Compliance & Risks
Survey 2 Factories took measures but are developing
This article is a second part of our three-part blog series, explaining the result of Trend Micro’s latest survey about industrial cybersecurity. We found some gaps of awareness between the IT and OT team. This post focuses on the technical measures.
Posts in this series
- Part 1: IT and OT with people, process, technology
- Part 3: Standard is way to institute collaboration
The State of Industrial Cybersecurity Part 2
Most factories have already implemented technical measures but are still in the development process
This article is a second part of our three-part blog series, explaining the result of Trend Micro's latest survey about industrial cybersecurity. The previous post showed the result of this survey- most IT and OT people recognize the biggest challenge is technology rather than people and process. We also found some gaps of awareness between the IT and OT team. This post focuses on the technical measures in smart factories.
Most factories have already implemented technical measures
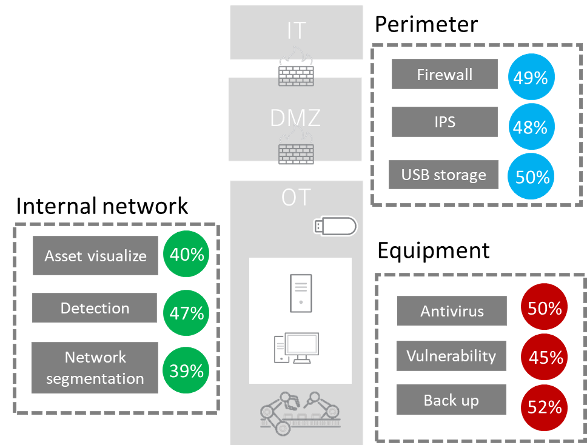
First, we categorized cybersecurity measures into three groups- perimeter, internal network, and equipment.
| PLACE | SPECIFIC TECHNICAL MEASURE | DESCRIPTION |
| Perimeter | Firewall | Separation by firewall of corporate IT network and factory network |
| IPS | Vulnerability attack protection (IPS) between corporate IT network and our factory network | |
| USB storage | Checking how secure an external device or USB storage is before bringing it in a factory network | |
| Internal network | Asset visualization | Asset visualization and configuration management |
| Detection | Detection of suspicious communications on a factory network | |
| Segmentation | Segmentation inside a factory network | |
| Equipment | Antivirus | Anti-virus measures in factory equipment (HMI, Engineering workstation, MES, etc.) |
| Vulnerability | Vulnerability measures in factory equipment (Applying patches, Introducing IPS, etc.) | |
| Backup | Making backups of factory equipment |
An estimated 80% of respondents answered that they have already implemented some measures in every group (Perimeter: 83%, Internal Network: 78%, Equipment: 82%). The technical measures on the internal network are lower than others, while most factories have been preparing some technical action on cybersecurity.
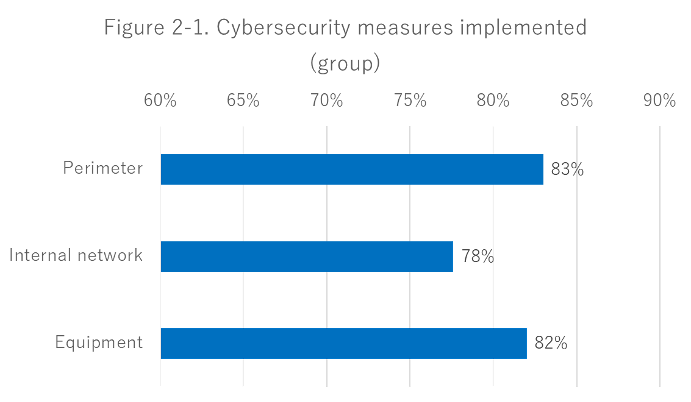
When we compared it by country, the result shows little difference. Perimeter measures are high in the US, while equipment measures rank high in Germany. Japan ranks each generally low, but there is little difference between the three groups.
Figure 2-2. Cybersecurity Measures Implemented (by countries)
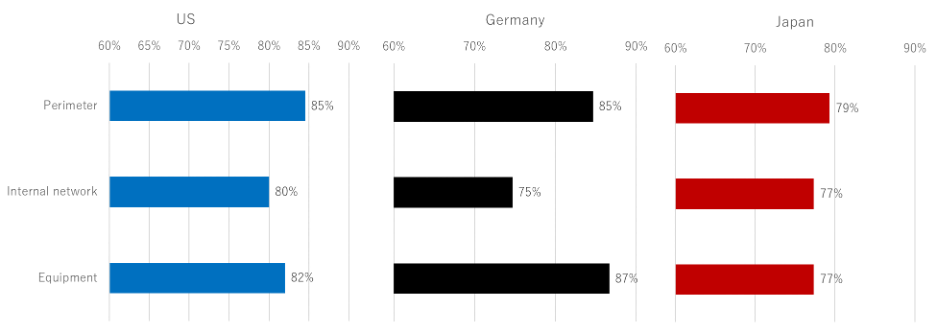
Specific measures are implemented less than 50% of the time
We also dive into the technical measures more specifically. The implementation rate of each measure are as follows:
- Fifty-two percent said they implement equipment backup
- Only 39% mentioned that they do network segmentation
- Less than half of the respondents said that specific measures are also implemented
Figure 2-3. Cybersecurity Measures Implemented (specific)
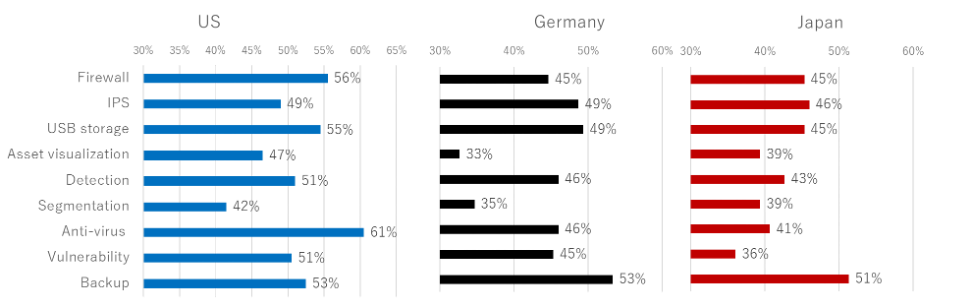
Looking at the implementation rate of specific measures by country, there are differences between the three countries.
In the US, 61% of the respondents implement the Antivirus on equipment, while 56% said they use a firewall. These figures are more than 10% higher than in other countries. It seems that firewall and antivirus, which are the basic measures in the IT world, are the measures most implemented for factories.
In Germany, 53% of respondents answered that they implement equipment backup, with IPS and USB storage coming in at second with 49%. These measures do not affect normal factory operations compared to other actions.
Lastly, 56% of respondents in Japan said they implement equipment backup. Other measures ranked low. It seems that the measure points vary depending on the factory.
Figure 2-4. Cybersecurity Measures Implemented (specific: by countries)
Most organizations understand the importance of process alongside technology, but few are involved in both IT and OT
We asked respondents if their organizations also consider their operation when introduction technical measures.
About 90% of respondents answered that they are building an operational process and an incident response process at the same time as technology. On the other hand, only 12% of organizations have involved both IT and OT teams in all stages of technology selection, operation and incident response construction. It can be seen that in most cases, technology and operation are decided only by either the IT or OT team.
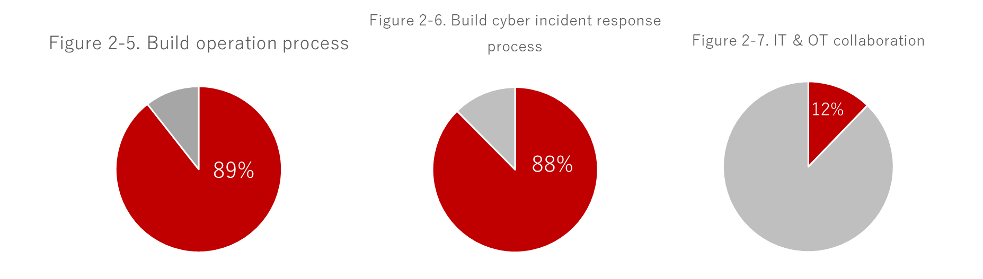
Figure 2-8 shows differences in the implementation rate of technical measures between organizations in which IT and OT participate in all stages and those in which they do not.
Collaborative organizations ranked higher in most implementation rates, compared to organizations with less collaboration. The most notable differences stand in firewall, IPS, and segmentation, which are network measures. Defense at the perimeter between IT and OT on the network and micro-segmentation within the OT network are more likely to be implemented, especially when both IT and OT participate in decision-making.
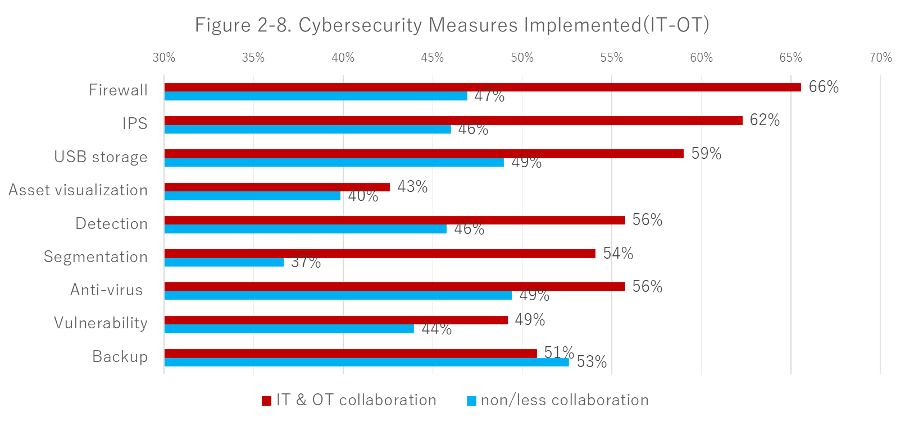
Moreover, we couldn't find a difference in some measures. The asset visualization ranked the lowest, with 40% of non-collaborative organizations and 43% of collaborative organizations answering that implement this measure.
Understanding assets and defining their importance is the first step in risk assessment, as described in IEC62443, the ICS cybersecurity international standard. Therefore, assets visualization tools and services are popular in the ICS security market.
However, results show that less than half of the organizations introduced it as a technology. Not being able to make an inventory of assets in a factory can cause omissions in countermeasures. It also means that the risks of threats and vulnerabilities cannot be evaluated in the first place. If an organization doesn't have a good grasp of the current situation, it will be difficult to set acceptable security levels and goal. Creating plans to fill the gap will also be challenging.
Visualization of assets is fundamental but is extremely difficult. It seems that the next issue is to tackle not only technology but also organizational and process aspects.
To read the survey's full report and results, click here.
If you want to know more about assessing cybersecurity risks in smart factory, read our whitepaper entitled "Practical Risk Assessments for Smart Factories", which intends to simulate risk assessment practices using a fictitious smart factory as an example.
In "Best Practices for Securing Smart Factories: Three Steps to Keep Operations Running", our expert team also explored recommended best practices to secure smart factories.

