HackTool.Win32.FScan.C
Gen:Variant.Fragtor.223239 (BITDEFENDER)
Windows


Threat Type: Hacking Tool
Destructiveness: No
Encrypted: No
In the wild: Yes
OVERVIEW
This Hacking Tool arrives on a system as a file dropped by other malware or as a file downloaded unknowingly by users when visiting malicious sites.
It does not have any propagation routine.
It does not have any backdoor routine.
It does not have any information-stealing capability.
TECHNICAL DETAILS
Arrival Details
This Hacking Tool arrives on a system as a file dropped by other malware or as a file downloaded unknowingly by users when visiting malicious sites.
Propagation
This Hacking Tool does not have any propagation routine.
Backdoor Routine
This Hacking Tool does not have any backdoor routine.
Rootkit Capabilities
This Hacking Tool does not have rootkit capabilities.
Information Theft
This Hacking Tool does not have any information-stealing capability.
NOTES:
This Hacking Tool does the following:
- It displays the list of parameters that can be used when executed without parameters in a console:
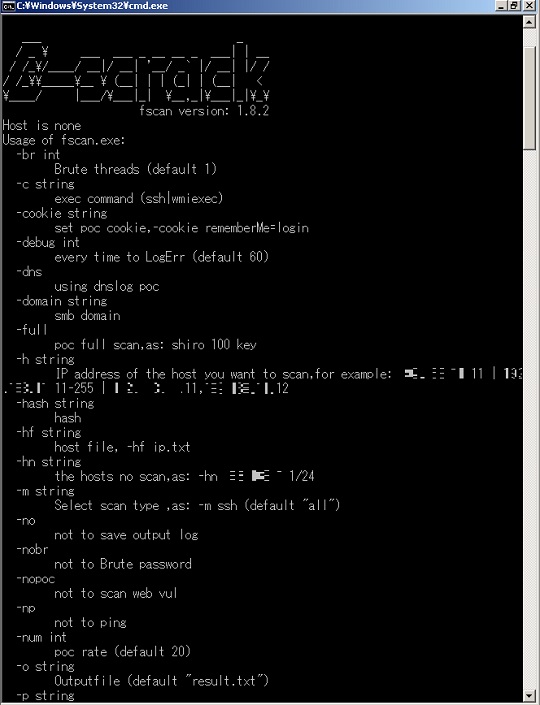
- It uses the following version of fscan:
- fscan 1.8.2
It accepts the following parameters:
- -br {Integer} → used to set the number of threads for brute force attacks. Default value is 1.
- -c {Command String} → used to execute SSH or WMI commands.
- -cookie {String} → used to set the cookie for the scanning process. It can also set the cookie for PoC.
- -debug {Integer} → used to set the interval for logging errors in seconds. Default value is 60.
- -dns → used to enable DNS resolution. It uses PoC which involves the use of DNS logs.
- -domain {Domain} → used to perform a scan on SMB domain.
- -full → used to enable a full scan using 100 shiro keys.
- -h {IP Address/es} → used to specify the target IP address/es for the scan.
- -hash {Hash Value} → used for Pass-the-Hash (PTH) attacks using NTLM hash.
- -hf {File Path} → used to specify a file that contains a list of target IP addresses.
- -hn {IP Address} → used to specify the IP address, in CIDR notation form, to be excluded from the scan.
- -m {String} → used to specify the scanning mode (e.g., -m ssh, -m netbios). Default value is "all".
- -no → used to specify that the scan results should not be saved to a file.
- -nobr → used to skip the brute force passwords.
- -nopoc → used to skip checking for web vulnerabilities by disabling the execution of PoC modules during scan.
- -np → used to skip the host survival detection process or ping host.
- -num {Integer} → used to set the rate of sending packets for web PoC scanning. Default value is 20.
- -o {File Path} → used to specify the file path where the scan results will be saved.
- -p {Port/s} → used to specify the ports to scan. Default value is "21,22,80,81,135,139,443,445,1433,1521,3306,5432,6379,7001,8000,8080,8089,9000,9200,11211,27017".
- -pa {Port} → used to add additional ports to the default port list for scanning.
- -path {Path} → used to provide remote file path for SMB and FastCGI scans.
- -ping → used to enable the use of the ping command for host survival detection instead of ICMP.
- -pn {Port} → used to specify the ports to be skipped during the scanning process.
- -pocname {String} → used to specify the name of the web vulnerability PoC to scan for.
- -pocpath {File Path} → used to specify the path to the directory containing the PoC files for web vulnerabilities.
- -portf {File Path} → used to specify a file that contains a list of ports to be scanned.
- -proxy {Proxy Server} → used to specify a proxy server to be used when performing a scan.
- -pwd {String} → use to set a specific password to be used when attempting to authenticate with the target services.
- -pwda {String} → used to add new passwords to the existing password dictionary for brute force attacks.
- -pwdf {File Path} → used to specify a file that contains a list of passwords to be used for brute force attacks.
- -rf {File Path} → used to specify a file that contains the public key for the Redis service.
- -rs {IP Address}:{Port} → used to specify an IP address and port for a reverse shell by writing a cron file on the target Redis server.
- -sc {String} → used to specify a shellcode for the MS17-010 (EternalBlue) exploit module (e.g., -sc add).
- -silent → used to enable silent scanning.
- -socks5 {IP Address}:{Port} → used to specify a SOCKS5 proxy for the scan.
- -sshkey {File Path} → used to specify the file path of a private SSH key for SSH connections.
- -t {Integer} → used to specify the number of scanning threads. Default value is 600.
- -time {Integer} → used to specify the timeout for port scanning. Default value is 3.
- -top {Integer} → used to control the display of top live hosts during the scanning process. Default value is 10.
- -u {URL} → used to specify a single URL for scanning.
- -uf {File Path} → used to specify a file that contains multiple URLs for scanning.
- -user {String} → used to specify a username for brute force attacks.
- -usera {String} → used to add a new username to the existing user dictionary for brute force attacks.
- -userf {File Path} → used to specify a file that contains multiple usernames for brute force attacks.
- -wmi → used to execute a command on a remote system using WMI.
- -wt {Integer} → used to set the timeout for web access. Default value is 5.
It takes advantage of the following exploit(s):
- if "-sc [String}" parameter is used:
SOLUTION
Step 1
Before doing any scans, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 8.1, and Windows 10 users must disable System Restore to allow full scanning of their computers.
Step 2
Scan your computer with your Trend Micro product to delete files detected as HackTool.Win32.FScan.C. If the detected files have already been cleaned, deleted, or quarantined by your Trend Micro product, no further step is required. You may opt to simply delete the quarantined files. Please check the following Trend Micro Support pages for more information:
Did this description help? Tell us how we did.
