos ransomware activity has been reported since 2019; in February this year, the US Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) published a cybersecurity advisory on the gang’s modus operandi.
Meanwhile, StopCrypt followed closely behind Phobos, making up 1.4% of the first quarter detections in 2024. The gang was most active in January with almost the same number of detections as Phobos, at 238, 35.5% less than LockBit’s 369 detections for that month. Earlier this year, a new StopCrypt variant with a multistage execution process using shellcodes for evasion was observed in the wild.
The relatively new player, TargetCompany, comes in fourth, with 571 total hits in the first quarter, making up 1.3% of total detections. Major player Conti follows closely behind with 554 detections; It should be noted that our telemetry detects the LockBit Green version as Conti, from which the version is based. Conti’s high number of detections could also be attributed to other ransomware groups using its leaked ransomware. While it didn’t make the top five most prolific ransomware families in the first quarter of this year, notorious BlackCat follows Conti by file detection, with 496 hits.
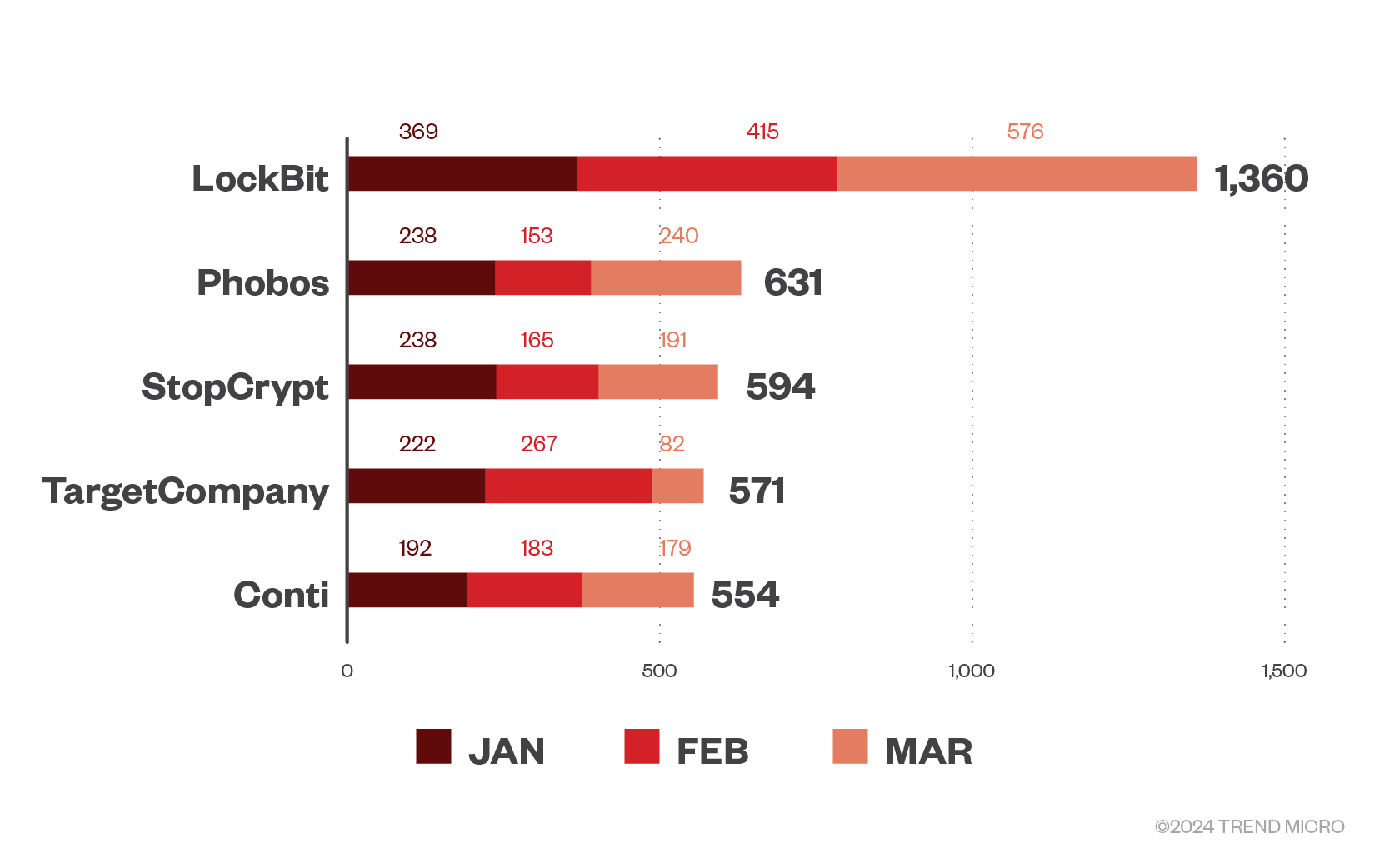
Figure 2. The top five ransomware families in machines per month for the first quarter of 2024, in terms of file detections
Source: Trend threat intelligence
Enterprises took the brunt of ransomware attacks in the first quarter
Ransomware actors targeted enterprises the most, with attacks peaking in March at 11,804, or 78.2%. Curiously, gangs focused the least on small- and medium-sized business in the first quarter of 2024, with attacks on this segment making up only 6.7%. This is in contrast to last year, when small businesses were more commonly targeted; it is assumed that small- and medium-sized businesses are more favorable targets due to their security infrastructure limitations.
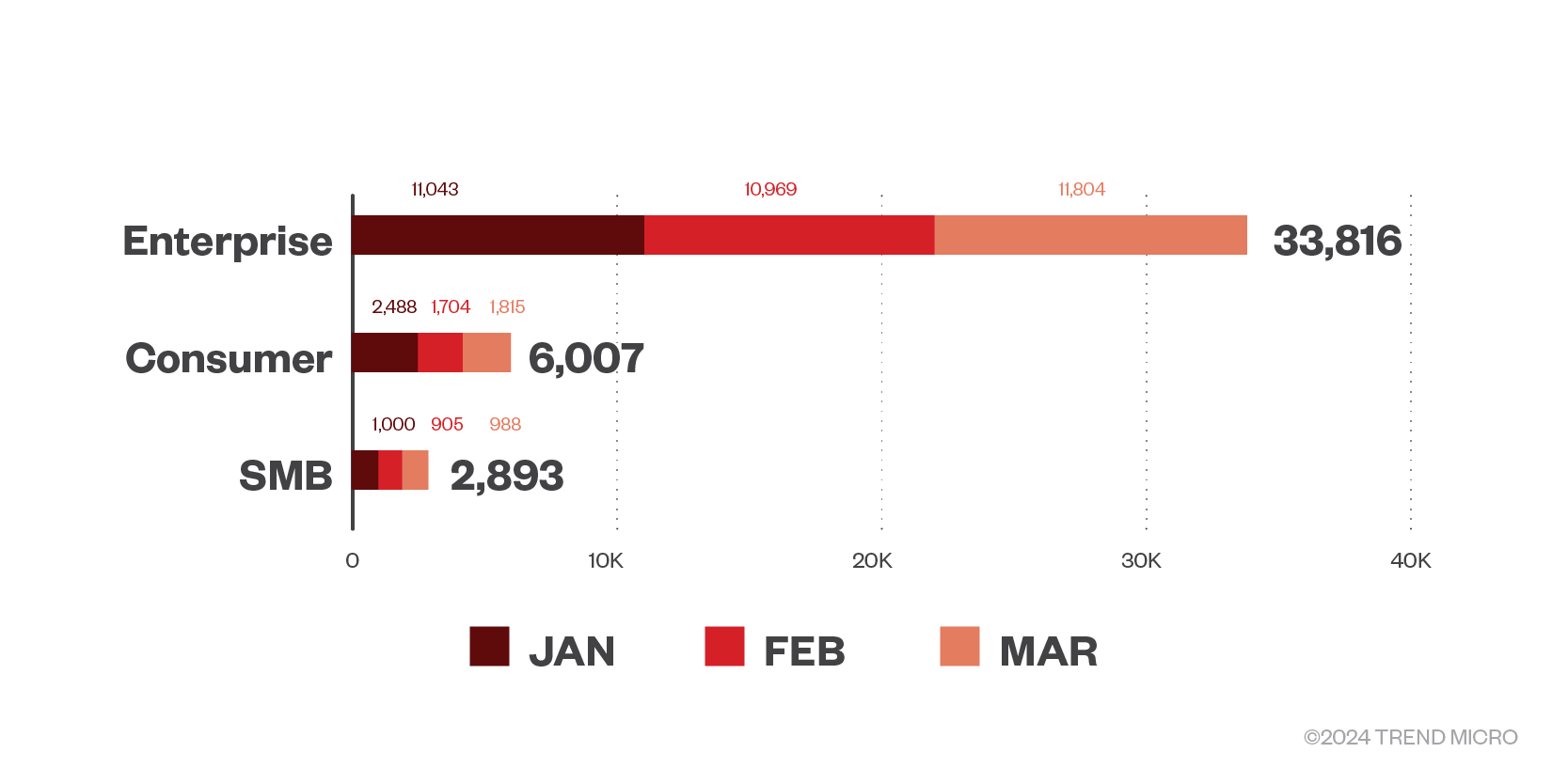
Figure 3. The distribution by business segment with the most ransomware detections in the first quarter of 2024 in terms of file detections
LockBit hit enterprises the most with Conti and BlackCat coming in fourth and fifth in terms of most active ransomware families targeting enterprises in the first quarter of 2024.
TargetCompany left an impression making up 1.5%, overtaking Phobos in targeting that business segment. TargetCompany has been observed to attack vulnerable database servers. In 2023, its latest version, Xollam, jumped on the phishing trend using malicious OneNote files to gain initial access to its victim’s systems.
LockBit also topped the ransomware families that targeted small- and medium-sized businesses, but its attacks on the segment is only a measly 2.0% of its total attacks in terms of file detections. Meanwhile, StopCrypt takes the top spot in families that hit consumer businesses.
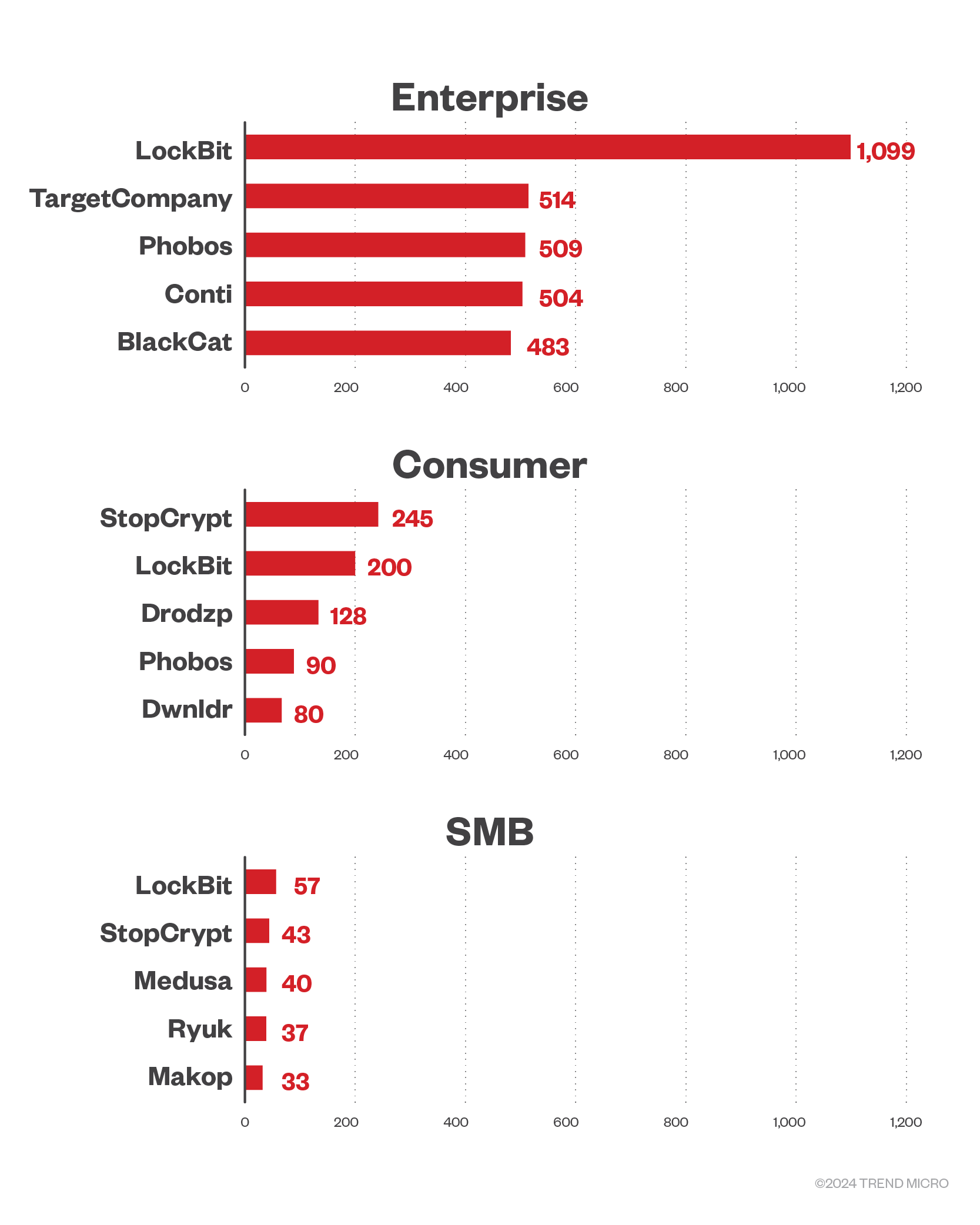
Figure 4. The top five ransomware families that targeted enterprises, consumer, and small- to medium-sized businesses in terms of file detections
Banking was the most targeted industry in Q1 2024
Ransomware gangs continue to target the banking sector the most in the first quarter of 2024 as it did in the second half of last year; this focus could be attributed to the continuous adoption of cryptocurrencies in that industry, and that the banking sector is among the industries with inherent characteristics that make for a wide attack surface.
Government sectors remain a favored target as conflicts between countries continue, followed by the technology sector. Previously a hot target during and after the pandemic, the healthcare industry has dropped to sixth place.
Conti and BlackCat were part of the top ransomware families in the top targeted sectors across three months, except for the tech sector in February when Akira, Egogen, and Phobos were the most active.
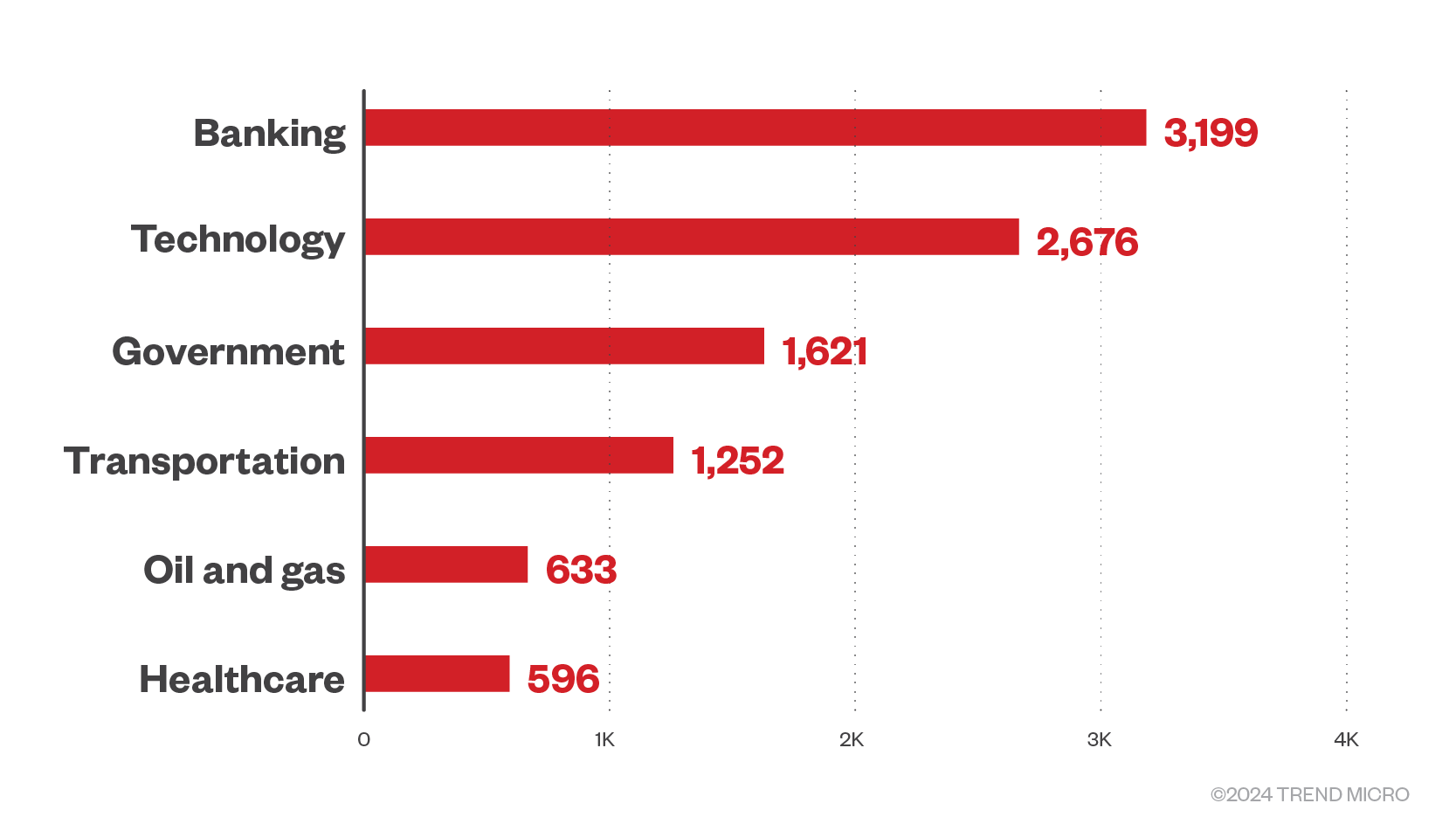
Figure 5. The top six industries targeted by ransomware families in the first quarter of 2024 by file detection
RaaS groups, on the other hand, focused their efforts on enterprises in the manufacturing sector, continuing the pattern established from the second half of 2023. This could be attributed to the increase in interconnectivity in the supply chain brought by the continued adoption of IIoT, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence that expands the attack surface. The manufacturing sector is also known to use legacy systems (which are prime exploit targets), making it a more attractive target to threat actors. This is true globally, with 25% of cyberattacks targeted at the manufacturing sector.
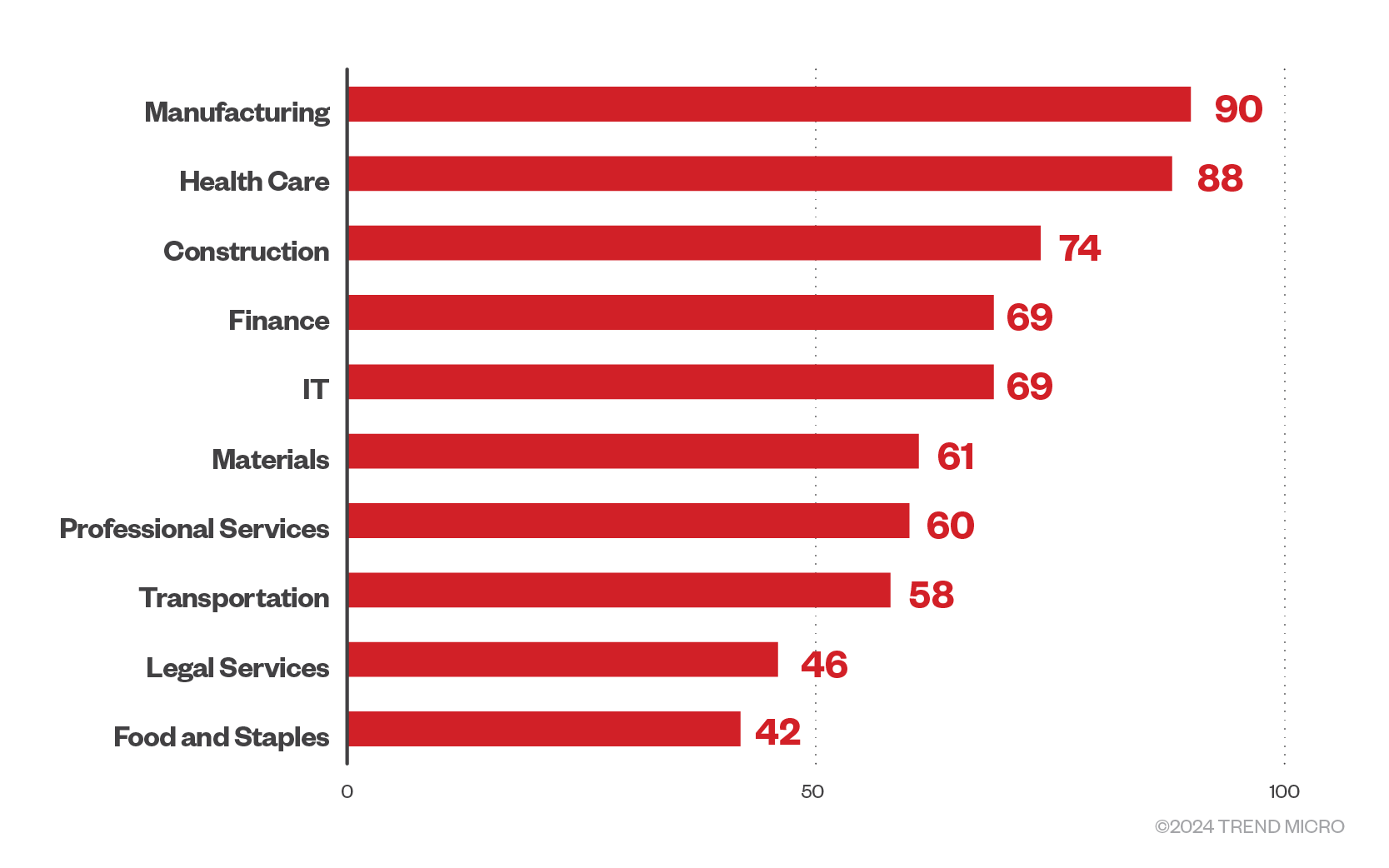
Figure 6. The top ten sectors targeted by RaaS groups in the first quarter of 2024.
Source: RaaS and extortion groups’ leak sites and Trend’s OSINT research
All three of the most active RaaS groups focused their energy on small businesses for the first quarter of 2024; this tactic has already been observed, as smaller organizations typically have less resources to respond to and recover from attacks.
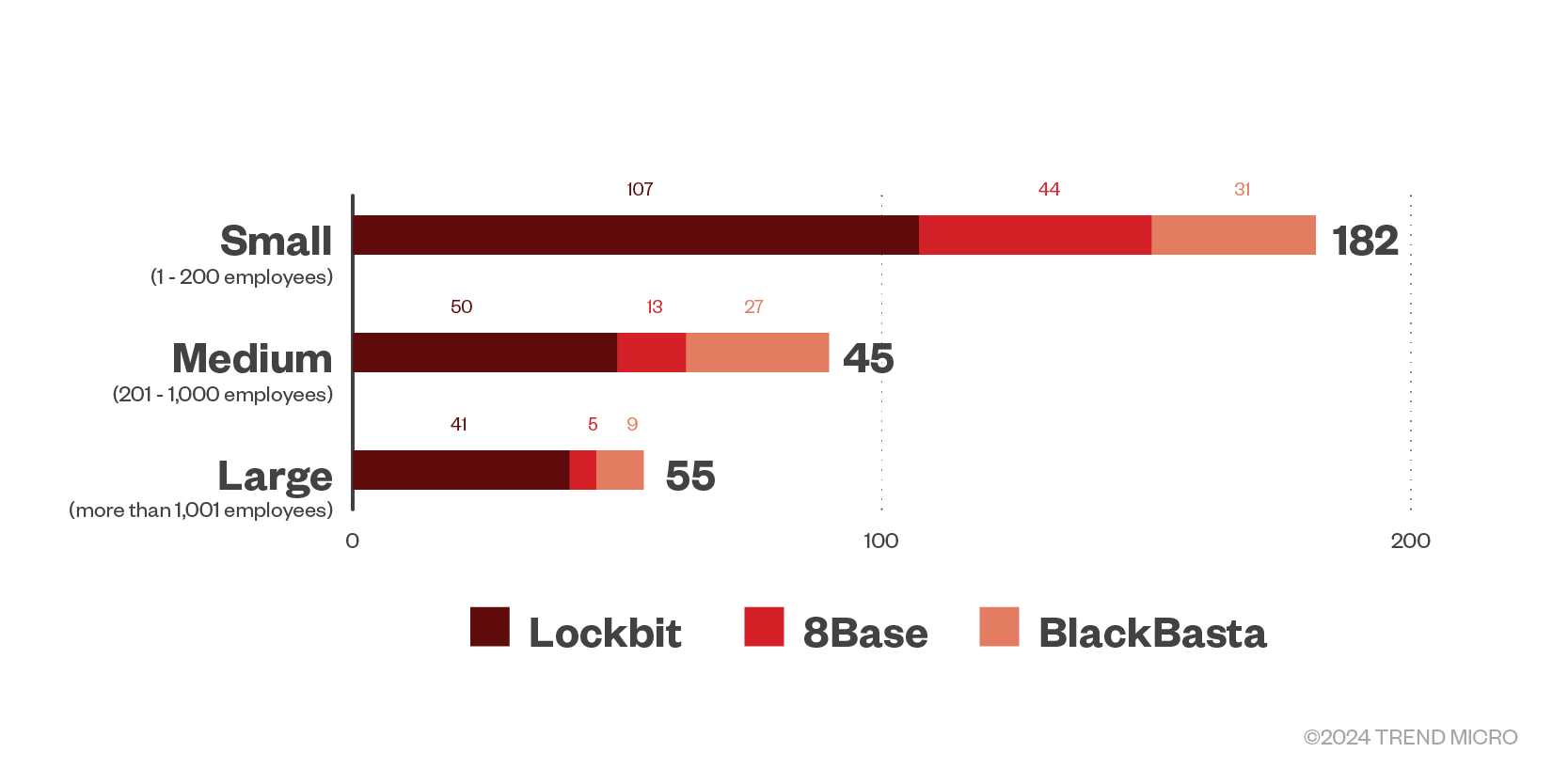
Figure 7. The distribution by organization size of LockBit, 8Base, and BlackBasta ransomware’s successful attacks in terms of victim organizations in the first quarter of 2024.
Source: RaaS and extortion groups’ leak sites and Trend’s OSINT research
Organizations in Turkey make up over a quarter of the victim count in the Q1 2024
Our threat intelligence showed that Turkey recorded 6,310 hits in terms of ransomware file detections, making up 14.6% of the total detections in the first quarter of 2024. Spikes like this have been previously observed in this region.
The United States comes in second with 5,052 detections, or 11.7%; previously, the United States held the top spot in terms of successful ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) and extortion attacks, according to ransomware group leak sites and Trend’s OSINT research.
Germany follows the US closely, making up 11.3% of the quarter’s detections, while Japan and Kuwait round out the top five countries most targeted by ransomware actors in the first quarter of 2024.
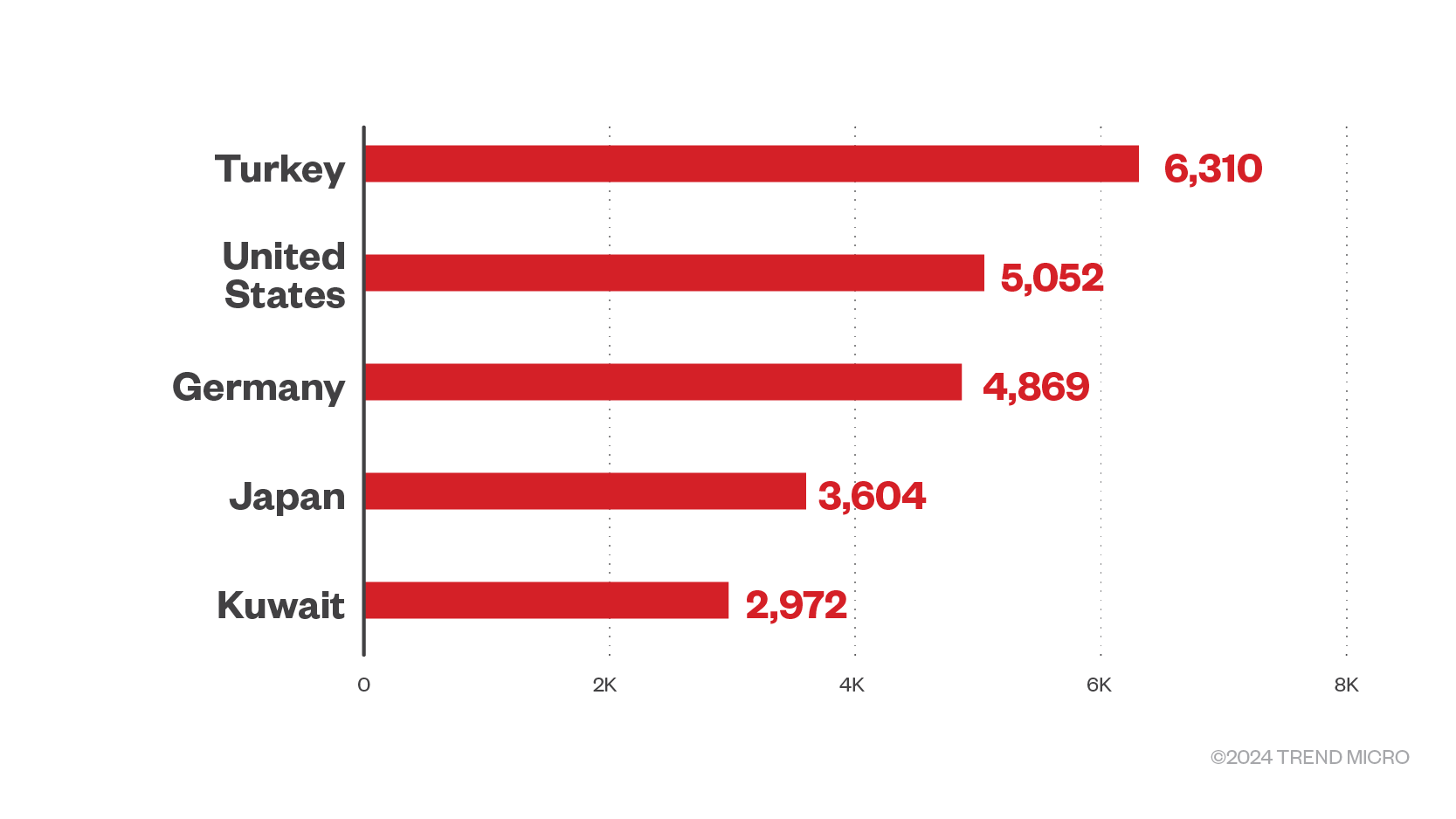
Figure 8. The top five countries targeted by ransomware gangs in the first quarter of 2024 in terms of file detections
Meanwhile, the United States continues to be the most targeted country by RaaS groups, with our analysis of leak sites revealing 521 declared victim organizations from the country. The United Kingdom and Canada continue to follow in its wake with 63 and 58 declared successful attacks on organizations from those countries respectively.
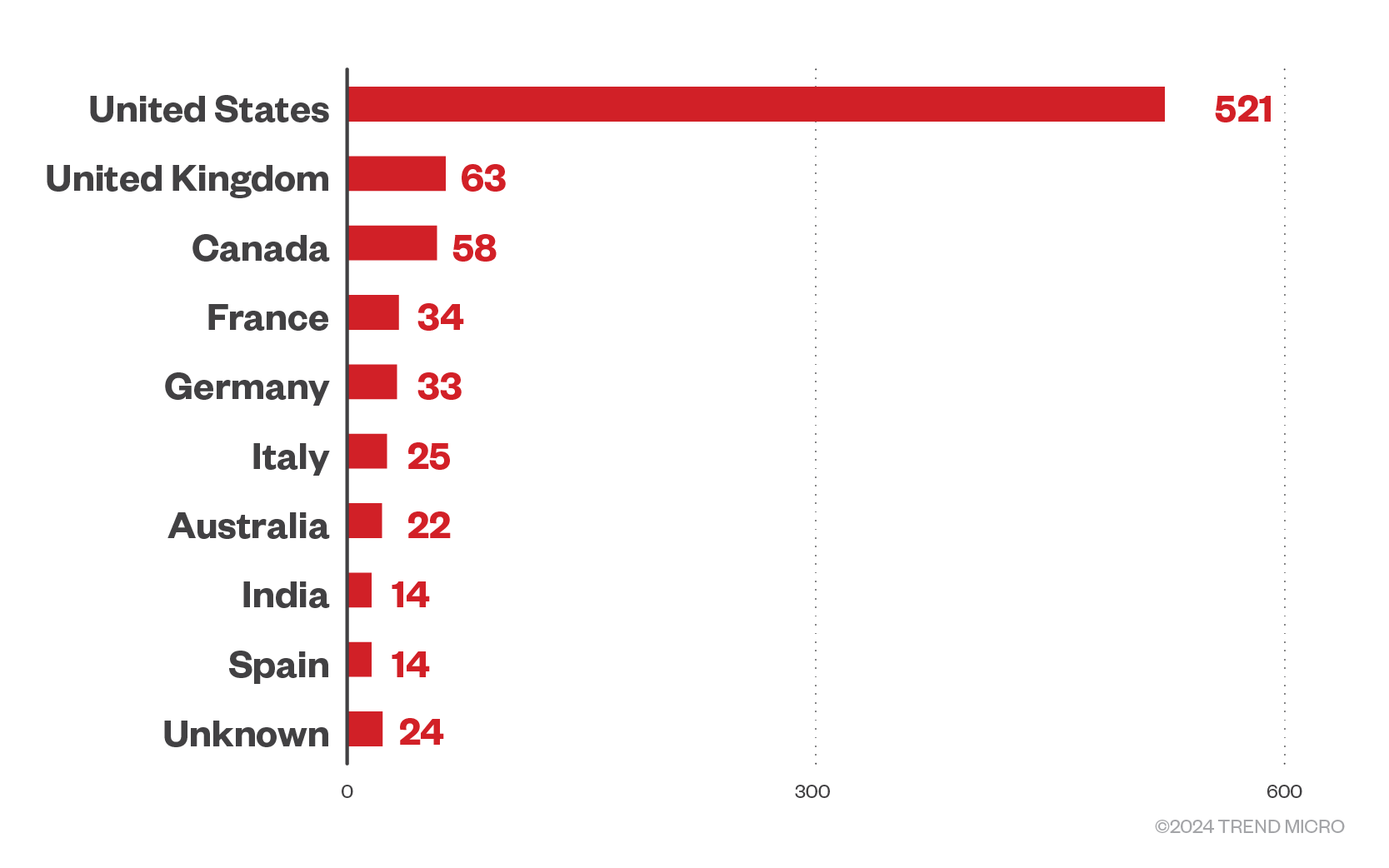
Figure 9. The top 10 countries affected by successful RaaS and extortion attacks in the first quarter of 2024
Source: RaaS and extortion group leak sites and Trend’s OSINT research
The three most active RaaS groups’ leak sites revealed it targeted North America the most, but also focused on Europe and the Asia Pacific region.
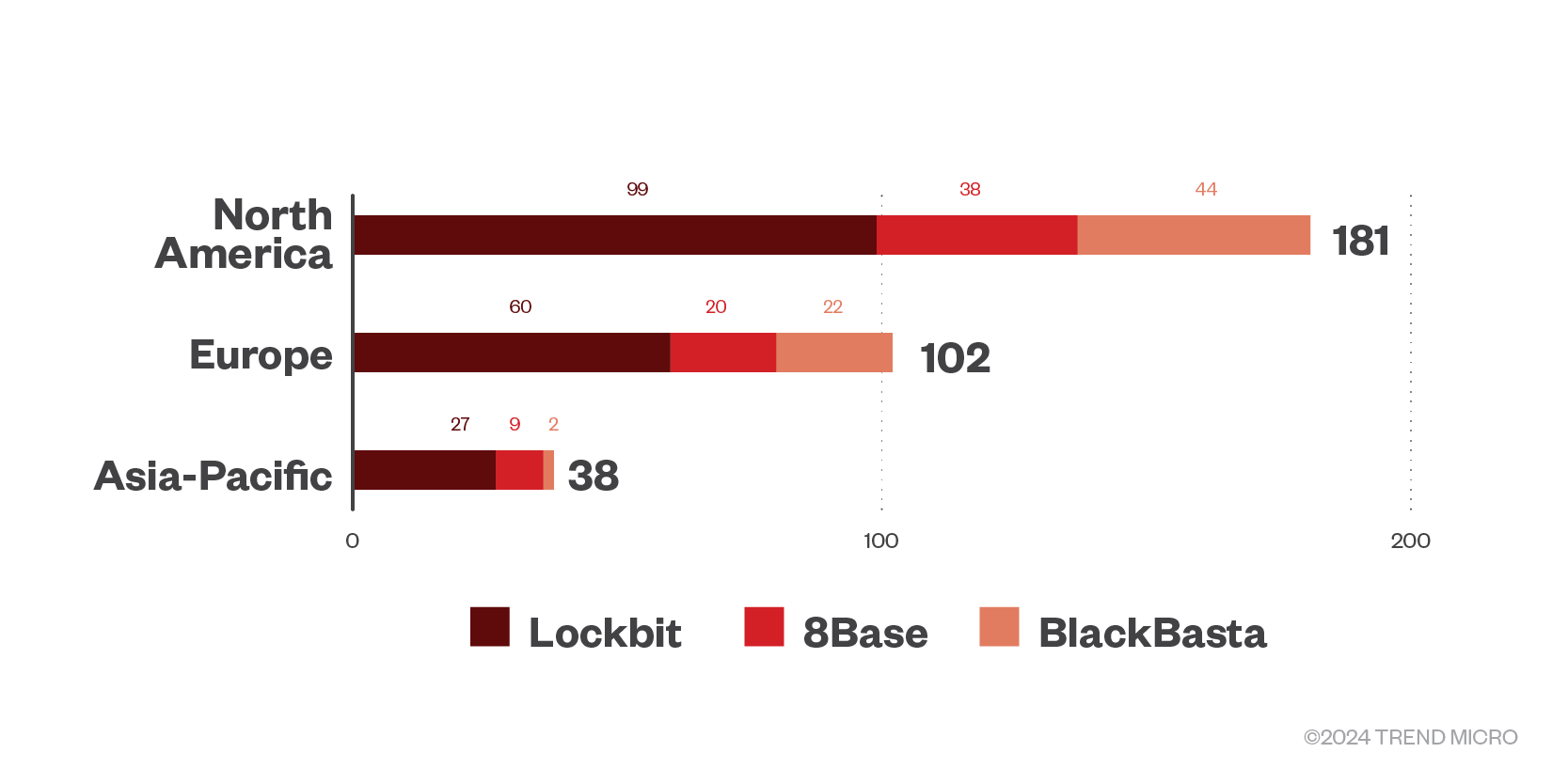
Figure 10. The top regions targeted by successful RaaS and extortion attacks in the first quarter of 2024
Source: RaaS and extortion group leak sites and Trend’s OSINT research
Stay ahead of the risk of ransomware attacks with a proactive approach to security
Despite an overall decrease in ransomware activity relative to the latter half of the previous year, the adaptability of certain ransomware families, notably LockBit, Phobos and 8Base, underscore the importance of constant vigilance and robust cybersecurity practices particularly for enterprises, which have emerged as prime targets in the first quarter of 2024.
While ransomware families continue to innovate, many groups continue to opt for easy ways in, as evidenced in LockBit and Conti’s leaked ransomware being used by other gangs. This contributed to the number of their detections despite the former’s takedown earlier this year and indictments of actors believed to be associated with the latter. Ransomware may have started slow in 2024, but the existing data implies that the threat actors are regrouping, rearming, and possibly preparing for more sophisticated, severe, and better targeted campaigns in the months to come.
Organizations can mitigate the risk of ransomware attacks by adopting a proactive cybersecurity mindset and implementing the following security best practices:
- Enable multifactor authentication (MFA). Organizations should implement policies that require employees who access or store company data on their devices to enable MFA as an added layer of protection to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Back up your data. Organizations should follow the “3-2-1 rule” to safeguard their important files: Create at least three backup copies in two different file formats, with one copy stored off-site.
- Keep systems up to date. Organizations should update all their applications, operating systems, and other software types as soon as vendors and developers release patches. Doing so minimizes the opportunities for ransomware actors to exploit vulnerabilities that enable system breaches.
- Verify emails before opening them. Malicious actors rely on tried-and-tested ways to compromise systems, such as using embedded links or executable downloads attached in emails sent to employees to install malware. Organizations should train their employees to be aware of such methods to avoid them.
- Follow established security frameworks. There’s no need to reinvent the proverbial wheel. Organizations can craft cybersecurity strategies based on the security frameworks created by the Center of Internet Security (CIS) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). The security measures and best practices outlined in these frameworks can guide members of an organization’s security team in developing their own threat mitigation plans.
Organizations can strengthen their cybersecurity infrastructure through multilayered detection and response solutions that can anticipate and respond to ransomware movements before operators can launch an attack. Trend Vision One™ is equipped with extended detection and response (XDR) capabilities that gather and automatically correlate data across multiple security layers — including email, endpoints, servers, cloud workloads, and networks — to prevent ransomware attack attempts.
Organizations can also benefit from solutions with network detection and response (NDR) capabilities, which can give them broader visibility over their network traffic. Trend Network One™ provides security teams with the critical network telemetry they need to form a more definitive picture of their environment, accelerate their response, and avert future attacks.
The supplementary data sheet for this report, including data from the leak sites of RaaS and extortion groups, Trend's OSINT research, and Trend threat intelligence, can be downloaded [here].
Like it? Add this infographic to your site:
1. Click on the box below. 2. Press Ctrl+A to select all. 3. Press Ctrl+C to copy. 4. Paste the code into your page (Ctrl+V).
Image will appear the same size as you see above.
Archive
- Phobos Emerges as a Formidable Threat in Q1 2024, LockBit Stays in the Top Spot: Ransomware in Q1 2024
- Rise in Active RaaS Groups Parallel Growing Victim Counts: Ransomware in 2H 2023
- LockBit, BlackCat, and Clop Prevail as Top RAAS Groups: Ransomware in 1H 2023
- LockBit, BlackCat, and Royal Dominate the Ransomware Scene: Ransomware in Q4 2022
- LockBit and Black Basta Are the Most Active RaaS Groups as Victim Count Rises: Ransomware in Q2 and Q3 2022

 Complexity and Visibility Gaps in Power Automate
Complexity and Visibility Gaps in Power Automate AI Security Starts Here: The Essentials for Every Organization
AI Security Starts Here: The Essentials for Every Organization The AI-fication of Cyberthreats: Trend Micro Security Predictions for 2026
The AI-fication of Cyberthreats: Trend Micro Security Predictions for 2026 Stay Ahead of AI Threats: Secure LLM Applications With Trend Vision One
Stay Ahead of AI Threats: Secure LLM Applications With Trend Vision One