
AI cybersecurity is a proactive approach that uses artificial intelligence (AI) to eliminate security blind spots, preemptively predict and prevent attacks, and transform security operations efficiency across an organization's entire digital estate.
Table of Contents
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a broad term used to describe machines or computers that use machine learning (ML) algorithms, neural networks, and other advanced technologies to simulate how the human brain works. These machines imitate human cognitive abilities to plan, reason, solve problems, carry out complicated tasks, and learn from experience.
The idea of using artificial intelligence to bolster cybersecurity has been around since at least the late 1980s. In the years since it was first introduced, AI cybersecurity has transformed the way organizations identify, mitigate, and minimize their exposure to cyber threats. This includes using AI-powered tools and technologies to:
- Identify, predict, and defend against hacks, data breaches, and cyberattacks
- Find and eliminate gaps and vulnerabilities in cybersecurity defenses
- Automate threat detection and response tools and solutions
- Increase the reach and effectiveness of threat intelligence
- Enhance and support cyber threat management
Key components of AI cybersecurity
Most AI cybersecurity solutions combine a variety of AI tools, technologies, and applications to provide the best protection possible.
Machine learning algorithms can be used to analyze data, discover patterns, learn from past experiences, and make predictions about future threats.
AI models use deep learning algorithms and neural networks to monitor, assess, and analyze huge volumes of data much faster than human security teams or traditional cybersecurity tools.
Generative AI (GenAI) and natural language processing tools can be used to investigate and respond to potential threats, offer recommendations for different incident response strategies, and create simplified reports on the results.
Automated AI agents can take over many of the more mundane or high-volume tasks previously performed by human security personnel. This frees security teams to focus on more critical tasks and enables organizations to respond to cyber threats more quickly and efficiently.
Traditional vs. AI cybersecurity
Traditional cybersecurity measures follow a clear set of pre-defined rules, policies, and playbooks to identify and respond to known threats. By contrast, AI cybersecurity can continuously learn, evolve, and adapt the way it works. This enables it to keep pace with new and emerging threats, respond to new vectors of attack as they appear, and stay ahead of bad actors.
The ability to learn from past experience and predict previously unknown outcomes enables AI cybersecurity tools to identify potential cyber threats in real time and respond to cyberattacks faster, more accurately, and more effectively than traditional security measures. It also equips organizations to defend their IT infrastructure proactively by preventing most cyberattacks before they happen.
Traditional Cybersecurity
AI Cybersecurity
Pre-defined rules, policies, and playbooks
Continuously learning, evolving, and adapting
Struggles with zero-day attacks and unknown threats
Detects novel and evolving threats
Time-consuming and resource intensive
Reduces response time and analyst workload
AI cybersecurity vs. AI security
While the terms “AI cybersecurity” and “AI security” are often used hand-in-hand, the two refer to very different parts of the security process.
AI cybersecurity is about the use of AI-enabled tools and technologies to support or enhance an organization’s cybersecurity defenses. AI security (also called “security for AI”) refers to the need for organizations of all sizes to protect their AI stacks and secure their AI systems, networks, and applications.
The latter includes protecting AI systems from adversarial attacks, preventing AI model poisoning or theft, ensuring the data integrity of machine learning pipelines, safeguarding AI infrastructure and training data, and making sure AI tools are developed used in a way that’s compliant with all laws, company policies, and industry regulations.
What are the benefits of AI cybersecurity?
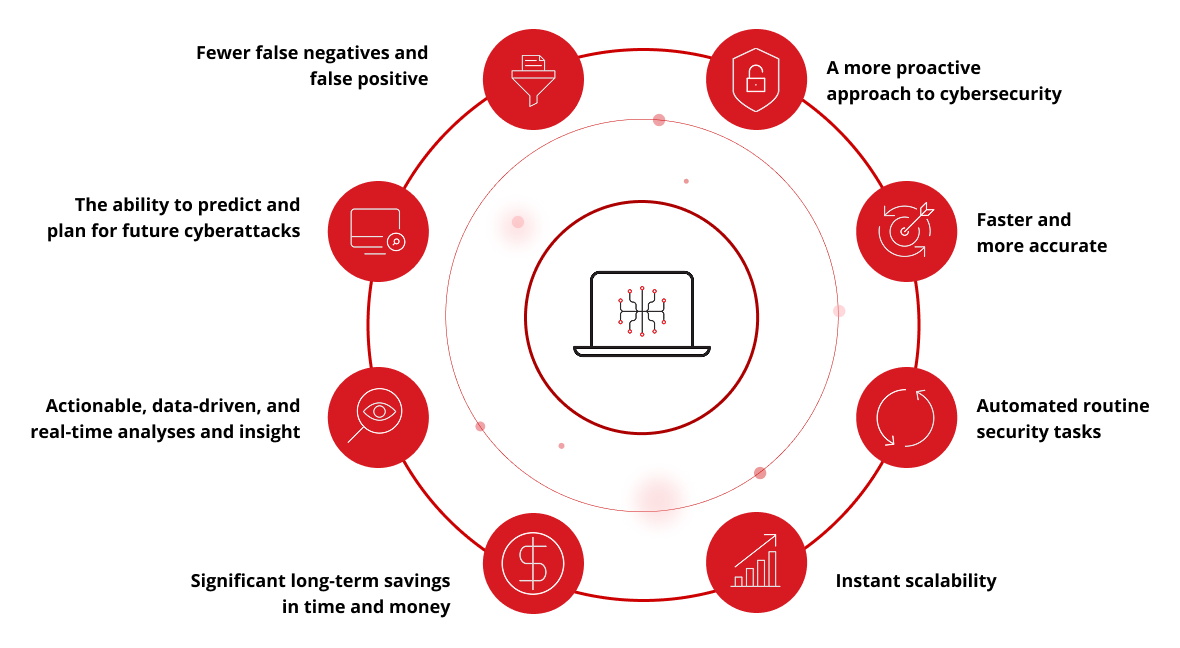
AI cybersecurity offers a number of benefits and advantages over traditional cybersecurity measures. These include:
- A more proactive approach to cybersecurity—AI cybersecurity tools can find, anticipate, and prevent cyberattacks before they happen rather than waiting until an attack occurs.
- Faster and more accurate threat detection and response—AI models can monitor, sift through, and analyze vast amounts of data to detect unusual patterns of activity, identify anomalies, and respond to the first signs of potential risks or attacks in real time.
- Automated routine security tasks—By automating log analyses, vulnerability scans, and other previously manual security functions, AI tools can free security teams to focus their time, efforts, and resources on more high-level or strategic tasks.
- Fewer false negatives and false positives—The greater accuracy of AI cybersecurity helps prevent security operations centers (SOCs) from being overwhelmed by irrelevant or false reports.
- The ability to predict and plan for future cyberattacks—By identifying and learning from past attacks, AI technologies can predict and anticipate new threats, take pree-emptive steps to reduce security risks and vulnerabilities before they can be exploited, and help organizations stay ahead of the latest tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) being used by cybercriminals.
- Actionable, data-driven, and real-time analyses and insights—AI tools provide real-time insights into network traffic and employee behaviors through detailed analytics and activity reports using data drawn from a variety of internal and external sources, including network and user traffic, security and activity logs, and the latest industry threat intelligence.
- Instant scalability—AI models can be scaled easily and inexpensively to keep pace with evolving IT infrastructures and changes in the frequency, quantity, and sophistication of cyberattacks.
- Significant long-term savings in time and money—By reducing the number of security breaches and attacks, AI cybersecurity can help organizations protect their data, safeguard their reputations, and significantly reduce the cost of remediation and recovery from cyberattacks.
What are the risks and challenges of AI cybersecurity?
Organizations must keep several risks and challenges in mind when integrating AI cybersecurity measures.
For one, there is the potential for AI cybersecurity technology to be exploited by the very cybercriminals it’s designed to stop. For example, cybercriminals can inject malicious content into AI data or manipulate AI algorithms to compromise security defenses. They can also use AI to attempt to escape detection or find and exploit vulnerabilities in an organization’s security systems.
Cybercriminals can also use their own AI tools to create more powerful, sophisticated, and targeted cyberattacks. This includes using AI to create deepfake photos and videos, trick employees into disclosing sensitive or proprietary information, or hack into an organization’s passwords and access controls.
The use of artificial intelligence in cybersecurity also raises concerns about data privacy. This extends to issues like the need to obtain consent and ensure transparency when collecting or using personal information, the potential for sensitive or confidential data to be compromised, misused, or stolen, and the requirement for organizations to comply with relevant laws and regulations concerning user privacy, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
In addition, AI models are generally trained on data drawn from existing sources of content. Any biases, discrimination, gaps, unfairness, or inaccuracies in that original data could lead those models to mimic the same failings or hamper their ability to make accurate predictions and decisions. It’s essential for organizations to make sure their AI models use only the highest-quality and most trusted sources of training data available.
Examples of how AI is used in cybersecurity
AI is already being used in a variety of ways to help organizations improve their cybersecurity posture. Some of the most innovative examples of AI cybersecurity tools and applications include:
- AI-powered malware detection systems that use machine learning algorithms to detect, identify, and block sophisticated malware threats that traditional anti-malware solutions might miss.
- AI-driven next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) that draw on the latest threat intelligence to protect organizations against both existing and new cyber threats.
- AI-based email and access controls that prevent phishing attacks by analyzing email content, sender data, and email metadata to identify and block phishing scams, tactics, and techniques.
- AI-informed behavioral analytics tools that can monitor and analyze user behavior and network traffic to detect abnormal or unauthorized activities, identify potential insider threats or compromised accounts, and eliminate security risks.
- AI cloud security solutions that enable organizations to protect confidential or sensitive data stored in the cloud, comply with regulations concerning cloud security, and safeguard their cloud-based assets from cyberattacks, breaches, or theft.
- AI-enhanced endpoint security systems to help organizations protect their endpoints and defend their systems and networks against malware, phishing schemes, ransomware, and other targeted attacks.
- AI-enabled Internet of Things (IoT) security solutions to protect both individual IoT devices and complete IoT networks from cyber threats.
- AI security information and event management (SIEM), network detection and response (NDR), and extended detection and response (XDR) platforms to automatically identify vulnerabilities in an organization’s cybersecurity infrastructure and proactively detect and prevent cyberattacks before they can cause any damage.
What is the future of AI cybersecurity?
As AI cybersecurity becomes both more powerful and more widely adopted, advances in technologies like machine learning, neural networks, generative AI, agentic AI, predictive AI analytics, data mining, and AI-powered red teams and digital twins have the potential to transform how organizations protect their data and assets.
Security operations centers (SOCs) will likely need to evolve to become much more AI-driven and to rely more consistently on AI security models, AI threat detection and response tools, and AI-informed decisions. AI cybersecurity tools and technologies will also likely become progressively more integrated with other security approaches, strategies, and technologies.
As the field of AI cybersecurity continues to evolve, organizations should make sure they stay on top of these and other trends to keep their AI security measures as robust, comprehensive, and up-to-date as possible.
Where can I get help with AI cybersecurity?
Trend Vision One™ AI Security uses the latest AI tools and technologies to help organizations adopt a fully proactive approach to AI security that stops cyberattacks and data breaches before they occur.
Powered by Trend Cybertron—the industry's first truly proactive cybersecurity AI—organization benefits from the culmination of 35 years of cybersecurity experience and 20 years of investment in the development of AI for security. Trend Cybertron uses extensive large language learning (LLM) models and proven AI datasets to dramatically improve the efficiency and effectiveness of cybersecurity defences.
The enterprise cybersecurity platform Trend Vision One™ also features advanced agentic AI tools that are designed to continuously evolve and adapt based on real-world cyberattacks and threat intelligence. This commitment to continuous improvement and innovation allows organizations to stay on top of the latest new and emerging cyber threats, and stay one step ahead of bad actors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is AI in cybersecurity?
AI in cybersecurity refers to the use of AI tools and technologies to protect an organization or business from hacks, data beaches, and cyberattacks.
How is AI used in cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity providers use AI to analyze cyber risks, identify gaps or vulnerabilities in an organization’s defenses, and respond more quickly to threats.
What is the main benefit of using AI for cybersecurity?
AI tools offer a faster, more accurate, more comprehensive, and more proactive approach to cybersecurity than human teams can achieve on their own.
Will AI replace cybersecurity?
While it could lead to some job losses, AI is more likely to be used as a tool by, rather than replacement for, cybersecurity professionals.
Which is better for the future, AI or cybersecurity?
AI and cybersecurity will likely work together in the future to improve security defenses and safeguard organizations from cyber threats.
Is AI a threat to cybersecurity?
Just as AI tools can bolster cybersecurity defenses, AI can also be used by bad actors to hack into or attack IT systems.
Is cybersecurity a dying field?
No, cybersecurity isn’t dying. As security risks evolve and cyberattacks become more sophisticated, cybersecurity is growing and evolving with them.
How effective is AI in cybersecurity?
AI tools can be an extremely effective way to enhance cybersecurity defenses, improve threat detection and response capabilities, and defend against cyberattacks.
Is AI useful in cybersecurity?
AI plays a crucial and growing role in helping organizations enhance, empower, and automate their cybersecurity defenses.
Will cybersecurity survive AI?
Cybersecurity is expected to survive AI, in part by using AI tools to identify, predict, and respond to new cyber threats when and as they emerge.
What is the success rate of using AI to detect cyberattacks?
AI can dramatically improve success rates for detecting cyberattacks. Some experts estimate the success rate for AI cybersecurity could be as high as 85 – 99%.
How big is the AI in cybersecurity market?
In 2023, the global AI cybersecurity market was estimated to be close to $22.4 billion.
Can AI stop all phishing threats?
No single technology can stop all phishing threats. But AI-powered tools can significantly improve the accuracy and efficiency of anti-phishing measures.
Which is the best AI for cybersecurity?
Some of the best AI tools for cybersecurity include AI-powered malware detection systems, AI cloud security, AI-driven next-generation firewalls (NGFWs), and AI endpoint security.
What types of AI are used in cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity AI tools include AI-powered anti-malware and anti-phishing defenses, AI threat detection, and AI authorization and access controls.
What does AI stand for in cybersecurity?
AI stands for “artificial intelligence.” In cybersecurity, AI tools help protect organizations from cyberattacks and cybercriminals.
What is responsible AI in cybersecurity?
Responsible AI focuses on developing and using AI cybersecurity tools in ways that are fair, ethical, transparent, safe, and respectful of human rights.
How can generate AI be used in cybersecurity?
Generative AI (GenAI) can be used to investigate, respond to, and mitigate cyberattacks and other threats quickly and efficiently.
What is the role of AI in cybersecurity?
AI can play a critical and growing role in improving the efficiency, accuracy, and effectiveness of cybersecurity.
How is AI shaping cybersecurity?
As cyberattacks become more frequent and sophisticated, AI technologies will help make cybersecurity defenses more robust, faster, and more powerful.