
AI security refers to both the tools, technologies, and security measures organizations use to secure their AI stack as well as the use of AI to augment cybersecurity systems to improve vulnerability detection, correlations and response actions moving your security operations teams from a reactive to a proactive security posture.
Table of Contents
The term “artificial intelligence” (AI) was first coined in the 1950s to describe computers and machines that mimic the structure and function of the human brain to carry out complicated tasks, solve complex problems, predict future outcomes, and learn from experience.
AI security (also called artificial intelligence security or “security for AI”) is a branch of cybersecurity that encompasses all the processes, practices, and measures organizations use to secure their AI stacks and safeguard their artificial intelligence systems, data, and applications from potential threats. This includes the use of AI-powered tools and technologies to:
- Secure every aspect of an organization’s AI network from endpoints to AI models
- Protect AI models, systems, and applications from a wide range of cyber threats, cybercriminals, and cyberattacks
- Identify and mitigate any gaps or vulnerabilities in AI security and cybersecurity defenses before they can be exploited
- Safeguard AI infrastructure and training data to prevent the corruption, poisoning, or data theft of AI models
- Ensure the data quality and integrity of AI large language models (LLMs), generative AI (GenAI) engines, and deep learning and machine learning (ML) pipelines
- Address potential ethical issues and concerns surrounding questions of bias, transparency, data privacy, and explainability
- Make sure all AI use, data, and development are fully compliant with relevant laws, company policies, and industry regulations
AI security versus AI cybersecurity
While the two terms sound almost identical, there’s an essential difference between AI security and AI cybersecurity.
AI security is about securing AI itself—protecting an organization’s AI stack and securing its AI systems, components, networks, and applications.
AI cybersecurity (also called “AI for security”) is about using AI tools and technologies to protect IT infrastructures from cybercriminals, cyberattacks, and other cyber threats. This includes using AI to:
- Analyze large volumes of data to detect patterns, identify anomalies, and highlight potential security risks
- Scan for and eliminate gaps and vulnerabilities in an organization’s cybersecurity defenses
- Identify and defend against data breaches and other cyberattacks in real time
- Automate threat detection and response tools to reduce the demand on security teams and improve the speed and accuracy of cyber defenses
- Leverage the latest threat intelligence to stay ahead of bad actors and stay on top of new or emerging vectors of attack
- Enhance an organization’s overall cyber threat management strategies and capabilities
The importance of securing AI systems
While the idea of artificial intelligence has been around for decades, recent advances in AI technology have transformed industries ranging from transportation and healthcare to cybersecurity. Unfortunately, the widespread adoption of AI has enabled malicious actors to exploit it, leading to a significant surge in the number, scope, and sophistication of cyberattacks.
As a result, organizations need to make sure they’re doing everything they can to maintain the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of their AI data, safeguard their AI tools and applications from new and emerging cyber risks and cyberattacks, and protect their AI models, systems, and algorithms from a wide variety of constantly evolving cyber threats.
Failure to safeguard and secure AI systems from any one of these threats could potentially open an organization up to attack, put their clients and partners at risk, and end up costing them millions of dollars in remediation expenses, ransom demands, lost sales, and lost productivity.
What are the risks to AI security?
The potential of artificial intelligence to revolutionize the field of cybersecurity is clearly promising. But there are a growing number of AI security risks and challenges that organizations need to consider when implementing an effective AI security strategy. These include:
- Risk of an increased attack surface—Integrating proprietary and third-party AI models into an organization’s IT infrastructure can dramatically expand its attack surface, increase the number of weak points bad actors can exploit, and leave AI systems vulnerable to more powerful or frequent cyberattacks.
- Risk of malicious or adversarial attacks on AI data and algorithms—Bad actors can gain unauthorized access to AI tools and data, manipulate AI data and algorithms to insert gaps or biases, jeopardize the ability of AI models to make accurate predictions or defend against future attacks, and manipulate, misuse, or steal AI models and algorithms.
- Risk of data poisoning, corruption, and manipulation—Cybercriminals can corrupt machine learning (ML) pipelines or “poison” AI models by deliberately changing their input data or inserting new data of their own to compromise AI tools and systems.
- Risks to AI training models—Cybercriminals can steal, manipulate, or reverse-engineer proprietary AI training models. They can also corrupt, breach, or tamper with the data used to develop and train AI models to compromise their accuracy, effectiveness, and integrity.
- Risk of bias, discrimination, data privacy, and a lack of transparency—Human error and cyberattacks can increase data privacy concerns and bias in AI models and potentially compromise principles of transparency, fairness, and accountability.
- Risk of non-compliance with industry and government regulations—Failure to protect sensitive, personal, or confidential data can result in heavy penalties and charges of non-compliance from both government and industry regulators, including the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
- Risk of attacks on third-party suppliers—Attackers can target AI systems anywhere along an organization’s supply chain to take advantage of weaknesses in the AI networks, components, frameworks, and software libraries of third-party partners, and then use those vulnerabilities to target other AI models anywhere else along the chain.
- Risks of AI model drift and decay—Over time, all AI models can be vulnerable to drift or decay. Bad actors can exploit decayed or drifting AI models to alter their behavior or compromise their accuracy and reliability.
- Risk of chatbot credential theft—Cybercriminals can steal chatbot credentials for AI providers like ChatGPT or buy stolen credentials on the dark web and use them to gain illegal access to proprietary AI tools and systems.
- Risk of deepfake photos, videos, and audio—Bad actors can use AI-generated deepfake images and videos to defraud organizations, extort individuals or companies, trick employees into granting access to critical systems, disclosing confidential information, or stealing valuable data.
- Risk of direct and indirect prompt injection attacks—Prompt injection attacks can use malicious code to trick large language models (LLMs) and other AI tools into leaking sensitive information, permitting unauthorized access, or deleting key documents.
- Risk of AI hallucination abuse—Bad actors can take advantage of common AI “hallucinations” to deliberately compromise the data AI models rely on and the decisions they make.
- Risks to cloud assets and infrastructure—Cybercriminals can hack into cloud-based AI models and corrupt or steal their data and other assets.
If organizations don’t make sure their AI security and cybersecurity measures are as robust, comprehensive, and up to date as possible, bad actors can exploit these and other risks to undermine the effectiveness and reliability of AI models, steal sensitive or private data, and potentially cause significant financial and reputational harm.
What are the benefits of AI security?
Organizations that implement AI security measures to secure their AI stacks benefit from a number of compelling advantages. These include enhanced abilities to:
- Protect their AI data from being compromised, corrupted, manipulated, breached, or stolen
- Secure AI models from hacks or cyberattacks by running real-time threat detection and response, threat hunting, and vulnerability scanning tools and technologies
- Safeguard AI infrastructures by proactively eliminating gaps or vulnerabilities in cyber defenses, managing and mitigating cyber risks, and protecting AI assets
- Secure AI users and local applications from malicious code attacks, illegal or unauthorized access, fraud and phishing schemes, and malware and ransomware attacks
- Control access to private and public AI services including large language model (LLM) applications
- Defend against zero-day attacks that target previously unknown software or hardware vulnerabilities to allow bad actors to steal data, breach confidential information, install malware and other viruses, or gain access to an organization’s IT infrastructure
Best practices for AI security
The most effective AI security solutions follow a number of industry-standard best practices to protect their AI tools and resources and enhance their security posture. These practices include:
- Developing a comprehensive AI security strategy that combines advanced threat modeling and threat hunting activities with AI-driven risk assessment capabilities, comprehensive AI security controls, and detailed incident response plans and procedures to protect an organization’s AI systems and data.
- Ensuring the quality, integrity, and reliability of AI training data to address issues surrounding transparency, bias, and explainability, and make sure AI models are as accurate and effective as possible.
- Implementing industry-standard AI security frameworks to establish a clear set of standards and guidelines to secure AI systems, eliminate any gaps or vulnerabilities in AI defenses, and maintain compliance with all relevant AI security regulations. This includes integrating security frameworks like the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Artificial Intelligence Risk Management framework, the MITRE Adversarial Threat Landscape for Artificial-Intelligence Systems (ATLAS) matrix and Sensible Regulatory Framework for AI Security, the Open Worldwide Application Security Project (OWASP) list of Top 10 Best Practices for Large Language Model (LLM) Applications, Google’s Secure AI Framework (SAIF), and the ISO/IEC 27001 standards for information security management systems (ISMS).
- Integrating AI security with existing security and cybersecurity measures to create seamless end-to-end protection from cyber threats for all AI and IT applications, tools, systems, and networks.
- Carrying out regular employee training and awareness programs to raise awareness of the latest threats and security measures among both cybersecurity teams and other employees, and foster a corporate culture based on continuous ongoing improvement.
- Continuously monitoring, assessing, and updating AI models to scan for and mitigate vulnerabilities in AI tools and systems, identify emerging threats when and as they arise, and constantly refine AI models and applications to improve their accuracy, performance, and reliability.
Examples of applications of AI cybersecurity
As artificial intelligence tools become more advanced, the potential uses and applications for AI in cybersecurity are similarly expanding on an almost daily basis.
Among other benefits, AI-driven cybersecurity applications can significantly enhance the reach and effectiveness of an organization’s cybersecurity defenses by automating their threat detection and incidence response activities, carrying out vulnerability scans and other proactive measures on a regular or ongoing basis, and using the latest threat intelligence and security analytics to predict, pre-empt, and protect organizations from both new and emerging cyber threats.
Some of the most effective and widely adopted applications of AI cybersecurity include the use of artificial intelligence in data protection, endpoint security, cloud security, advanced threat hunting, fraud detection, and identity and access management (IAM).
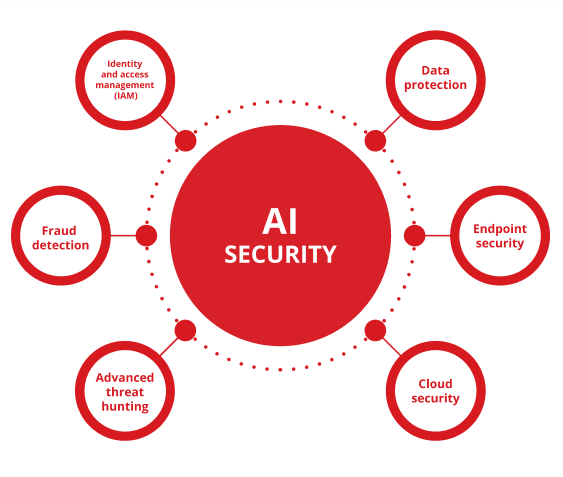
- Data protection
Organizations can use AI to classify and encrypt their confidential or sensitive information, monitor access to systems to detect data breaches faster and more accurately, protect AI data from loss or corruption, and secure their AI stack from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. However, sensitive information blind spots in AI environments can lead to severe data breaches and compliance issues, making it crucial to identify and mitigate those vulnerabilities proactively.
- Endpoint security
AI-enabled endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions can help protect laptops, desktops, computer servers, mobile devices, and other network endpoints in real time by proactively detecting and blocking malware, ransomware, and other cyberattacks before they occur.
- Cloud security
AI-powered cloud security technologies can monitor and control access to cloud environments around the clock, identify any abnormalities or suspicious activity, alert security teams to potential threats as they happen, and protect cloud-based data and applications from unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Advanced threat hunting
Advanced AI threat hunting tools can quickly and easily analyze data logs, network traffic patterns, and user activities and behaviors to look for malicious attacks, catch cybercriminals in the act before they can cause any lasting damage, and safeguard AI systems and infrastructure from advanced persistent threats (APTs) and other cyberattacks.
- Fraud detection
Organizations in the banking and financial services industries can use machine learning (ML) algorithms, neural networks, and other advanced AI technologies to detect potentially fraudulent activities, block unauthorized access to banking or other online accounts, and prevent identity theft in financial and ecommerce transactions.
- Identity and access management (IAM)
AI-enabled identity and access management (IAM) solutions can help organizations monitor and secure every step of their authentication, authorization, and access management processes to make sure they follow all AI company policies and playbooks, maintain compliance with industry regulations, prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data, and keep hackers out of their systems.
Where can I get help with AI security?
The Trend Vision One™ is an all-in-one AI cybersecurity-driven platform.
Trend Vision One features a powerful set of industry-leading AI tools and technologies that can detect, predict, and prevent cyber threats far more rapidly and effectively than traditional human-led security teams. Achieving effective AI stack security requires protecting every layer, from data to infrastructure to users, by ensuring visibility into shadow AI deployments, enforcing strict access controls for compliance, and establishing guardrails for AI APIs to prevent misuse and model poisoning. These capabilities enable organizations to secure their entire AI stack and protect their AI data, applications, and systems from the vast majority of cyberattacks before they occur.
Trend Vision One also includes the unmatched AI-powered capabilities of Trend Cybertron: the world’s first truly proactive cybersecurity AI. Drawing on Trend Micro’s proven collection of large language models (LLM), datasets, advanced AI agents, and more than 20 years of investment in the field of AI security, Trend Cybertron can analyze historical patterns and data to predict attacks that are specific to each customer, enable organizations to achieve remediation times that are 99% faster than traditional incidence response, and transform an organization’s security operations from reactive to proactive virtually overnight.
Trend Cybertron was also designed to continuously evolve and adapt to keep pace with changes in an organization’s needs and stay on top of the latest tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) being employed by cybercriminals. This allows organizations to make sure that both their AI security and AI cybersecurity defenses are always as robust, complete, and up to date as possible.
Michael Habibi is a cybersecurity leader with over 12 years of experience, specializing in product development and strategic innovation. As Vice President of Product Management at Trend Micro, Michael drives the alignment of the endpoint product strategy with the rapidly evolving threat landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is AI security?
Security for AI (or “AI security”) is the use of different tools, practices, and technologies to secure an organization’s AI stack.
What is the meaning of AI in security?
AI refers to “artificial intelligence.” AI is used in security to improve an organization’s cybersecurity defenses and protect AI stacks.
How can AI be used in security?
AI can be used to protect AI networks, models, systems, endpoints, and applications from cyberattacks, data corruption, and other threats.
What is AI in cybersecurity?
AI in cybersecurity refers to the use of AI tools and technologies to help protect organizations from cyberattacks.
Is AI a security risk?
Like any technology, AI can be used to either improve security measures or launch more powerful cyberattacks.
Is AI security a good career?
AI security is a growing field that offers numerous challenging and well-paid career opportunities.
How much do AI security officers make?
Depending on their experience and location, AI security officers can earn anywhere from $60,000 to $120,000+ per year.
How do I get into AI security?
Online training courses, degrees in computer science or cybersecurity, and AI security certifications are all good starting points for a career in AI security.
What is the difference between cybersecurity and AI security?
Cybersecurity refers to tools or systems that protect organizations from cyberattacks. AI security is about safeguarding an organization’s AI stack.
Can AI do cybersecurity?
Under human supervision, AI technologies can dramatically improve the speed, accuracy, and effectiveness of nearly every aspect of cybersecurity.
What is the difference between traditional and AI cybersecurity?
While their goals and methods are the same, AI cybersecurity can provide faster, more accurate, and more proactive protection than traditional cybersecurity.
Does cybersecurity require coding?
While coding can be a valuable skill for many cybersecurity jobs, there are numerous positions in cybersecurity that don’t require any coding experience or expertise.
Why is AI a threat to security?
AI can be used by bad actors to hack into IT systems, steal confidential data, corrupt AI stacks, or launch sophisticated cyberattacks.
What is an example of an AI data breach?
AI deepfakes have been used to simulate the voices or video images of real people, convincing employees of organizations to share confidential information that should have been kept private.
Is the AI security app safe?
Ultimately, the safety of a security app depends on the trustworthiness of its developer, not its price. Stick to major, independently tested brands and avoid apps from unknown sources.
What are the risks of security with AI?
Some common risks associated with AI security include expanded attack surfaces, data poisoning and corruption, and risks to AI data, algorithms, and training models.
Is my AI system high risk?
Organizations can reduce risks to AI systems by analyzing their current defenses, following industry best practices, and implementing comprehensive AI security and cybersecurity strategies.
Should I trust an AI detector?
While AI detectors can be effective tools, they can also make mistakes. Therefore, their results should only be used as a preliminary signal to prompt further investigation, which must rely on human judgment.
How to be careful with AI?
A truly careful approach to AI requires different actions from users and creators. Whether you are using or building it, the fundamental rule is to treat AI as a powerful but imperfect tool—not an infallible expert or a secure confidant.
How do I secure AI?
A comprehensive security posture for the AI stack leaves no gaps, applying protection across every component—from the users and the data they generate to the models, microservices, and underlying infrastructure.

