The Most Common Cloud Misconfigurations That Could Lead to Security Breaches
The cloud has helped fast-track the digital transformation of organizations amid a global pandemic. Its dependability and flexibility have enabled them to migrate expeditiously to remote work during challenging times. However, swift cloud adoptions could lead to mistakes — more commonly referred to as misconfigurations — brought about by oversights, errors, or ill-informed cloud service configuration choices. And while it’s perfectly understandable to be wary of complex security threats in the cloud, organizations should also be on the lookout for simple misconfigurations that could ultimately lead to the unintended exposure of mission-critical information and assets.
Misconfigurations might seem straightforward and avoidable, but they are the most significant risks to cloud environments. In fact, 65 to 70% of all security challenges in the cloud arise from misconfigurations. Under the hood, the cloud comprises a multitude of settings, policies, assets, and interconnected services and resources that make it a sophisticated, if daunting, environment to fully understand and properly set up. This is especially true for organizations that have been pushed to migrate quickly to the cloud since remote work became the new norm. Unfortunately, when organizations start using any new technology too quickly without fully understanding its many intricacies, misconfigurations can ensue.
As an attack vector, misconfigurations can be insidious and were the reason behind massive breaches in recent years. In 2018 and 2019, cloud misconfiguration breaches cost companies almost US$5 trillion. For example, in 2020, more than 440 million Estee Lauder records that included user email addresses and audit, error, CMS, middleware, and production logs were exposed because of a database that was not password-protected. In 2020, the adult website CAM4 inadvertently leaked 10.88 billion records that included users’ personally identifiable information (PII), payment logs, and password hashes because of an unsecured Elastic Search database.
Misconfigurations have been among the leading causes of massive financial and reputational harm in enterprises and government entities. Thus, cloud adopters need to know the commonly occurring misconfigurations in order to mitigate them before malicious actors get wind of them and cause more significant harm. Using data that we gathered through Trend Micro Cloud One™ – Conformity within a one-year period (June 30, 2020 to June 29, 2021), we looked at the top 10 Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure services with the highest misconfiguration rates with regard to the implementation of Cloud Conformity rules.
The top 10 AWS services with the highest misconfiguration rates
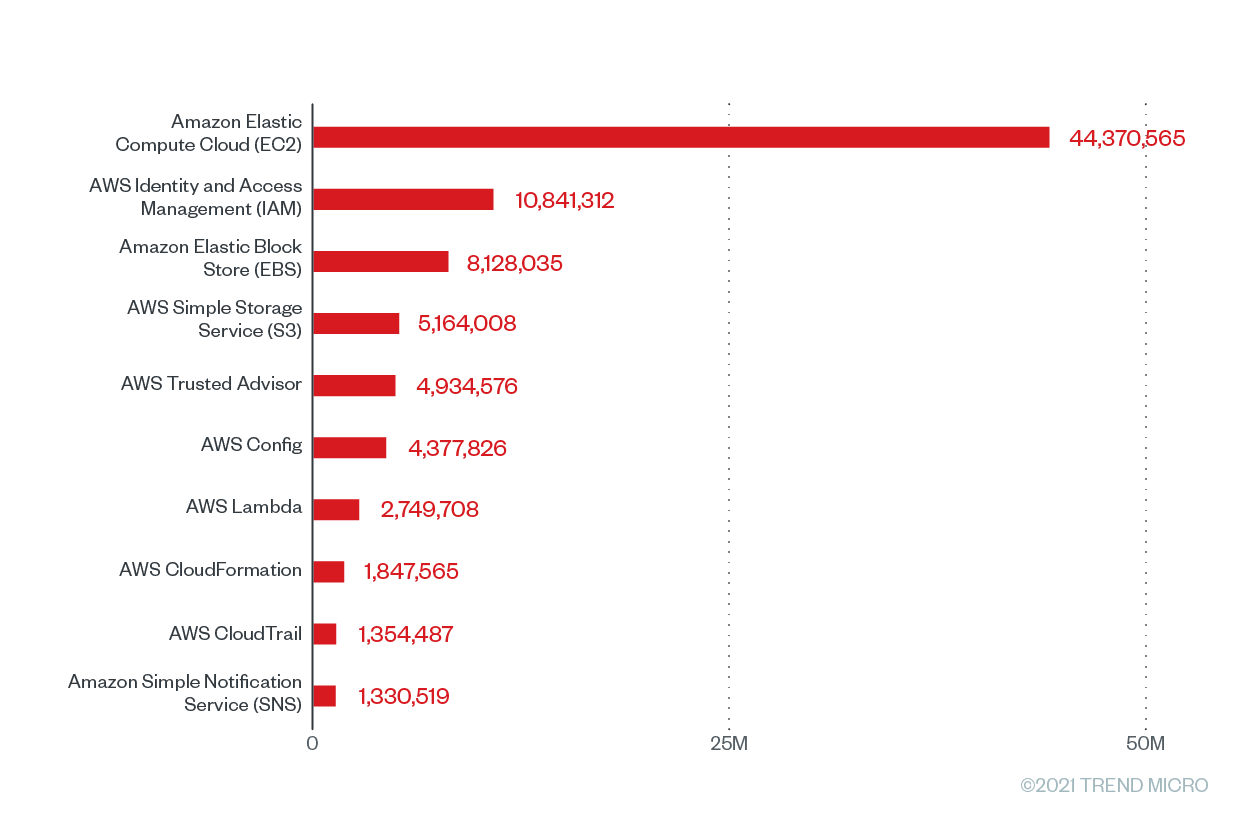
We looked at the top 10 AWS services with the greatest number of Cloud Conformity checks, as shown in Figure 1, which are the result of Cloud Conformity rules being scanned or run against our Cloud Conformity customers’ configuration of infrastructures or resources. A single cloud service can have numerous Cloud Conformity rules regularly scanning it to check for vulnerabilities and risks. These scans will subsequently result in checks. Each Cloud Conformity rule comes with a corresponding implementation, and the checks that run against the rules determine the success or failure of these implementations. It should be noted that the number of checks does not represent the level of misconfiguration or the risk level of a particular service. Cloud Conformity users can choose to run a few or numerous checks simultaneously against their infrastructures and resources.
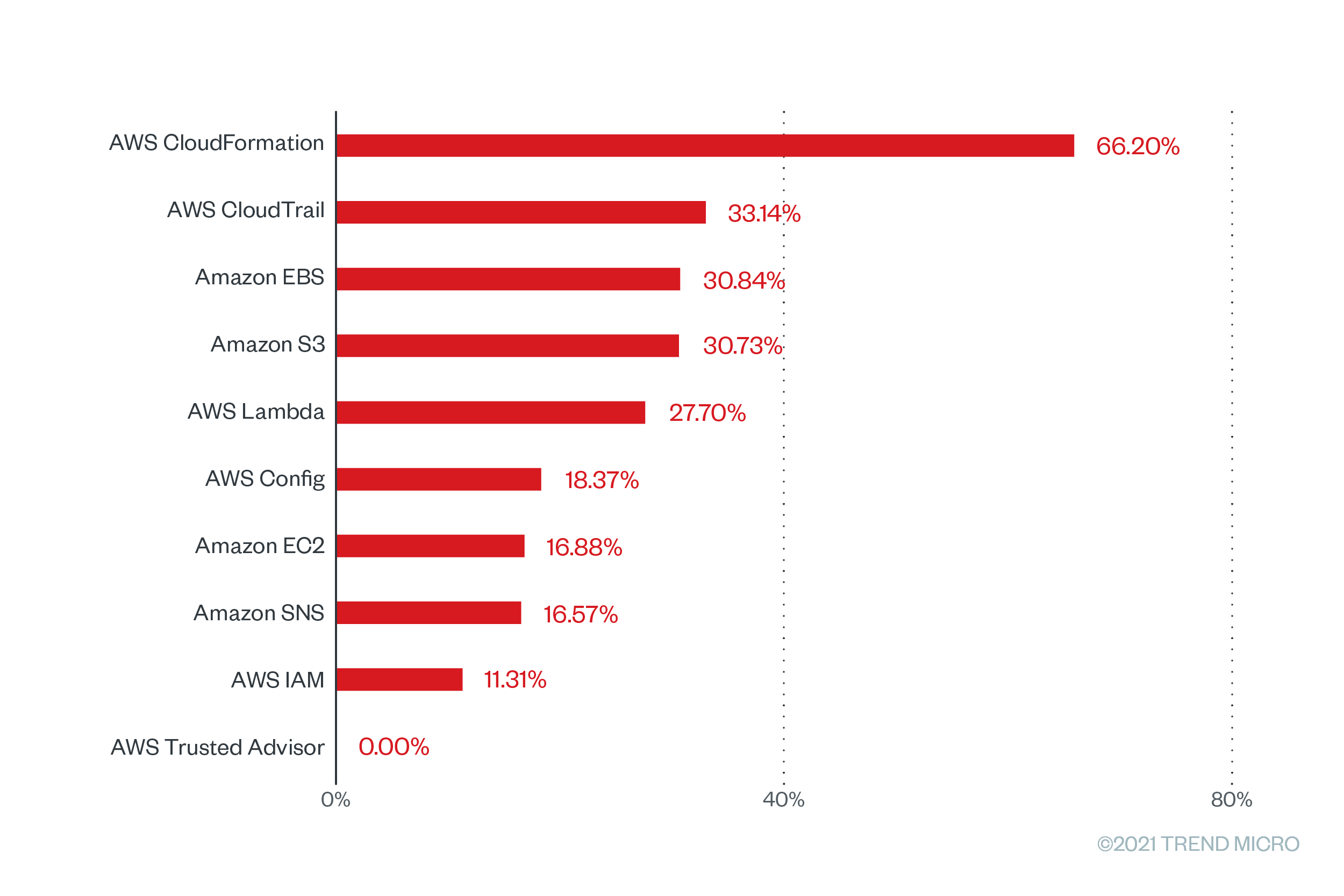
We then highlighted their respective misconfiguration rates, as shown in Figure 2, which are the percentage of rules found to be unsuccessfully implemented after a scan. It’s important to note that misconfigurations alone do not make applications unsecure. However, they can give malicious actors a way into the cloud environment to the detriment of organizations. Cloud services are also secure; in fact, cloud service providers (CSPs) do their part in the shared responsibility model by designing, implementing, and constantly reviewing their infrastructure to the highest standards. Yet misconfigurations can still occur when cloud assets and services are set up incorrectly on the customer side, leaving an impact on the quality of cloud applications.
Figure 1. The top 10 AWS services with the greatest number of checks that were run based on Trend Micro Cloud One – Conformity data from June 2020 to June 2021
Figure 2. The misconfiguration rates of the top 10 AWS services with the greatest number of checks that were run based on Trend Micro Cloud One – Conformity data from June 2020 to June 2021
The top misconfigured rule that has a high severity rating and a misconfiguration rate of a whopping 100% is “AWS CloudTrail configuration changes,” a Cloud Conformity rule for the AWS CloudTrail service. AWS CloudTrail allows users to regularly log and monitor account activity related to actions performed across the AWS infrastructure. It also has a feature that allows users to see AWS account activity history, enabling a more streamlined and efficient security auditing, resource change tracking, and troubleshooting. When left disabled, configuration changes will not be monitored and recorded. This means that users will not know who took action, what action was taken, when the action took place, and which resources were affected by the action.
For the Amazon EBS service, the top misconfigured high-severity rule is “App-tier EBS encrypted,” which also has a misconfiguration rates of 100%. When this feature is not enabled, the data stored in AWS EBS volumes attached to app-tier EC2 instances will be exposed. This includes data at rest on the volume, disk input and output operations, and all of the snapshots taken from the volume.
Meanwhile, “enable Amazon S3 block public access for AWS accounts” is the top misconfigured rule under the Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3), with a severity classification of “very high” and a misconfiguration rating of 68.97%. This feature allows bucket owners to efficiently set up controls to limit public access to their Amazon S3 data. When this is not enabled, simple configuration mistakes or errors can open Amazon S3 bucket data to the public, which can result in data breaches.
To counter potential misconfigurations and security risks, Amazon provides its users with a set of best-practice recommendations in the form of the AWS Well-Architected Framework and preventative security best practices and monitoring and auditing guidelines for keeping Amazon S3 buckets secure. But even with readily available and detailed documentation, it’s still possible for users to fall short and leave Amazon S3 buckets open and publicly accessible. In a research paper that we published last year, titled “Securing Weak Points in Serverless Architectures: Risks and Recommendations,” we discussed the risks associated with open buckets that contained sensitive data and buckets that were not completely open but were indexing accessible data.
In recent years, we saw how organizations reeled from the effects of misconfigured Amazon S3 buckets. This year, over 1.6 million files of citizens from dozens of municipalities were compromised because of 86 unprotected Amazon S3 buckets in the municipalities’ information management software.
The most common misconfigurations in AWS
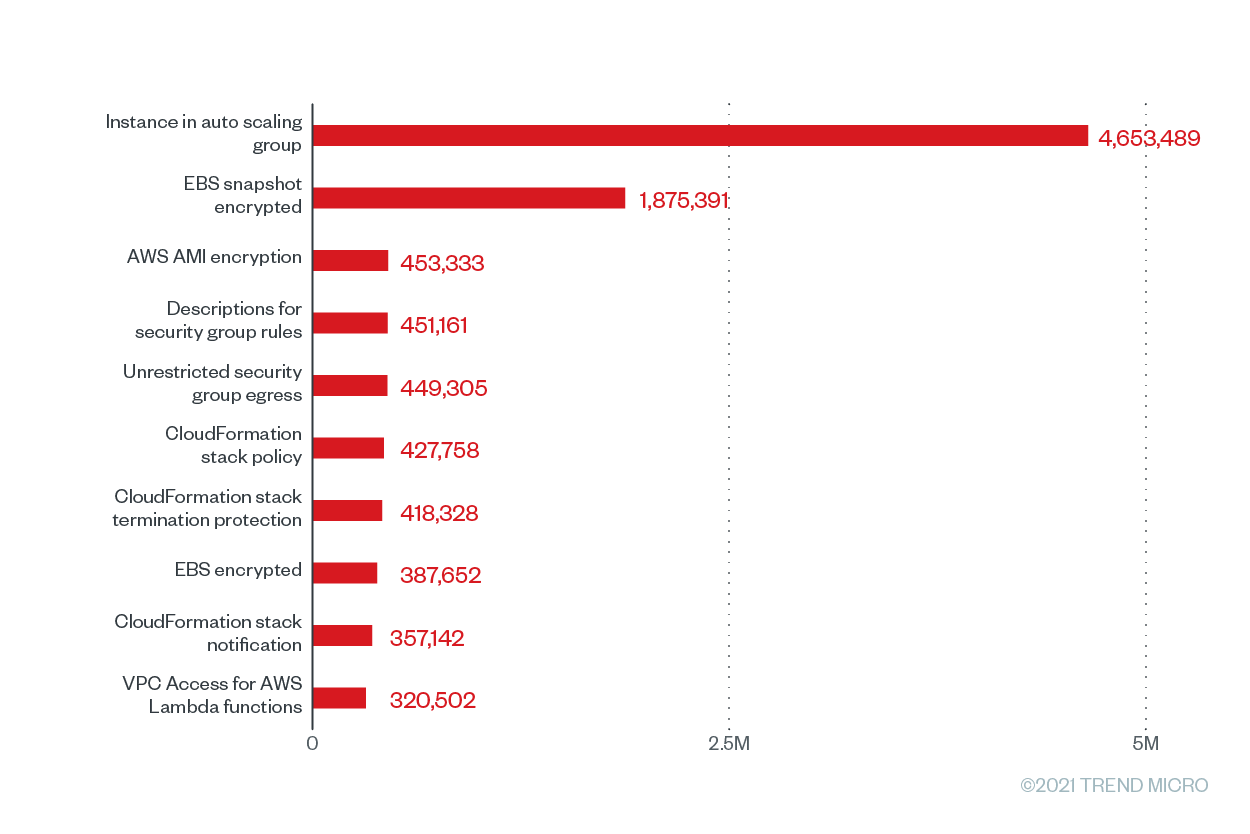
Figure 3. The top 10 Trend Micro Cloud One – Conformity configuration rules according to the number of misconfigurations for AWS from June 2020 to June 2021
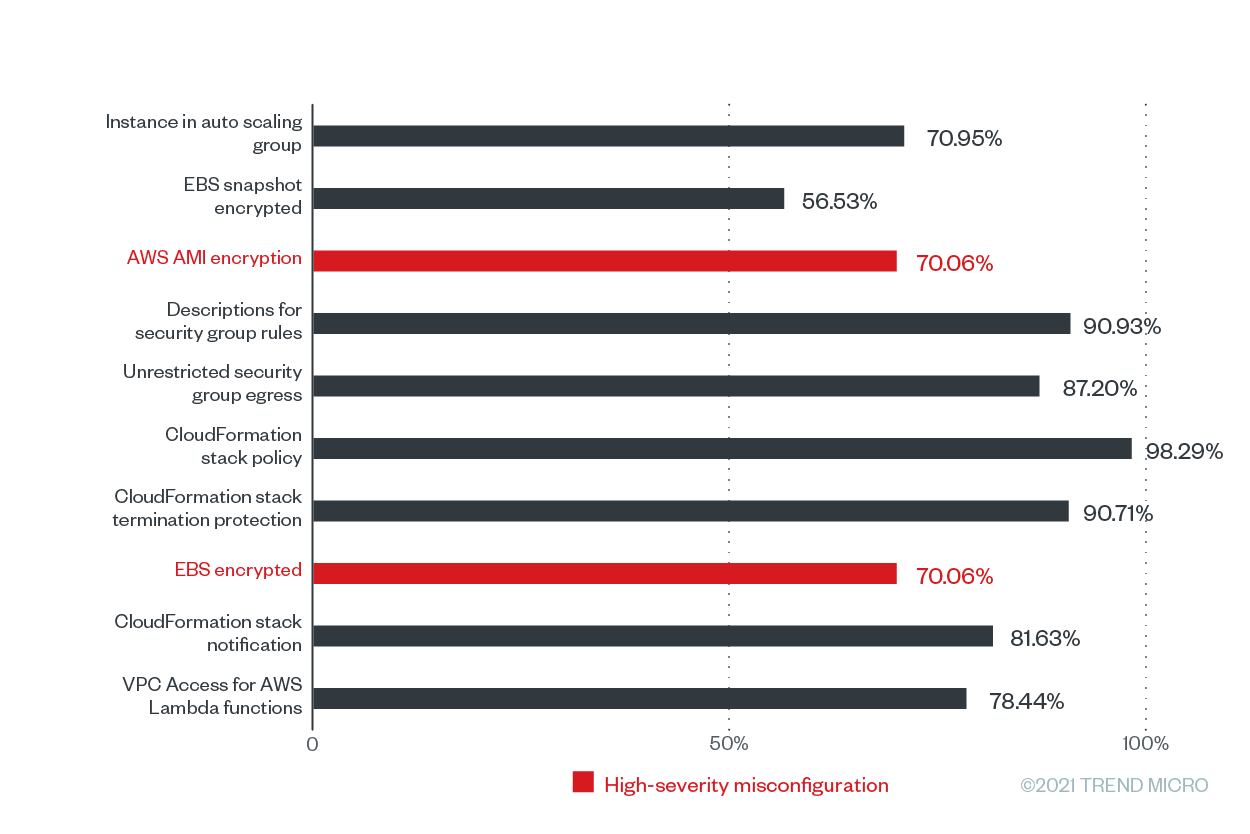
Figure 4. The misconfiguration rates of the top 10 Trend Micro Cloud One – Conformity configuration rules according to the number of misconfigurations for AWS from June 2020 to June 2021
In this list, two rules, namely “AWS AMI encryption” and “EBS encrypted” are high-severity misconfiguration rules that have the same substantial misconfiguration rate of 70.06% across the Cloud Conformity userbase. These rules can help ensure that compliance standards such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA), Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS), and National Institute of Standards and Technology 800-53 (Rev. 4) are followed.
Both of these high-severity misconfigurations are related to storage (bucket/blob) misconfigurations and encryption, as well as ensuring that sensitive data is not publicly exposed, which could lead to data breaches, operational downtime, and costly fines. This was the case with a channel management software services company that exposed 10 million files that included the PII and financial information of travel industry customers.
The top 10 Microsoft Azure services with the highest misconfiguration rates
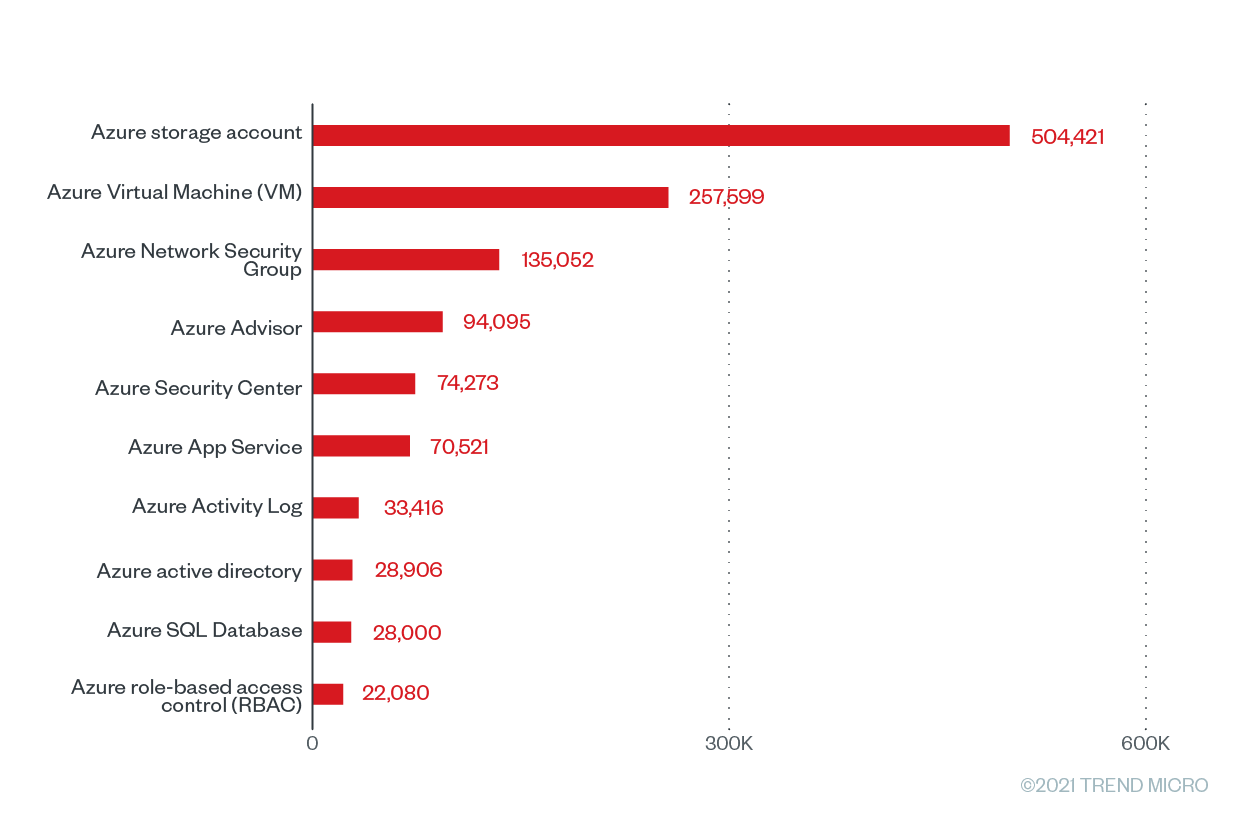
Figure 5. The top 10 Microsoft Azure services with the greatest number of checks that were run based on Trend Micro Cloud One – Conformity data from June 2020 to June 2021
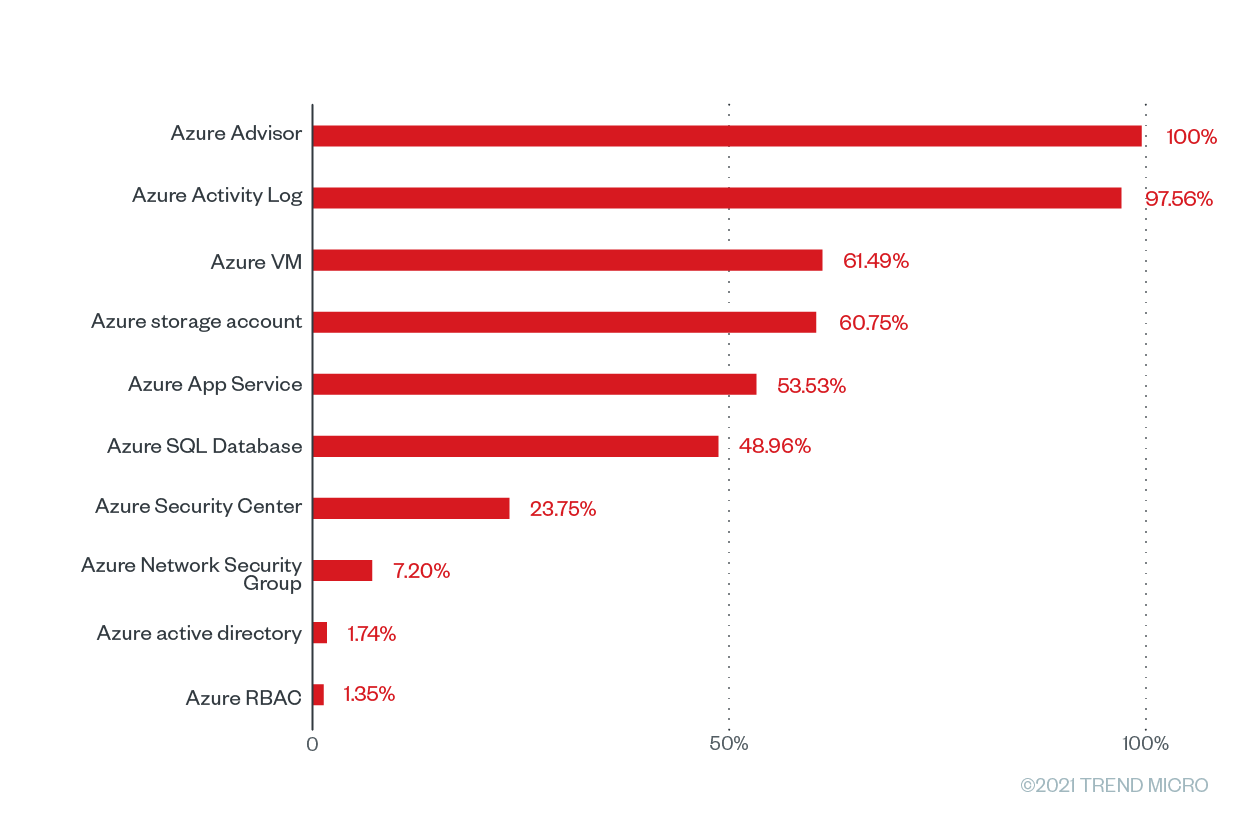
Figure 6. The misconfiguration rates of the top 10 Microsoft Azure services with the greatest number of checks that were run based on Trend Micro Cloud One – Conformity data from June 2020 to June 2021
The Azure Advisor service tops the list with 94,095 Cloud Conformity checks and misconfigurations and a misconfiguration rate of 100%. Azure Activity Log, an Azure tool that “provides insight into subscription-level events,” is at a close second place, with a misconfiguration rate of 97.56% from 33,416 checks and 32,602 misconfigurations. It’s essential for users to regularly check the Azure Activity Log, as it provides data that pertains to configuration changes. Accurately collecting and analyzing Azure Activity Log data can enable users to keep an eye out for potentially malicious activity across their systems.
The top misconfigured rules for this Azure service are related to PostgreSQL, a fully managed database-as-a-service platform. "Create alert for ‘delete PostgreSQL database’ events" and “create alert for ‘create/update PostgreSQL database’ events” both have a high misconfiguration rate of 99.10%. When left improperly configured, PostgreSQL databases can be abused for cryptocurrency mining, as the PGMiner botnet operation discovered in 2020.
Meanwhile, the on-demand computing resource Azure Virtual Machines (VMs) has the third highest percentage of misconfiguration at 61.49% with 257,599 checks and 158,406 misconfigurations. The Azure VM rules with the highest misconfiguration rates at 100% are "install approved extensions only” and “enable automatic OS upgrades.” When vulnerable extensions are used in Azure environments, it can lead to elevation of privilege and remote execution attacks. Recently, malicious actors abused the Azure OMIGOD vulnerabilities in the Open Management Infrastructure (OMI) framework used by several Azure VM management extensions. Microsoft has since issued extension updates for these vulnerable extensions.
The Azure storage account, a service that holds all Azure storage objects, has a misconfiguration percentage of 60.75% coming from 504,421 checks and 306,433 misconfigurations. Because data breaches are so rampant and costly, enterprises must ensure that their storage accounts are as secure as possible. This year, improperly configured Azure storage accounts inadvertently exposed millions of files that contained sensitive information such as medical records, personal information, contracts, and invoices. Following the Azure storage account is the Azure App Service, which has a misconfiguration rate of 55.53% from 70,521 checks and 37,748 misconfigurations.
The most common misconfigurations in Azure
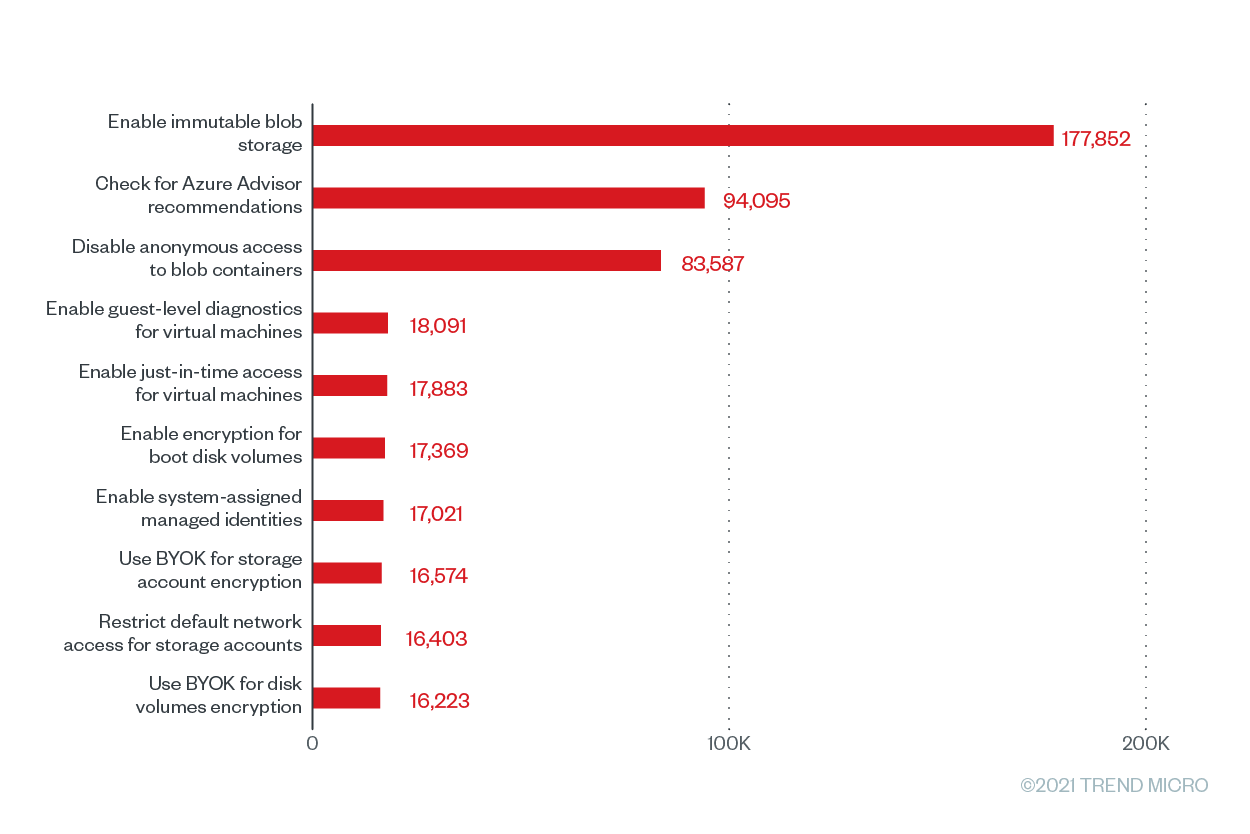
Figure 7. The top 10 Trend Micro Cloud One – Conformity configuration rules according to the number of misconfigurations that were run for Microsoft Azure from June 2020 to June 2021
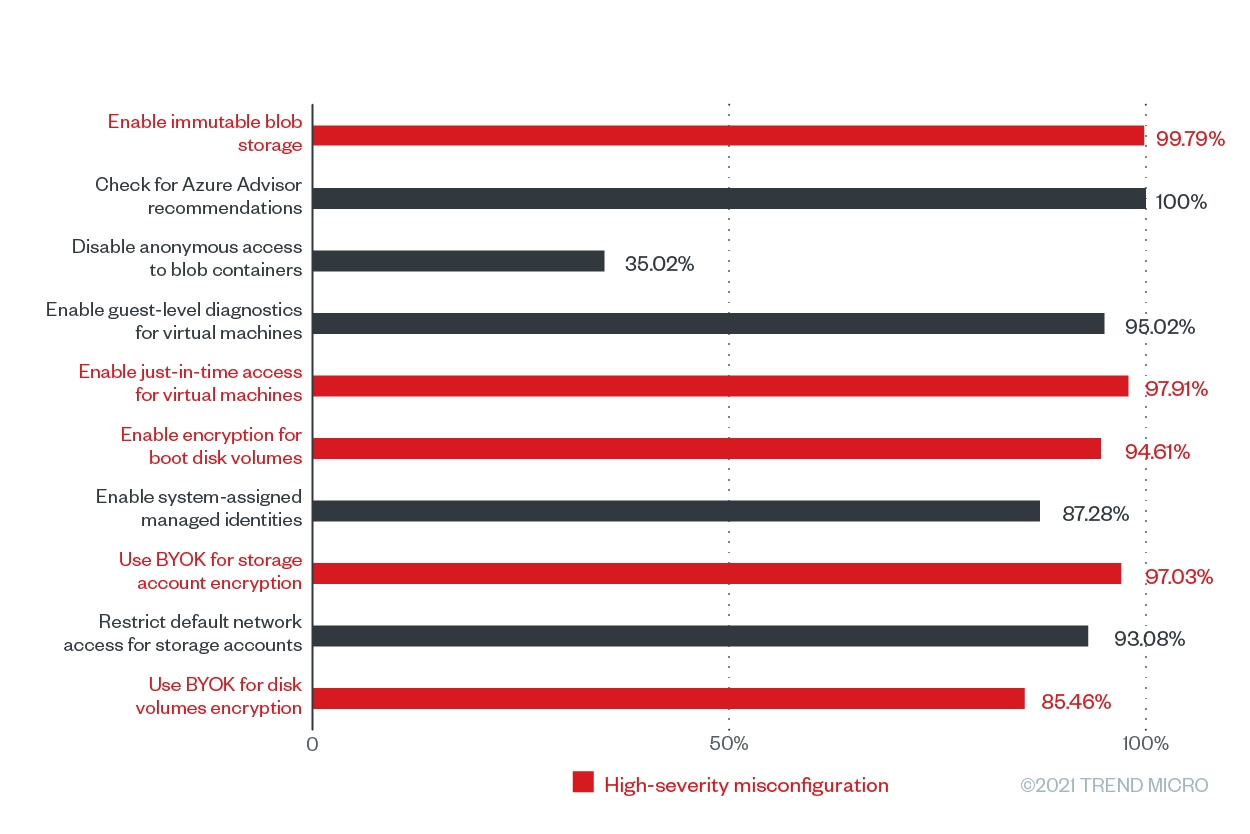
Figure 8. The misconfiguration rates of the top 10 Trend Micro Cloud One – Conformity configuration rules according to the number of misconfigurations for Microsoft Azure from June 2020 to June 2021
Our data shows that the top misconfigured rule for Microsoft Azure in terms of its misconfiguration rate was “check for Azure Advisor recommendations,” which has a misconfiguration rate of 100% and and a total number of 94,095 misconfigurations. This rule’s severity rating depends on the severity rating of Azure Advisor, a tool that helps users improve the cost-effectiveness, performance, reliability, and security of their resources by providing detailed resource configuration analyses and usage telemetry.. Failure to check Azure Advisor recommendations might keep users unaware of attacks that are already compromising their cloud environments. Azure Advisor, which integrates with Azure Security Center, flags threats such as cryptocurrency mining and brute-force attacks for users to mitigate and remediate.
Following the top misconfigured rule closely is “enable immutable blob storage,” a high-severity storage (bucket/blob) misconfiguration that has a misconfiguration rate of 99.79% and 177,852 misconfigurations across our customer base. The immutable blob storage allows users to store business-critical data in a write-once, read-many (WORM) state, which effectively disables the modification and deletion of data for a user-specified time frame. And with ransomware attacks becoming increasingly sophisticated, as in modern ransomware attacks that use double extortion methods, this extra layer of security can keep mission-critical data secure by keeping it from being altered or deleted by any user — or malicious actor — for a certain period.
Aside from “enable immutable blob storage,” there are four other high-severity misconfigurations in this top 10 list, namely:
Azure configuration rule | Misconfiguration category |
Identity and access management (IAM) misconfiguration, exploitable service behind open ports | |
Storage (bucket/blob) misconfiguration, Data encryption issues | |
Use Bring Your Own Key (BYOK) for storage account encryption | Data encryption issues |
Storage (bucket/blob) misconfiguration, Data encryption issues |
When Azure VMs are misconfigured, malicious actors can launch DDoS and brute-force attacks. Azure provides recommendations to keep Azure VMs secure.
Another common misconfiguration for Microsoft Azure was “disable anonymous access to blob containers,” with 83,587 misconfigurations and a misconfiguration rate of 35.02%. It’s important to note that this feature is not enabled by default. However, if users enable this feature to share data conveniently, anyone can read data in a container and its blobs. To avoid breaches, Microsoft recommends enabling anonymous access only when specific application scenarios require it. The company also advises users to use the Azure Metrics Explorer to track all anonymous requests made to a storage account.
Cryptocurrency mining attacks, which take advantage of victims’ computing resources, have proved to be a popular choice for malicious actors with regard to compromising Azure environments. Last year, misconfigured Azure Kubernetes clusters used for machine-learning (ML) applications were compromised to deploy cryptocurrency miners. Earlier this year we’ve reported that TeamTNT, a threat actor that focus on cloud and container environments, compromised thousands of Kubernetes clusters to mine cryptocurrencies. Attackers leveled up their cryptocurrency mining attacks by hiding in plain sight this year: They used TensorFlow pods that ran legitimate images from the official Docker Hub account to run malicious code and mine cryptocurrency.
Apart from illicit cryptocurrency mining activities, attackers this year have also been observed deploying heavily obfuscated malware called Siloscape on misconfigured Kubernetes clusters to run malicious containers and steal critical data.
Avoiding mistakes: How can organizations prevent misconfigurations in the cloud?
For organizations looking to prioritize digital transformation, all roads lead to cloud adoption. And while CSPs generally do a good job at securing the infrastructure of the cloud services they offer, users must understand that they might introduce or overlook misconfigurations that could be detrimental to their organizations. Seemingly simple misconfigurations, which sadly are not a rarity, could lead to devastating events such as data breaches or ransomware attacks.
It’s important to understand that the cloud is not a turnkey security solution. It is therefore urgent for organizations to know the important part that they must play in keeping their cloud environments secure.
Here are some security recommendations for keeping misconfigurations and threats at bay:
- Granting least-privilege access. With regard to access, users should be given only the necessary access or permission that they need in order to operate. This is referred to as the principle of least privilege. Admin or root privileges should be given only to those who require them. If a user with admin access becomes compromised, a malicious actor could be enabled to compromise the entire network. By limiting the number of people with admin and root privileges, the risk of compromise effectively becomes lower.
- Adhering to the shared responsibility model. The shared responsibility model highlights the delegation of responsibility between the CSP and the user. When users understand the operational tasks that they’re responsible for, the risk of misconfigurations occurring is minimized. For example, some VMs or instances have preconfigured deployment services provided by the CSPs. Once users use these, they must understand that they are responsible for the monitoring, upkeep, and patching of the configuration for security and compliance. Both AWS and Microsoft Azure provide guidance explaining the shared responsibility model to their users.
- Educating and training team members. It’s vital for team members to understand their responsibilities with regard to security. From identifying unsecure practices to promptly reporting security issues, everyone should be educated and trained on which threats and misconfigurations to watch out for. AWS users who are concerned about security misconfigurations can also join the AWS Partner Network, where they can get security support via tools, consulting, training, and managed services.
- Creating and implementing security policies, standards, and procedures. Effective and detailed security policies, standards, and procedures should be defined and implemented to minimize the risk of misconfigurations. Policies pertaining to the use of open-source components, remote access, password creation and management, encryption and decryption, and database management should be created and strictly enforced.
Trend Micro solutions
The Trend Micro Cloud One – Conformity solution provides continuous security, compliance, and governance in a software-as-a-service (SaaS) platform designed to help organizations manage misconfigurations of cloud resources in a multicloud environment — helping cloud builders have the confidence that their cloud infrastructure is configured and compliant to grow and scale their business. Conformity is part of the Trend Micro Cloud One™ platform, a security services platform for organizations building in the cloud. It delivers flexible and scalable all-in-one security that helps DevOps and security engineers securely build and innovate as they migrate to and build in the cloud.
Looking to audit your environment to see you hold up? Sign up for a free 30-day Cloud One trial today.
Like it? Add this infographic to your site:
1. Click on the box below. 2. Press Ctrl+A to select all. 3. Press Ctrl+C to copy. 4. Paste the code into your page (Ctrl+V).
Image will appear the same size as you see above.
- Cracking the Isolation: Novel Docker Desktop VM Escape Techniques Under WSL2
- Azure Control Plane Threat Detection With TrendAI Vision One™
- Forecasting Future Outbreaks: A Behavioral and Predictive Approach to Proactive Cyber Risk Management
- Fault Lines in the AI Ecosystem: TrendAI™ State of AI Security Report
- The Industrialization of Botnets: Automation and Scale as a New Threat Infrastructure

 Fault Lines in the AI Ecosystem: TrendAI™ State of AI Security Report
Fault Lines in the AI Ecosystem: TrendAI™ State of AI Security Report Cracking the Isolation: Novel Docker Desktop VM Escape Techniques Under WSL2
Cracking the Isolation: Novel Docker Desktop VM Escape Techniques Under WSL2 Ransomware Spotlight: DragonForce
Ransomware Spotlight: DragonForce Stay Ahead of AI Threats: Secure LLM Applications With Trend Vision One
Stay Ahead of AI Threats: Secure LLM Applications With Trend Vision One