Email remains a primary entry point for cyberattacks that are growing faster, stealthier, and more adaptive. Many of these high-risk threats bypass traditional detection, exposing organizations to credential theft, data breaches, and ransomware. Without advanced email security, the gap between attacker innovation and defender response will only widen—putting users, data, and business continuity at increasing risk.
Malicious actors are constantly innovating their tactics to exploit vulnerabilities, and defenders must respond with equally dynamic strategies. One tactic that has gained popularity in recent times is the use of QR-based phishing, or “quishing”, which involve QR codes embedded in emails or attachments that appear to be routine communications—such as login verification requests or file-sharing links.
Through Trend Vision One™ Email and Collaboration Security, organizations made significant strides and achieved substantial gains in combating these threats — detecting and blocking over 45 million high-risk email threats in 2023, followed by nearly 57 million after Microsoft 365™ and Google Workspace™ in 2024. While the 27% year-over-year -increase may reflect stronger defenses or evolving attacker strategies, the persistently high threat volume underscores the need for continuous vigilance. These figures reinforce the importance of proactive, AI-powered email security to stay ahead of sophisticated email-based threats.
This report explores Trend Vision One™ telemetry and examines the key developments that shaped the email-based threat landscape in 2024.
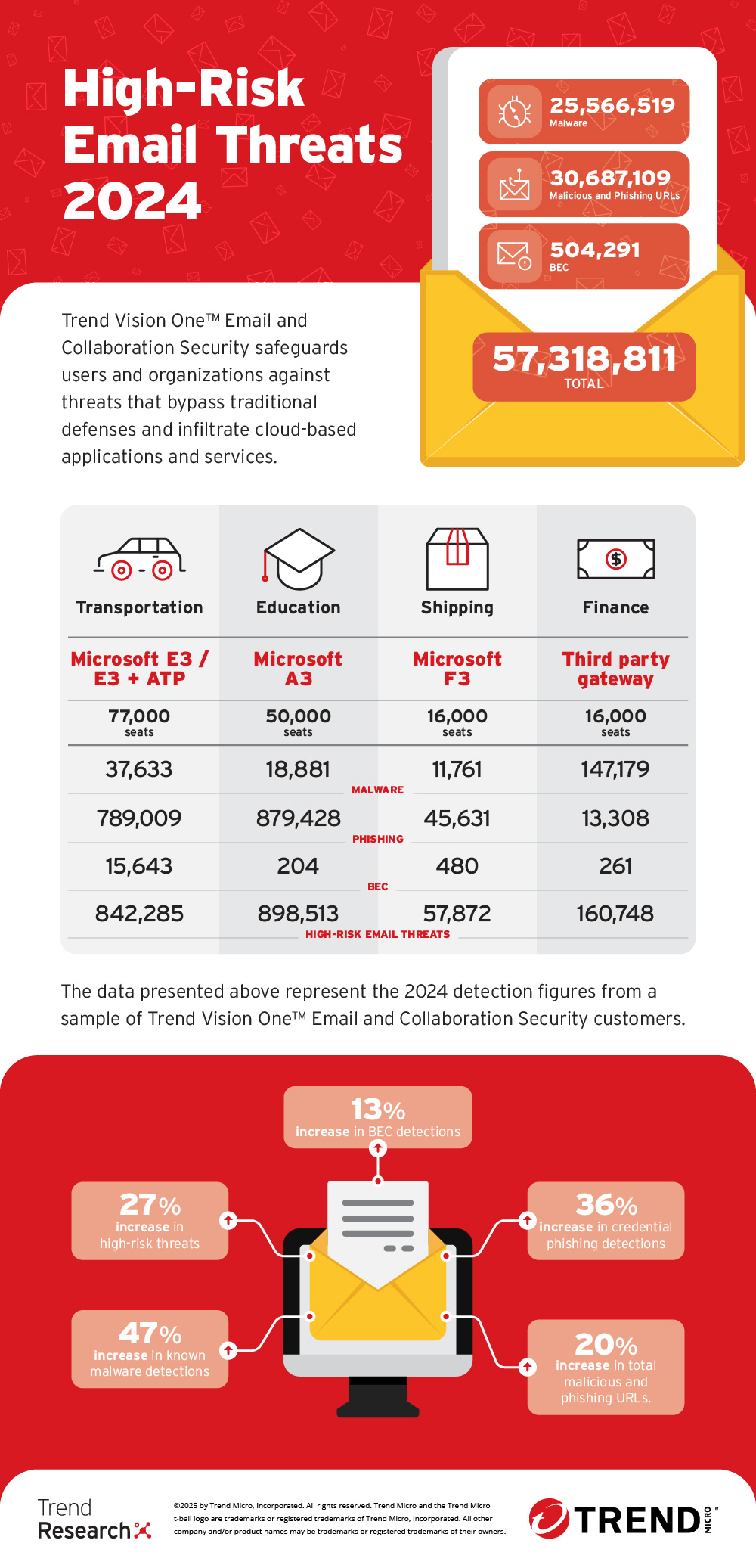
Trend Vision One Email and Collaboration Security Detections after Microsoft 365™ and Google Workspace™
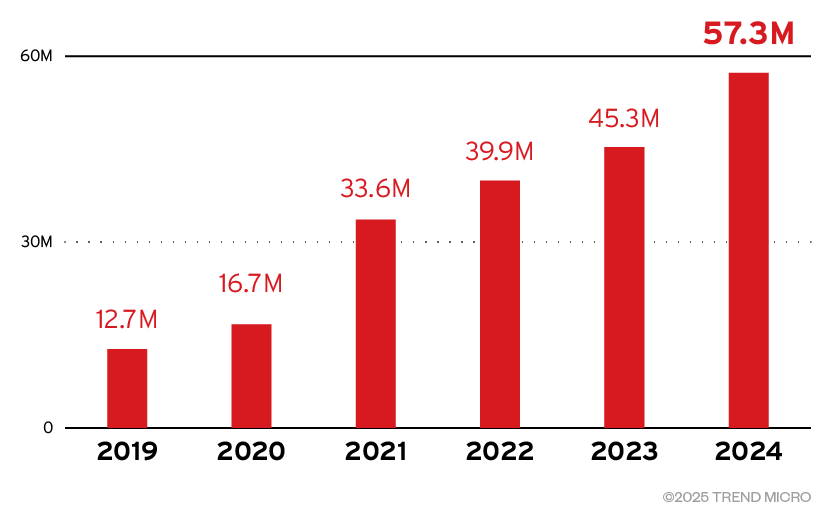
Figure 1. Detected high risk threats after Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace from 2019 to 2024
Since 2019, Trend has consistently detected and blocked phishing attacks that bypassed Microsoft 365™ and Google Workspace™ defenses. With continuous AI-driven enhancements, Trend Vision One excelled at identifying high-risk threats—including phishing, BEC, malicious, ransomware, scams etc. Notably, QR-code phishing played a significant role in the 27% increase in threat detections from 2023 to 2024, underscoring the rising sophistication of email-based attacks.
Dynamic Trends in Malware: Known Variants Surge Amid Tactical Changes
Trend telemetry reveals that malware delivered through email remains a potent threat. Known malware detections surged by 47%, even as unknown malware dropped by 39%. This difference points to evolving attacker strategies, with malicious actors increasingly relying on proven malware families while leveraging commoditized cybercrime tools available through underground markets.
The sharp rise in known malware also reflects advancements in detection capabilities, enabling faster classification and mitigation of threats. Conversely, the decline in unknown malware suggests improved detection techniques that rapidly adapt to new payloads and continuously accelerate signature updates. Trend’s ongoing contributions have further enriched our threat intelligence resource pool, enhancing our ability to proactively convert previously unknown malware into known threats. Organizations must remain vigilant and ensure robust threat-intelligence-backed defenses capable of adapting to the evolving malware landscape.
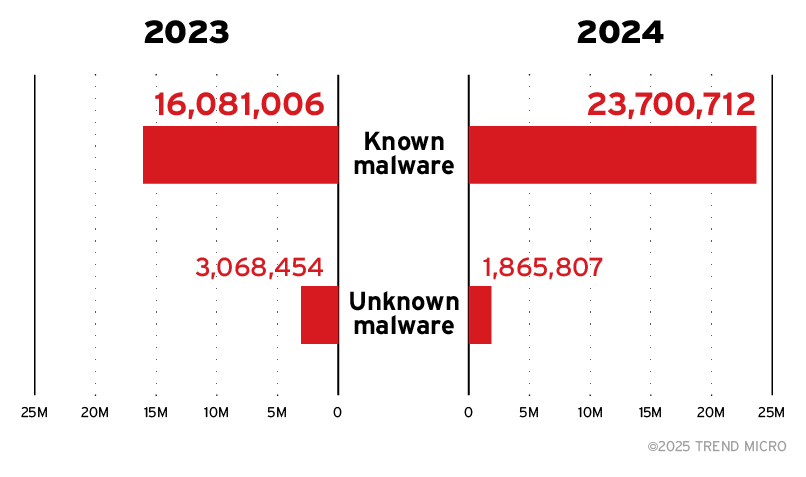
Figure 2. Detections for known malware (top) increased by 47%, while unknown malware detections declined by 39%
Ransomware detections stabilized while maintaining high levels of activity. Total ransomware detections remained relatively flat (63,449 in 2023 compared to 63,278 in 2024), yet the sustained volume highlights the importance of vigilance in mitigating risks. Threat actors are shifting from large-scale ransomware campaigns to targeted, high-stakes attacks, reflecting a push for maximum financial impact.
Organizations are advised to invest in comprehensive incident response planning and reinforce tiered defenses — incorporating endpoint controls, secure backups, and enhanced behavior-driven detection systems — to counter targeted ransomware efforts.

Figure 3. Ransomware detections showed little change from 2023 to 2024
A PikaBot spam wave campaign used hijacked email threads and malicious attachments to deliver malware, leveraging techniques similar to those previously employed by QakBot.
Earth Kasha launched a campaign using ANEL malware-laced documents to target government and military organizations in Asia, marking the return of the ANEL backdoor.
Earth Preta launched campaigns in Brazil, deploying the Astaroth banking malware through obfuscated JavaScript in malicious ZIP attachments disguised as tax documents.
RansomHub ransomware used a tool called EDRKillShifter to disable endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems, enabling the malware to evade security measures and execute its attack more effectively.
URL Sandboxing and Phishing Trends: Evolving Beyond Static Detection
Phishing and malicious URLs continued escalating in 2024, with detections rising by over 20% compared to prior years. URL sandboxing detections surged by an astonishing 211%, demonstrating attackers’ growing reliance on dynamic and evasive techniques designed to bypass static controls.
These URLs also include the rising threat of QR-based phishing ("quishing") attacks, which embed QR codes in email attachments or messages—often disguised as legitimate notifications, such as multi-factor authentication prompts or document-sharing alerts. When scanned, these codes redirect users to malicious websites, in an attempt to bypass traditional security filters. These attacks contributed to the 20% increase in the total malicious and phishing links from 2023 to 2024, as each scan often led to a phishing URL.
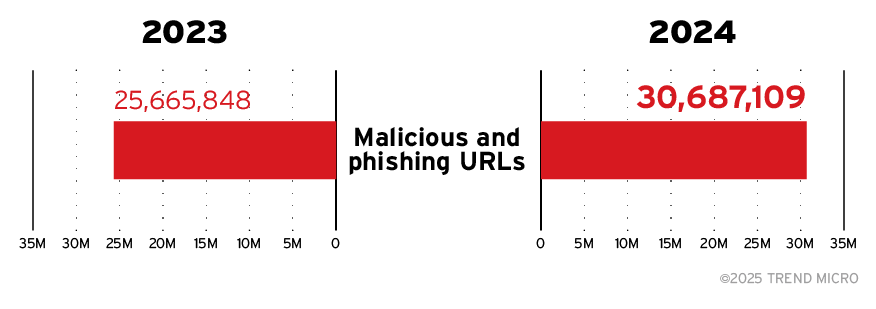
Figure 4. Total malicious and phishing URL detections for 2023 and 2024 indicate a 20% year-on-year increase
On the defensive end, organizations have made notable strides in combating visually deceptive phishing. With brands investing heavily in browser detections, streamlined takedowns of phishing domains coupled with user education retain their pivotal role in squashing visual deception campaigns.
Meanwhile, sandboxing's ability to analyze behaviors such as delayed payloads, redirects, and script execution remains critical for modern email defenses.
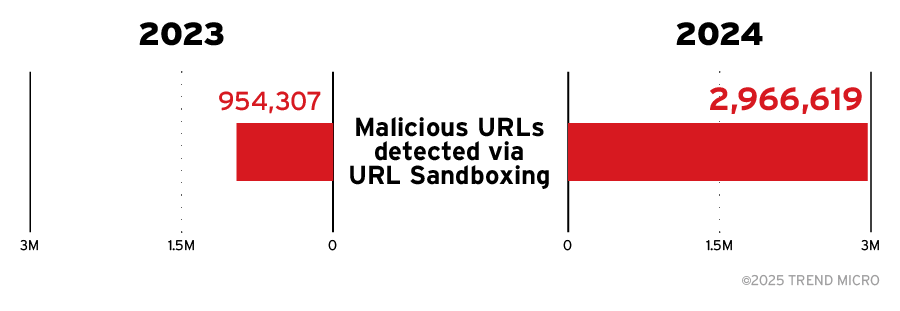
Figure 5. There was a considerable increase in malicious URLs detected via sandboxing techniques in 2024
Managed Detection and Response (MDR) successfully identified and prevented a spear phishing attack that attempted to deploy the More_Eggs backdoor, showcasing proactive threat detection and response capabilities.
Earth Baxia conducted spear-phishing attacks in South and Southeast Asia, exploiting GeoServer vulnerabilities to deploy backdoors and establish persistent access within targeted networks.
Water Makara carried out a spear-phishing campaign targeting the Asia-Pacific region, using obfuscated JavaScript in malicious ZIP attachments to deliver a backdoor and steal sensitive information.
Earth Kapre, also known as RedCurl, used spear-phishing emails and custom tools like RedCurlStealer to infiltrate corporate networks and exfiltrate confidential business data.
The APT group Blackwood deployed the sophisticated, multi-stage NSPX30 implant using phishing and adversary-in-the-middle (AiTM) techniques to hijack unencrypted software update requests, enabling stealthy cyberespionage attacks against targets in China, Japan, and the UK.
Overall phishing and credential phishing attacks increased in 2024
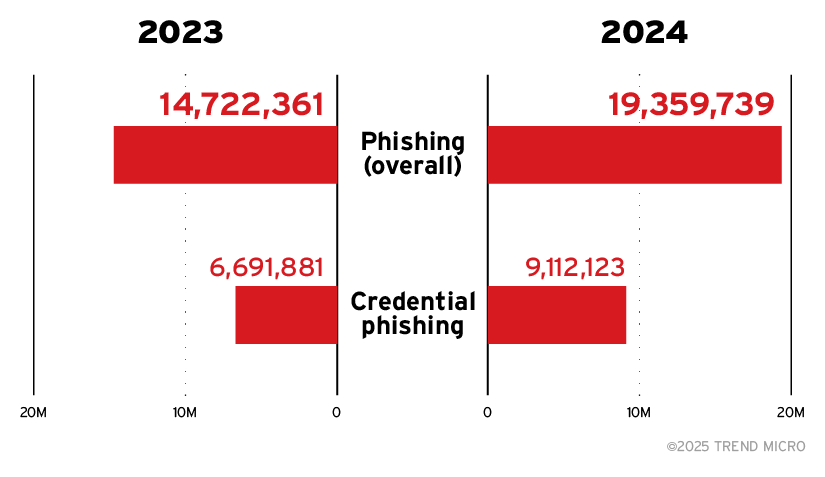
Figure 6. There was an uptick in detections for both phishing (overall) and credential phishing from 2023 to 2024
Trend telemetry reveals a notable 31% rise in overall phishing incidents, from nearly 15 million to over 19 million, indicating a broad escalation in phishing activity over the evaluated periods. Credential phishing saw an even sharper rise of 36%, highlighting an intensified focus on credential theft by attackers, as noted in our 2024 Midyear Cybersecurity Threat Report.
In contrast, detections of known phishing links surged by 84%, suggesting both effective identification and the continued prevalence of established phishing campaigns. Taken together, these trends emphasize the urgent need for organizations to strengthen their defenses — particularly in spam filtering, credential protection, and the use of AI-driven tools for identifying evolving phishing tactics.
A Mekotio banking trojan campaign targeted users in Latin America by distributing malicious MSI installers via phishing emails, aiming to steal banking credentials and sensitive information.
Earth Krahang executed cyberespionage attacks targeting government and education sectors worldwide, using spear-phishing emails, custom malware, and compromised routers to steal data and maintain persistent access.
Earth Simnavaz attacks involved the use of spear-phishing emails with links to fake login pages, which aimed to harvest credentials from government and military personnel in the Middle East and Asia.
Trend assisted in the takedown of LabHost, a phishing-as-a-service platform that facilitated large-scale credential theft by providing cybercriminals with phishing kits, fake websites, and data harvesting tools targeting victims worldwide.
BEC detections through authorship analysis jumped by 77%, while overall BEC activity shows a modest increase.
Business Email Compromise (BEC) incidents saw a measurable 13% increase, while enhancements powered by Trend Vision One's authorship-analysis technology Writing Style DNA led to a 77% jump in impersonation fraud detections.
Authorship analysis employs AI-driven techniques to identify suspicious messages by comparing the writing style against sophisticated AI-generated historical profiles of high-level executives.
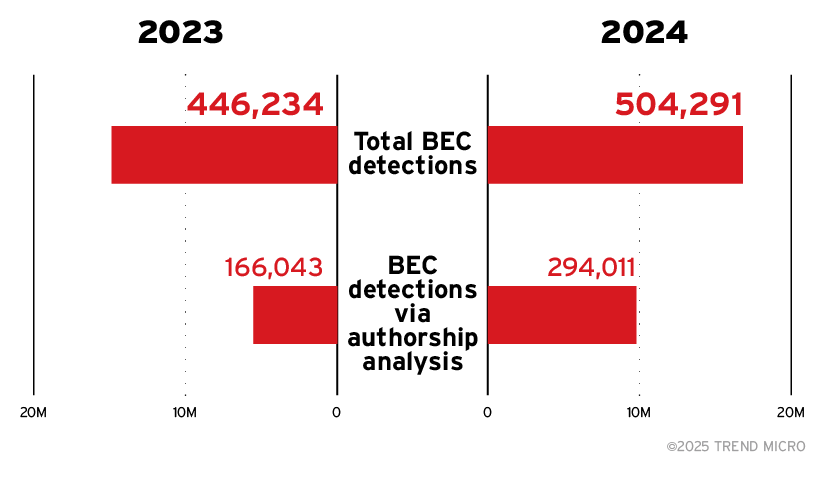
Figure 7. Total BEC incidents saw a 13% increase, while detections using authorship analysis jumped by 77%
In Q4 2024, the average wire transfer amount in BEC attacks surged to $128,980 — nearly doubling Q3’s $67,145 — even as the total number of such attacks fell by 21 percent.
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) warned that cybercriminals are increasingly using deepfake videos and synthetic content in BEC schemes, leveraging AI-generated audio and video to impersonate executives and authorize fraudulent financial transactions.
Enhance protection across email, identity, endpoint, and cloud services with Trend Vision One™ Email and Collaboration Security
To defend against today’s-evolving cyber threats, organizations need more than siloed tools, they need a unified, AI-powered enterprise cybersecurity platform that secures users, data, and communication across all layers.
Trend Vision One™ Email and Collaboration Security delivers exactly that: a cloud-native, multi-layered solution that extends protection across email and collaboration platforms, identity, endpoint and cloud services, enabling a proactive and integrated defense posture.
By augmenting native security with machine learning, behavioral-analysis, and identity-based detection, this solution proactively mitigates risks from AI-generated phishing, BEC, ransomware, malware, and other sophisticated email-based attacks.
With advanced features like sandbox analysis for dynamic threat identification exploit detection, and risk-based policy enforcement, organizations can detect malicious payloads, prevent data leakage, and safeguard their users in real-time—closing the gap between attacker innovation and defender response.
With speed and precision to enhance detection capabilities, Email and Collaboration Security leverages AI-driven correlated intelligence detection, Writing Style DNA and Computer Vision technologies.
Organizations should consider a comprehensive multilayered security solution such as Trend Vision One — Email and Collaboration Protection, which takes the following actions:
- AI-driven correlated intelligence analyzes user relationships, communication flows, and email interactions to detect sophisticated email threats. This includes social graphs, email intentions, and end-user feedback. The technology goes beyond email to cover other communication applications and proactively mitigate risks. In fact, correlated intelligence in email security provides in-depth insights into an account compromise and the indicators including risk events, data source, impact scope, event risk level, and further detection details.
- Writing Style DNA uses machine learning to analyze the authenticity of emails by comparing suspicious messages to the writing patterns of known senders,—an effective defense against business email compromise (BEC) and impersonation fraud.
- Meanwhile, Computer Vision inspects visual elements,like logos and login forms in emails, using optical character recognition (OCR) and reputation intelligence to detect credential phishing attempts through fraudulent sites that evade traditional filters.
These innovations significantly enhance detection accuracy while reducing false positives, ensuring that legitimate communications aren’t disrupted. But the solution goes even further— making it an effective layer of defense against both known and emerging threats.
Email and Collaboration Security integrates seamlessly with cloud collaboration applications via vendor APIs without disrupting existing workflows or admin functionalities. Features such as RiskAI enable real-time visibility into potentially compromised accounts, while automated actions like historical URL rescanning and threat prioritization simplify IT remediation efforts. Combined with sandbox analysis, URL time-of-click inspection, and multi-layered threat correlation, the solution delivers a powerful defense against phishing, ransomware, malware, and zero-day email threats.
Additionally, Managed XDR capabilities extend protection beyond email to endpoints and servers, empowering organizations to achieve unified threat detection, response, and investigation across their entire IT environment.
As part of the broader Vision One platform, this solution embraces industry-leading threat intelligence to deliver unified, adaptive, scalable security for evolving collaboration ecosystems. Fully integrated into Trend Vision One, Trend Cybertron™—the industry's first proactive cybersecurity AI—enhances detection and response with specialized LLM models, machine learning, natural language processing, and AI agents. Built on 35 years of threat intelligence and two decades of AI investment, it combines security expertise with Trend Micro’s global threat intelligence and vulnerability research. This unified solution not only defends against current threats but proactively anticipates and mitigates future challenges.
Like it? Add this infographic to your site:
1. Click on the box below. 2. Press Ctrl+A to select all. 3. Press Ctrl+C to copy. 4. Paste the code into your page (Ctrl+V).
Image will appear the same size as you see above.
последний
- They Don’t Build the Gun, They Sell the Bullets: An Update on the State of Criminal AI
- How Unmanaged AI Adoption Puts Your Enterprise at Risk
- Estimating Future Risk Outbreaks at Scale in Real-World Deployments
- The Next Phase of Cybercrime: Agentic AI and the Shift to Autonomous Criminal Operations
- Reimagining Fraud Operations: The Rise of AI-Powered Scam Assembly Lines
 Complexity and Visibility Gaps in Power Automate
Complexity and Visibility Gaps in Power Automate AI Security Starts Here: The Essentials for Every Organization
AI Security Starts Here: The Essentials for Every Organization The AI-fication of Cyberthreats: Trend Micro Security Predictions for 2026
The AI-fication of Cyberthreats: Trend Micro Security Predictions for 2026 Stay Ahead of AI Threats: Secure LLM Applications With Trend Vision One
Stay Ahead of AI Threats: Secure LLM Applications With Trend Vision One