APT & Targeted Attacks
SideWinder Uses South Asian Issues for Spear Phishing, Mobile Attacks
While tracking the activities of the SideWinder group, we identified a server used to deliver a malicious LNK file and host multiple credential phishing pages. In addition, we also found multiple Android APK files on their phishing server.
While tracking the activities of the SideWinder group, which has become infamous for targeting the South Asia region and its surrounding countries, we identified a server used to deliver a malicious LNK file and host multiple credential phishing pages. We learned that these pages were copied from their victims’ webmail login pages and subsequently modified for phishing. We believe further activities are propagated via spear-phishing attacks.
The group’s targets include multiple government and military units, mainly in Nepal and Afghanistan. After the gathered credentials are sent, some of the phishing pages will redirect victims to different documents or news pages. The themes and topics of these pages and documents are related to either Covid-19 or recent territory disputes between Nepal, Pakistan, India, and China. Furthermore, it seems that these lures are distributed via phishing links.
We also found multiple Android APK files on their phishing server. While some of them are benign, we also discovered malicious files created with Metasploit. One of the normal applications, called “OpinionPoll,” is a survey app for gathering opinions regarding the Nepal-India political map dispute, which seems to be another political lure similar to the one they used in the spear-phishing portion. We believe these applications are still under development and will likely be used to compromise mobile devices in the future.
SideWinder has been very active in 2020. Earlier this year, we published a report on how the SideWinder APT group used the Binder exploit to attack mobile devices. The group also launched attacks against Pakistan, Bangladesh, and China using lure files related to Covid-19.
Analysis of the malicious document
The use of malicious documents is one of SideWinder’s most common infection vectors. We collected several different samples from the campaign, including:
1. An LNK file that downloads an RTF file and drops a JavaScript file
2. A ZIP file containing an LNK file, which downloads an HTA file (with JavaScript)
3. An RTF file that drops a JavaScript file
4. A PDF file with an embedded JavaScript stream
5. A DOCX file with an external link to an OLE object (RTF file), which contains and drops a JavaScript file
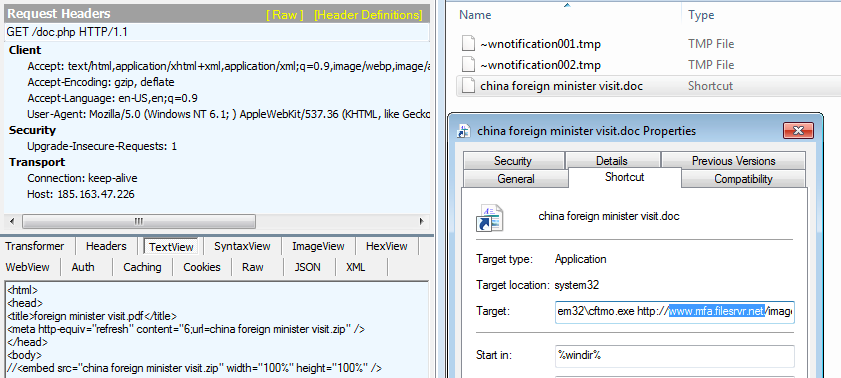
All of these cases end up with either the downloading or dropping of files and then the execution of JavaScript code, which is a dropper used to install the main backdoor + stealer.
The downloaded RTF files exploit the CVE-2017-11882 vulnerability. It drops a file named 1.a (a JavaScript code), which drops the backdoor + stealer into a folder in ProgramData and directly executes it or creates a scheduled task to execute the dropped files at a later time.
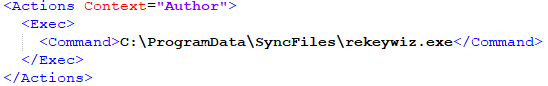
The content of the newly created folder contains a few files, including Rekeywiz (EFS REKEY wizard, FA86B5BC5343CA92C235304B8DCBCF4188C6BE7D4621C625564BEBD5326ED850), which is a legitimate Windows application.

This application loads various system DLL libraries, including shell32.dll, which sideloads DUser.dll, one of shell32’s DelayImports.
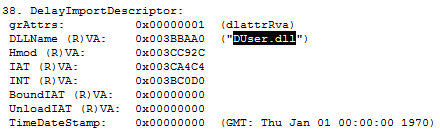
However, a fake DUser.dll gets loaded into the process. This fake DLL library decrypts the main backdoor + stealer from the .tmp file in the same directory.
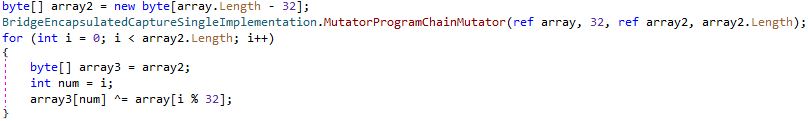
The decryption process is a simple XOR, where the key is the first 32 bytes from the encrypted file and the payload are the remaining bytes. The decrypted payload is the main backdoor .NET executable binary.
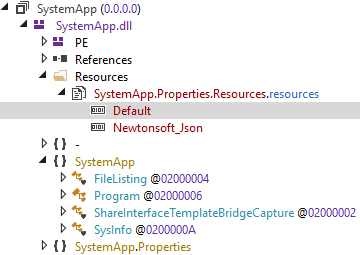
In Resources, the Default resource contains the encrypted configuration. After decryption (using the same principle as with the main backdoor + stealer), the configuration reveals which file formats the attackers are targeting.
The main functions of the backdoor + stealer are:
1) Downloading the .NET executable and running it
2) Collecting system information and uploading it to the command-and-control (C&C) server
3) Uploading selected files to the C&C server
The collected information is in JSON format (hence why the Newtonsoft_Json library stored in Resources is loaded) and includes information such as privileges, user accounts, computer system information, antivirus programs, running processes, processor information, operating system information, timezone, installed Windows updates, network information, list of directories in Users\%USERNAME%\Desktop, Users\%USERNAME%\Downloads, Users\%USERNAME%\Documents, Users\%USERNAME%\Contacts, as well as information on all drives and installed apps.
The spear-phishing attack
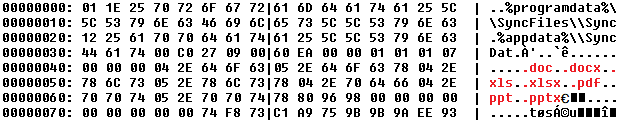
We found several interesting dynamic DNS domains resolving to a server that was used to deliver SideWinder’s malicious documents. The subdomains of these dynamic DNS domains are designed to be similar to the domains of their victims’ mail servers. For example, “mail-nepalgovnp[.]duckdns[.]org” was created to pretend to be the original Nepal government’s domain “mail[.]nepal[.]gov[.]np”. Digging deeper, we found that it hosted several phishing pages.
These pages were copied from the webmail servers of various targets and then modified for spear-phishing attacks designed to steal login credentials. Although it’s not clear to us how these phishing pages are delivered to the victims, finding the original webmail servers that they copied to make these phishing pages allows us to identify who they were targeting.
Analysis of the phishing pages revealed that most of them would redirect to the original webmail servers, which they copied after the victims sent out their login credentials. However, we also found some of them will either redirect to documents or news pages. These documents and news are probably interesting in some way to their targets and are used to make them click and log in to the phishing pages. While several of the documents are related to Covid-19, we also found some documents or news related to territorial issues in South Asia, including:
- “India Should Realise China Has Nothing to Do With Nepal’s Stand on Lipulekh” – a news article that discusses India-China conflicts in May.
- “India reaction after new pak map.pdf” – a document talking about India’s response to the new political map revealed by Pakistan in August.
- “Ambassador Yanchi Conversation with Nepali_Media.pdf” – a document describing an interview with China's ambassador to Nepal regarding Covid-19, the Belt and Road Initiative, and territorial issues in the Humla district.
The following table shows their targets, related phishing domains, and lure documents used in each of the phishing attacks.
Date |
Phishing Domain |
Targeted Organization |
Targeted Mail server |
Redirection after login |
2019 Nov |
|
Government of Nepal |
mail.nepal.gov.np |
Redirect to file “IMG_0002.pdf” |
2019 Nov |
|
Ministry of Defence, Nepal |
mail.mod.gov.np |
Redirect to original mail server |
2019 Dec |
mail-mofagovnp.zapto[.]org |
Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Nepal |
mail.mofa.gov.np |
Redirect to web news “China, Nepal sign trade, infrastructure and security deals” |
2019 Dec |
|
Government of Nepal |
mail.nepal.gov.np |
Redirect to file |
2020 Jan |
imail.aop.gov-af[.]org |
Administrative Office of the President, Afghanistan |
imail.aop.gov.af |
Redirect to web page “Observation Of Technology Use in Afghanistan Government Sector” |
2020 Jan |
mail-nscaf.myftp[.]org |
Afghanistan National Security Council |
mail.nsc.gov.af |
Redirect to https://wikipedia.org/USB_Killer |
2020 Jan |
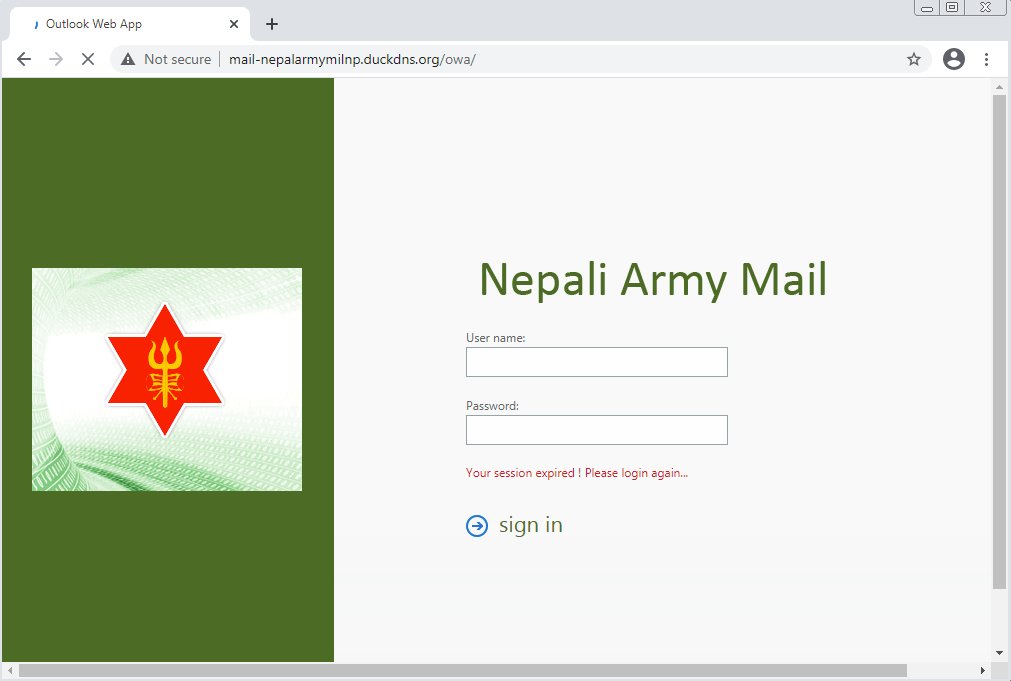
mail-nepalarmymilnp.duckdns[.]org |
Nepali Army |
mail.nepalarmy.mil.np |
Redirect to PDF “EN Digital Nepal Framework V8.4 15 July 2019.pdf” |
2020 Jan |
mail-mofagovnp.hopto[.]org |
Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Nepal |
mail.mofa.gov.np |
Redirect to PDF “national-security-vol-3-issue-1-essay-SSimkhada.pdf” |
2020 Jan |
webmail.mohe.gov-af[.]org |
Ministry of Higher Education, Afghanistan |
webmail.mohe.gov.af |
Redirect to original mail server |
2020 Feb |
|
Ministry of Defense, Sri Lanka |
mail.defence.lk |
Login Error |
2020 Feb |
mail.moha.gov-np[.]org |
Ministry of Home Affairs, Nepal |
mail.moha.gov.np |
Redirect to original mail server |
2020 Feb |
mail.nsc.gov-af[.]org |
Afghanistan National Security Council |
mail.nsc.gov.af |
Redirect to original mail server |
2020 Feb |
mail.arg.gov-af[.]org |
Presidential Palace, Afghanistan |
mail.arg.gov.af |
Redirect to original mail server |
2020 Feb |
mail.arg.gov-af[.]org |
Presidential Palace, Afghanistan |
mail.arg.gov.af |
Redirect to original mail server |
2020 Feb |
|
Center for Education and Human Resource Development, Nepal |
mail.doe.gov.np |
Redirect to file “Para Basic Course Joining Instruction.docx” |
2020 Mar |
mail-nepalgovnp.duckdns[.]org |
Government of Nepal |
mail.nepal.gov.np |
Redirect to original mail server |
2020 Mar |
|
Nepal Electricity Authority |
mail.nea.org.np |
Redirect to original mail server |
2020 Mar |
mail-nepalgovnp.duckdns[.]org |
Government of Nepal |
mail.nepal.gov.np |
Redirect to file “central data form.pdf” |
2020 Mar |
mail-nepalarmymilnp.duckdns[.]org |
Nepali Army |
mail.nepalarmy.mil.np |
Redirect to file “Corona Virus Preparedness and Response.pdf” |
2020 Mar |
mail-nepalpolicegov.hopto[.]org |
Nepal Police |
mail.nepalpolice.gov.np |
Redirect to file “1987 Conducting training on COVID-19 and keeping it in readiness.pdf” |
2020 Apr |
mail-nrborg.hopto[.]org |
Nepal Rastra Bank |
mail.nrb.gov.np |
Redirect to file ”fiu.pdf” |
2020 May |
mail-nepalarmymilnp.duckdns[.]org |
Nepali Army |
mail.nepalarmy.mil.np |
Redirect to web news “India Should Realise China Has Nothing to Do With Nepal’s Stand on Lipulekh” |
2020 Jun |
mail-nepalarmymilnp.duckdns[.]org |
Nepali Army |
mail.nepalarmy.mil.np |
Showing login failed message |
2020 Jul |
|
Qatar Charity |
mail.qcharity.org |
Redirect to original mail server |
2020 Jul |
|
Myanma Posts and Telecommunications |
webmail.mpt.net.mm |
Redirect to original mail server |
2020 Aug |
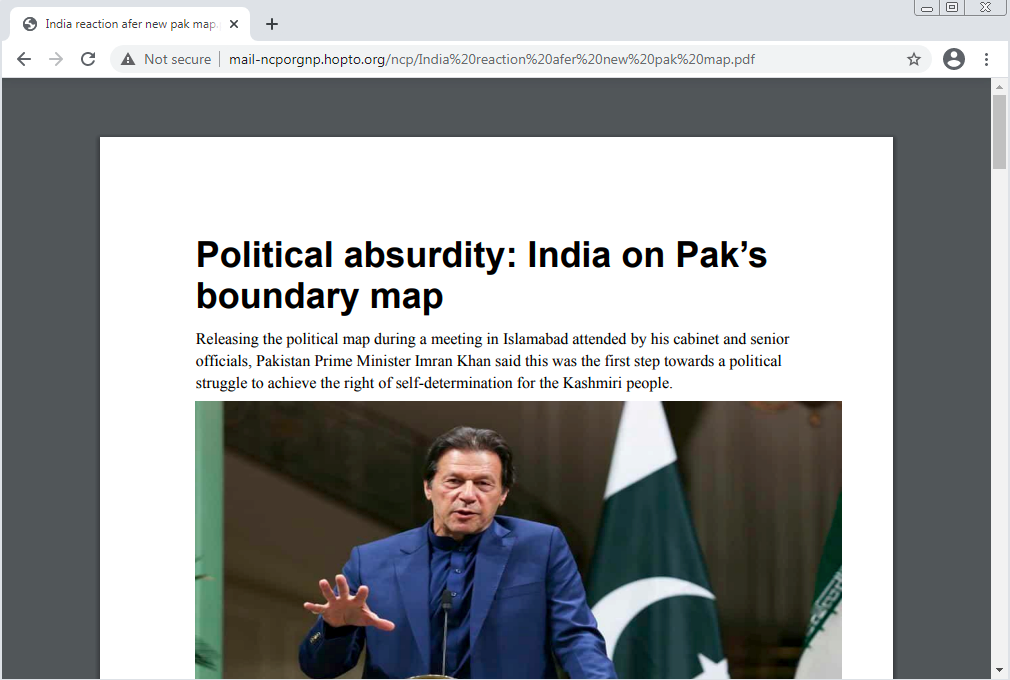
mail-ncporgnp.hopto[.]org |
Nepal Communist Party |
mail.ncp.org.np |
Redirect to file “India reaction after new pak map.pdf” |
2020 Aug |
mail-nscaf.myftp[.]org |
Afghanistan National Security Council |
mail.nsc.gov.af |
Redirect to 10[.]77[.]17[.]10/Software/03-Applications |
2020 Sep |
mail-mofgovnp.hopto[.]org |
Ministry of Finance, Nepal |
mail.mof.gov.np |
Redirect to file “1987 Covid.pdf” |
2020 Sep |
mail-ncporgnp.hopto[.]org |
Nepal Communist Party |
mail.ncp.org.np |
Redirect to document “The spectre of a new Maoist conflict in Nepal” |
2020 Sep |
imail.aop.gov-af[.]org |
Administrative Office of the President, Afghanistan |
imail.aop.gov.af |
Redirect to file “SOP of Military Uniform .pdf” |
2020 Oct |
mail-nepalpolicegovnp.duckdns[.]org |
Nepal Police |
mail.nepalpolice.gov.np |
Redirect to file “2077-07-03 1239 Regarding investigation and action.pdf” |
2020 Oct |
|
Civil Aviation Authority of Nepal |
mail.caanepal.gov.np |
Redirect to original mail server |
2020 Oct |
mail-apfgovnp.ddns[.]net |
Armed Police Force, Nepal |
mail.apf.gov.np |
Redirect to original mail server |
2020 Oct |
mail-nscaf.myftp[.]org |
Afghanistan National Security Council |
mail.nsc.gov.af |
Redirect to file “IT Services Request Form.pdf” |
2020 Nov |
mail-ntcnetnp.serveftp[.]com |
Nepal Telecom |
webmail.ntc.net.np |
Redirect to original mail server |
2020 Nov |
mail-kmgcom.ddns[.]net |
Kantipur Media Group |
mail.kmg.com.np |
Redirect to original mail server |
2020 Nov |
|
Federal Parliament of Nepal |
mail.parliament.gov.np |
Redirect to original mail server |
2020 Nov |
|
Public Procurement Monitoring Office, Nepal |
mail.ppmo.gov.np |
Redirect to original mail server |
2020 Nov |
mail-mfagovcn.hopto[.]org |
Ministry of Foreign Affairs, China |
mail.mfa.gov.cn |
Redirect to file “Ambassador Yanchi Conversation with Nepali_Media.pdf” |
Android applications
We also identified multiple Android APK files on their server. Interestingly, these Android applications still seem to be under the initial development phase as they are basic, still use the default Android icons, and have no practical function for users.
We noticed two applications among them, named “My First APP” and “Opinion Poll,” that seemingly have no malicious behavior. My First APP demonstrates login & register processes, while Opinion Poll acts as an opinion polling application for the Indian-Nepalese political map dispute. The first application is likely an Android demo application for beginners, while the second one starts with an explanation of “Opinion Writing,” followed by a survey.
Another two applications were built from JavaPayload for Metasploit that will load extra code from the remote server configured in the sample. While we were unable to retrieve the payload, according to the Manifest that requests numerous privacy-related permissions like location, contacts, call logs, etc., we can infer that it goes after the user’s private data. These two samples appear to be debug versions as they have no activities or any other component except Metasploit.
We also identified a malicious version of the My First APP application that added Metasploit whose class names have been obfuscated.
SideWinder has used malicious apps as part of its operation before. In the campaign referenced earlier, the group used malicious APKs disguised as photography and file manager tools to lure users into downloading them. Once downloaded into the user’s mobile device, the malicious APKs launch a series of fairly sophisticated procedures that includes rooting the device to stealthily deploy the payload, as well as exploiting CVE-2019-2215 and MediaTek-SU vulnerabilities for root privileges. The payload’s ultimate goal is to gather information from the compromised device and then send it back to its C&C server.
In the case of these newer APKs, it seems that the goal is to gather user information as well. Unlike the earlier apps, which were already on the Google Play Store, all the APK files found on their server are not mature enough for a deliberate attack. In our opinion, these are still in the initial stage, and the payloads (directed at mobile users) are still being refined further.
Conclusion
As seen with their phishing attacks and their mobile device tools’ continuous development, SideWinder is very proactive in using trending topics like Covid-19 or various political issues as a social engineering technique to compromise their targets. Therefore, we recommend that users and organizations be vigilant and follow social engineering best practices to protect themselves from these kinds of campaigns.
Indicator of Compromise
Android Part IoCs
Indicator |
Package name |
Label |
C2 server |
Detection |
0c182b51ff1dffaa384651e478155632c6e65820322774e416be20e6d49bb8f9 |
com.example.firstandoidapp |
My First App |
- |
|
061b0379a12b88488db8540226e400e3f65fef9a4c1aa7744da9f17e1d93d78d |
com.example.opinionpoll |
OpinionPoll |
- |
|
fb6ac9d93fd47db3d32f6da6320344a125e96754a94babb9d9d12b6604a42536 |
com.metasploit.stage |
MainActivity |
https://185.225.19[.]46:4589 |
AndroidOS_Metasploit.HRX |
468b74883536938ef3962655dfcc3ca4097ca9b5b687dfc1fef58d50e96dc248 |
com.metasploit.stage |
MainActivity |
tcp://185.225.19.46[:]4875 |
AndroidOS_Metasploit.HRX |
a377e5f4bf461b86f938959256b7ab8b1b40bb9fd3cd45951c736a22366a8dd1 |
com.example.firstandoidapp |
My First App |
tcp://185.225.19.46[:]4875 |
AndroidOS_Metasploit.HRX |
Malicious documents and related payloads IoCs
Indicator |
Description |
Detection |
TrendX |
1CBEC920AFE2F978B8F84E0A4E6B757D400AEB96E8C0A221130060B196ECE010 |
docx |
Trojan.W97M.CVE20170199.FAIL |
|
7238F4E5EDBE0E5A2242D8780FB58C47E7D32BF2C4F860C88C511C30675D0857 |
RTF file |
Trojan.W97M.SIDEWINDER.A |
|
75C158CEA14E338C8D9D32ED988C7032DA9AE6D54F5B1126ED6A83F71B9E03BF |
1.a JS file |
Trojan.JS.SIDEWINDER.A |
Downloader.JS.TRX.XXJSE9EFF018 |
AB6E8563214EEB747ABF77F9CC50796CC6A0C0562C6BEC720D7F2C978D34C412 |
Fake DUser.dll |
Trojan.MSIL.SIDEWINDER.A |
|
CBD5C68F5C4345B68F018D9E5810574E8036A2BC4D826BE5C8779E8019449957 |
Final payload |
Trojan.Win32.SIDEWINDER.B |
|
34446F7F60F730FCCA145155D10D1AFF0A1153B085836DF38313772CD03C8D70 |
RTF file |
Trojan.W97M.CVE201711882.YQUOOWV |
|
7238F4E5EDBE0E5A2242D8780FB58C47E7D32BF2C4F860C88C511C30675D0857 |
RTF file |
Trojan.W97M.SIDEWINDER.A |
|
AB7C1967BF1FEFDFFDE93626B78EB30994655AB02F59E0ADB0935E3E599A953F |
RTF file |
Trojan.W97M.SIDEWINDER.A |
|
2548A819E4C597BA5958D2D18BAA544452948E5B00271570192CCD79ABE88E8D |
1.a JS file |
Trojan.JS.SIDEWINDER.A |
Downloader.JS.TRX.XXJSE9EFF018 |
ED5E1D6E914DE64A203F2F32AB95176FC7EFFF3A520915971D5FE748E79D611C |
1.a JS file |
Trojan.JS.SIDEWINDER.A |
Downloader.JS.TRX.XXJSE9EFF018 |
96BF8F579ACB8D9D0FF116D05FDADEF85953F11E5B2E703041FDAE0ABF5B75DC |
1.a JS file |
Trojan.JS.SIDEWINDER.A |
Downloader.JS.TRX.XXJSE9EFF018 |
940265867D5668956D64ADF9FC4B9C6CF9E7FCFCF5C21BA7BF0BEA77B5EDD047 |
Fake DUser.dll |
Trojan.MSIL.SIDEWINDER.A |
|
B22946CFEFE8646CB034F358C68CAAE5F30C1CF316CFFEAF77021C099E362C64 |
Fake DUser.dll |
Trojan.MSIL.SIDEWINDER.A |
|
89E392FA49C6A6AEB9056E3D2F38B07D0DD7AF230CD22E3B01C71F05A3AECA0B |
Fake DUser.dll |
Trojan.MSIL.SIDEWINDER.A |
|
EB2D82DD0799196FCF631E15305676D737DC6E40FF588DCF123EDACD023F1C46 |
Final payload |
Trojan.Win32.SIDEWINDER.B |
|
7ECAEFCB46CDDEF1AE201B1042A62DD093594C179A6913A2DE47AB98148545DD |
Final payload |
Trojan.Win32.SIDEWINDER.B |
|
799260B992C77E2E14F2D586665C570142D8425864455CAB5F2575015CD0B87A |
Final payload |
Trojan.Win32.SIDEWINDER.B |
|
brep.cdn-edu[.]net |
RTF delivery server |
|
|
www.mfa.filesrvr[.]net |
RTF delivery server |
|
|
www.google.gov-pok[.]net |
RTF delivery server |
|
|
ap-ms[.]net |
C&C |
|
|
cdn-sop[.]net |
C&C |
|
|
fqn-cloud[.]net |
C&C |
|
|
ms-trace[.]net |
C&C |
|
|
imail.aop.gov-af[.]org |
Phishing Domain |
|
|
mail-apfgavnp.hopto[.]org |
Phishing Domain |
|
|
mail-apfgovnp.ddns[.]net |
Phishing Domain |
|
|
mail-kmgcom.ddns[.]net |
Phishing Domain |
|
|
mail-mfagovcn.hopto[.]org |
Phishing Domain |
|
|
mail-mofagovnp.hopto[.]org |
Phishing Domain |
|
|
mail-ncporgnp.hopto[.]org |
Phishing Domain |
|
|
mail-nepalarmymilnp.duckdns[.]org |
Phishing Domain |
|
|
mail-nepalgovnp.duckdns[.]org |
Phishing Domain |
|
|
mail-nepalpolicegov.hopto[.]org |
Phishing Domain |
|
|
mail-nepalpolicegovnp.duckdns[.]org |
Phishing Domain |
|
|
mail-nrborg.hopto[.]org |
Phishing Domain |
|
|
mail-nscaf.myftp[.]org |
Phishing Domain |
|
|
mail-ntcnetnp.serveftp[.]com |
Phishing Domain |
|
|
mail.arg.gov-af[.]org |
Phishing Domain |
|
|
mail.moha.gov-np[.]org |
Phishing Domain |
|
|
mail.nsc.gov-af[.]org |
Phishing Domain |
|
|
webmail.mohe.gov-af[.]org |
Phishing Domain |
|
|

