![]() Download Tracking the Activities of TeamTNT: A Closer Look at a Cloud-Focused Malicious Actor Group
Download Tracking the Activities of TeamTNT: A Closer Look at a Cloud-Focused Malicious Actor Group
TeamTNT, one of the most prolific and persistent malicious actor groups in recent memory, embarked on a number of campaigns in 2020 and early 2021. Most of these campaigns — although varying in tools, techniques, and scope — targeted cloud environments.
TeamTNT had apparently been active in some form since 2011, but it was only in 2020 that the group started to garner attention. In April last year, it launched a short-lived campaign that capitalized on Covid-19 by choosing names related to the pandemic for its malware and deployment URLs. A month later, we published an entry about how TeamTNT was targeting open Docker daemon ports to distribute cryptocurrency miners. It instigated another campaign just before 2020 ended, deploying TNTbotinger, an IRC (Internet Relay Chat) bot with distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) capabilities. This year, it had focused even more on the cloud, with its campaigns encompassing different cloud-based services and software.
Infection routines and payloads
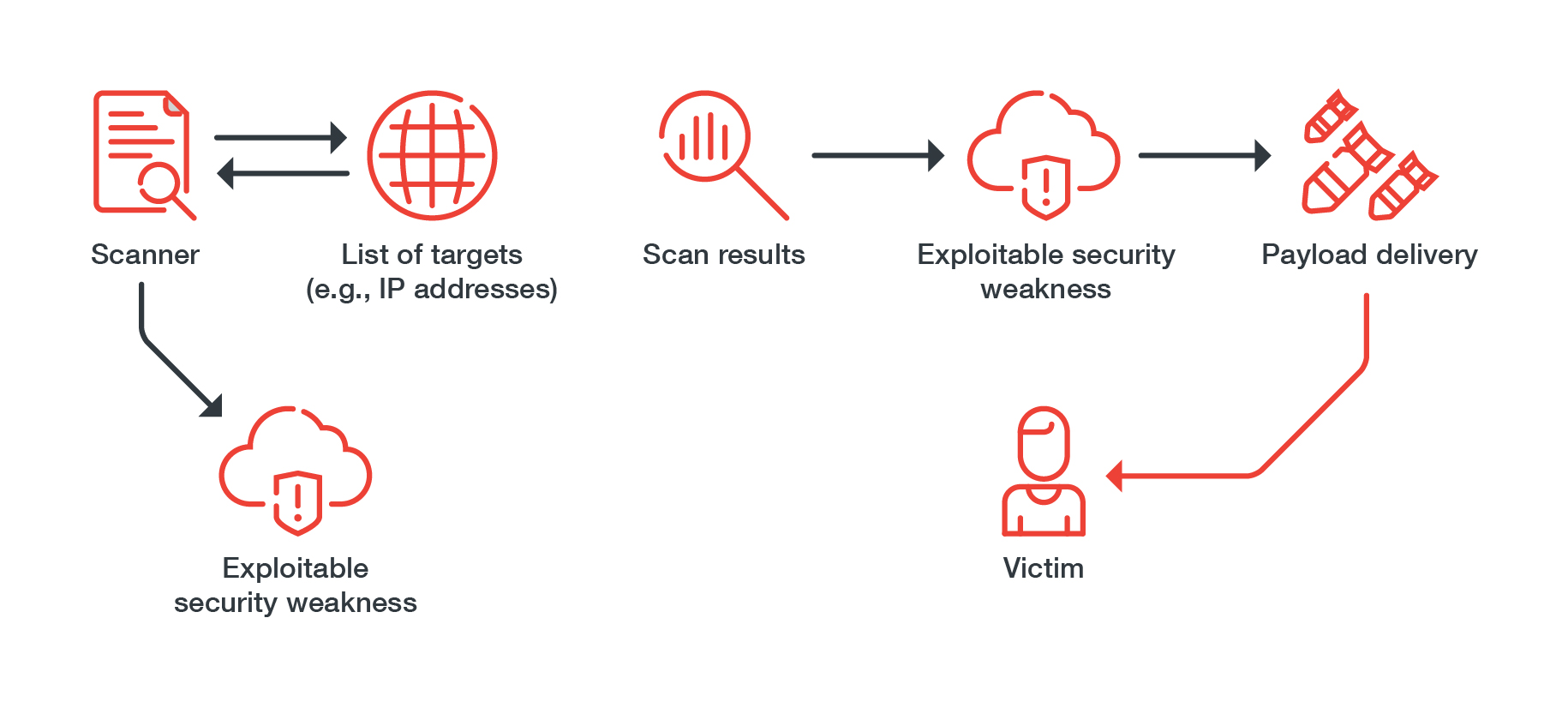
TeamTNT’s infection routines generally follow a pattern, where the group does reconnaissance by using its scanner to determine suitable victims. After it narrows down its targets, it scans for misconfigurations and other security weaknesses it could exploit, such as:
- Unsecured Redis instances
- Vulnerable internet-of-things (IoT) devices
- Exposed Docker APIs
- Leaked credentials
- Devices accessible via Secure Shell (SSH)
If it finds a system with exploitable security weaknesses, it starts delivering its payloads, which include:
- Credential stealers
- Cryptocurrency miners
- IRC bots
- Local network scanners
- Reverse/Bind shells
Figure 1. A common infection routine used by TeamTNT
Tools and techniques
For many of TeamTNT’s activities, the theft of credentials is often one of the group’s goals, if not the primary one. The group uses a number of techniques in its credential harvesting routines. To narrow down its main targets for credential theft, TeamTNT uses its own scripts that contain functions designed to search for credentials for specific services and software. It also implements persistence mechanisms in some of its campaigns, as in its SSH credential theft campaign, in which it creates local users and ensures that selected users are reachable over SSH in order to gain persistence post-compromise.
TeamTNT also makes extensive use of backdoors and rootkits. One of the more notable tools used by the group is Diamorphine, an open-source rootkit that has a variety of functions designed to hide the presence of the group’s malicious cryptocurrency mining.
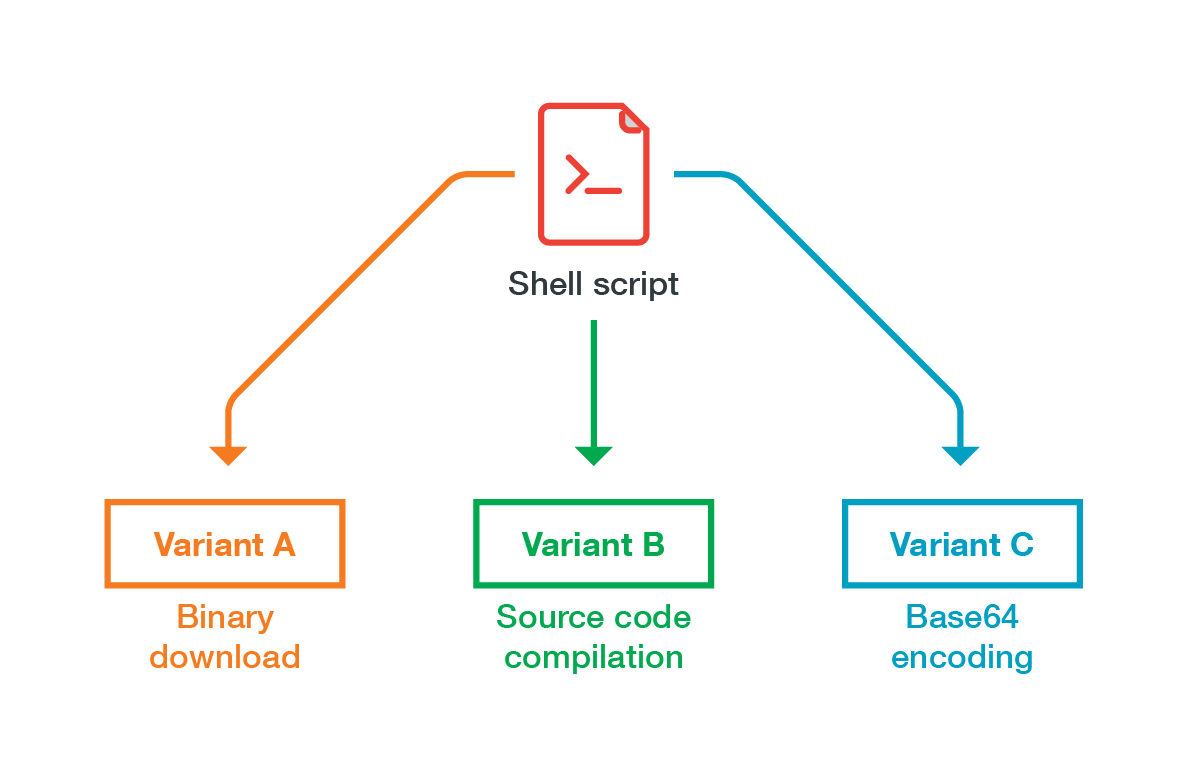
IRC bots have featured heavily in TeamTNT’s campaigns. The group often uses them for command-and-control operations, specifically to send commands to infected clients. These bots have evolved and gained new capabilities, such as the ability to download binaries or encrypt strings.
Figure 2. The variants of TeamTNT’s IRC bot
The group’s payloads also boast their own functionalities. In the battle for limited resources, for instance, some of TeamTNT’s cryptocurrency miners have the ability to find and neutralize competing malware such as Kinsing. Some payloads were fairly simple in early implementations, but they eventually evolved into more sophisticated forms with obfuscation and persistence mechanisms.
Defusing TeamTNT and other malicious actor groups
The increasing use of cloud-based services, software, and infrastructure has made the cloud an attractive target for groups like TeamTNT. A successful theft of cloud credentials or a cryptocurrency-mining routine that ends up infecting the whole system could have far-reaching consequences on an organization — not least in terms of operational disruption and even reputational damage. Our paper “Tracking the Activities of TeamTNT: A Closer Look at a Cloud-Focused Malicious Actor Group” aims to help enterprises understand how the group carries out its activities, and provide them with insights and actionable recommendations on protecting themselves against malicious actor groups like TeamTNT.
Like it? Add this infographic to your site:
1. Click on the box below. 2. Press Ctrl+A to select all. 3. Press Ctrl+C to copy. 4. Paste the code into your page (Ctrl+V).
Image will appear the same size as you see above.
Recent Posts
- Deepfake It ‘til You Make It: A Comprehensive View of the New AI Criminal Toolset
- Proactive Security: The Role of Exposure Management and Detection-Response Capability
- The Trend Micro Underground Series
- The Road to Agentic AI: Defining a New Paradigm for Technology and Cybersecurity
- Stay Ahead of AI Threats: Secure LLM Applications with Trend Vision One
 Unveiling AI Agent Vulnerabilities Part III: Data Exfiltration
Unveiling AI Agent Vulnerabilities Part III: Data Exfiltration AI in the Crosshairs: Understanding and Detecting Attacks on AWS AI Services with Trend Vision One™
AI in the Crosshairs: Understanding and Detecting Attacks on AWS AI Services with Trend Vision One™ Trend 2025 Cyber Risk Report
Trend 2025 Cyber Risk Report The Road to Agentic AI: Defining a New Paradigm for Technology and Cybersecurity
The Road to Agentic AI: Defining a New Paradigm for Technology and Cybersecurity