Ransomware Spotlight: Magniber
Top affected countries and industries
according to Trend Micro data
In this section, we examine the Magniber ransomware’s attempts to compromise organizations in 2022 based on Trend Micro™ Smart Protection Network™ country and regional data. It’s important to note that this data covers only Trend Micro customers and does not contain all victims of Magniber.
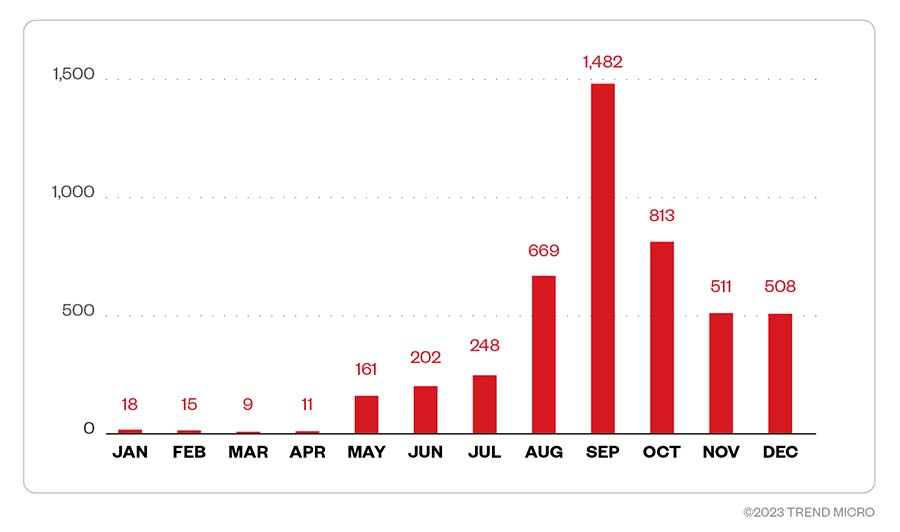
Malicious attackers behind Magniber started slow in 2022, with less than 20 attacks per month in the first quarter of the year. The attack attempts steadily increased as the year progressed, with attackers making the most of September 2022, which recorded the largest number of attack attempts at 1,482 detections. Attack attempts diminished during the last quarter of the year but remained high with 508 detections in December. The following figure details the total number of attempted attacks by Magniber in 2022.
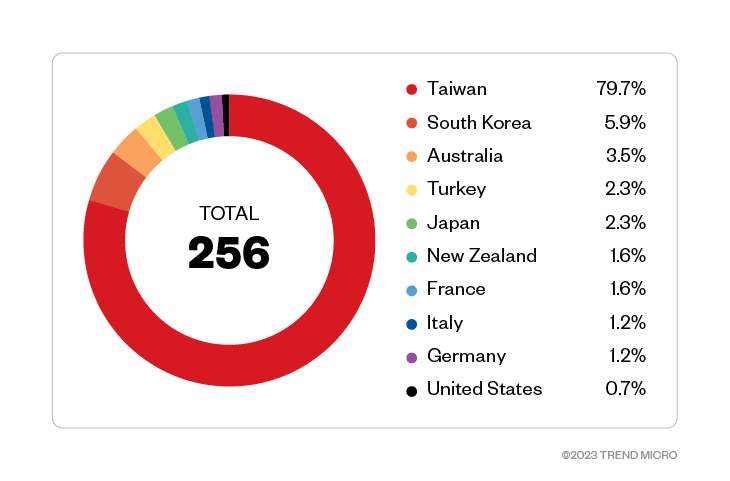
The highest number of Magniber attacks was detected in Taiwan with a total of 204 attack attempts, which makes up most of the attack attempt detections at approximately 76.1% of the total. South Korea, initially targeted by Magniber when it was first detected, has the second most attack attempts with a large margin at 15, followed by Australia with nine. Turkey and Japan follow with six detections each. Our data shows that Magniber has expanded its targets beyond Asian countries. Note that the data in Figure 2 is limited to feedback provided by customers, majority of whom preferred not to disclose their locations.
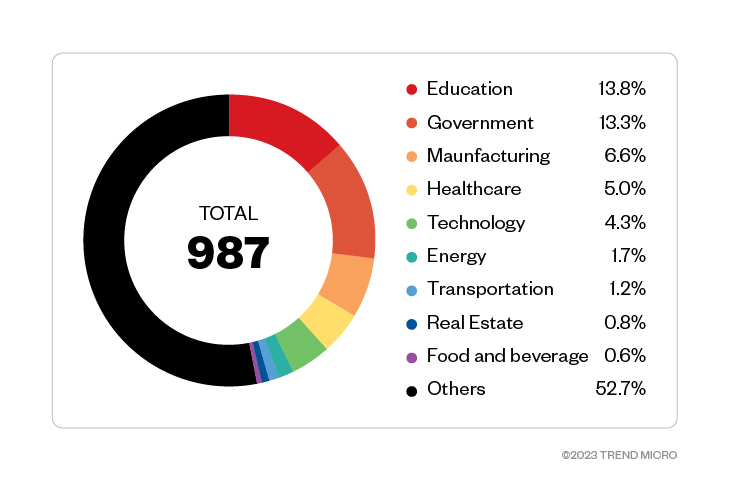
Industry data, on the other hand, showed that educational organizations, the government, and manufacturing industries experienced the largest number of Magniber ransomware attack attempts, followed by the healthcare and technology industries. Other industries that experienced less attempted attacks were the energy, transportation, and real estate industries.
In total, there were 987 total detections of Magniber attack attempts across industries in 2022 from customer feedback detailing the industries in which they belong.
Infection chain and techniques
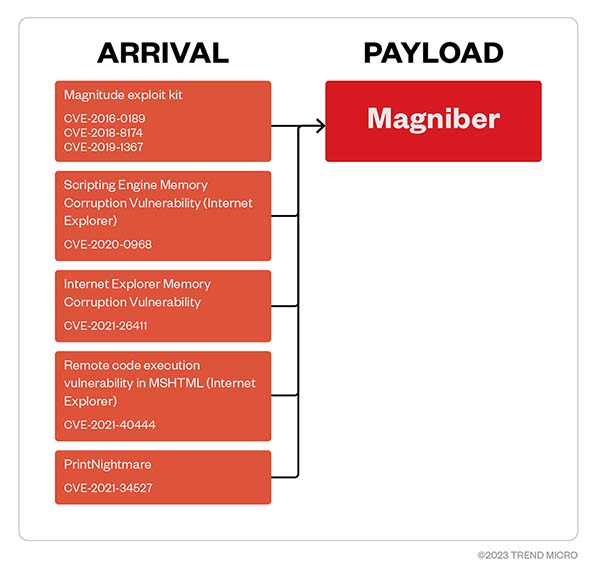
We found that the Magniber ransomware exploits different vulnerabilities, but while it uses a more straightforward kill chain compared to the newer double-extortion ransomware campaigns, its simplicity does not make it any less effective. The following figure details various vulnerabilities exploited to deliver its payload:
Figure 4. Vulnerabilities exploited to deliver Magniber ransomware
Initial Access
- Magniber threat actors leverage different vulnerabilities for initial access such as the aforementioned Magnitude exploit kit (CVE-2016-0189, CVE-2018-8174, and CVE-2019-1367), the Internet Explorer Scripting Engine Memory Corruption Vulnerability (CVE-2020-0968), the Internet Explorer Memory Corruption Vulnerability (CVE-2021-26411), the Internet Explorer remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability in MSHTML (CVE-2021-40444), and PrintNightmare (CVE-2021-34527).
Command and Control
- Magniber has the capability to send collected information to its command and control (C&C) and the payment browser.
Defense Evasion
- Magniber injects itself to all processes except iexplore.exe and excluding system and processes not running in a WoW64 environment. The ransomware uses NtQuerySystemInformation API to obtain running processes in the machine.
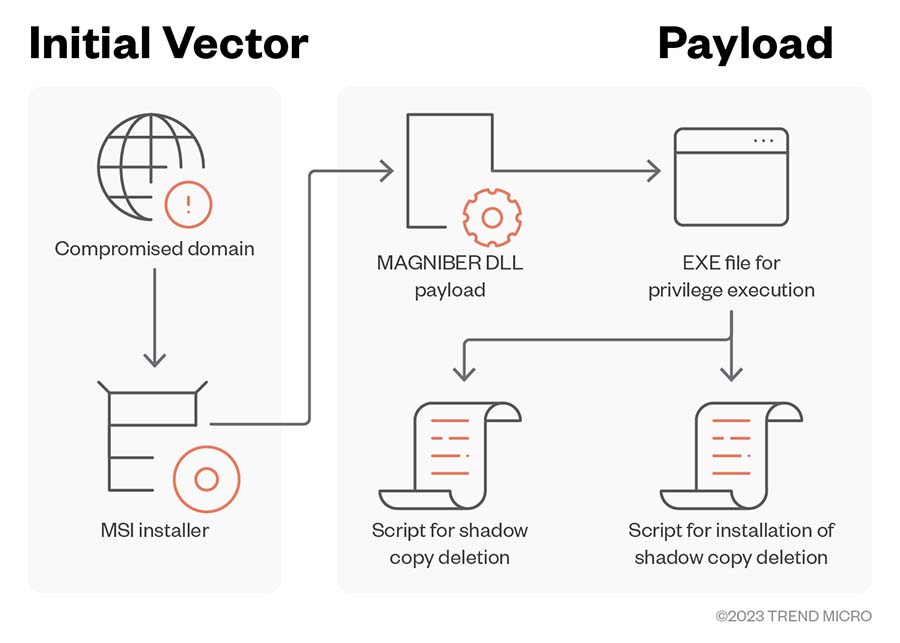
- Recent Magniber infections leverage fake installers (.msi) by calling the encrypted ransomware DLL through the CustomAction table, as well as the CPL file format to execute its payload.
- Magniber uses a malformed digital signature block to bypass execution blocks by MOTW. Recently, it was found exploiting CVE-2022-44698 to bypass MOTW with a fake digital signature.
- It uses a file detected as Fodscript that drops a script file to delete shadow copies from the target machine.
Discovery
- Magniber uses NtQuerySystemInformation API to obtain running processes in the machine.
- It searches for specific files, folders, and attributes and encrypts them if they match its specified criteria.
Privilege Escalation
- Magniber uses a file detected as Fodscript that drops two script files: One of the script files modifies the registry entries that fodhelper.exe checks in order to manipulate fodhelper.exe into executing the second script with high privilege and bypassing UAC.
Collection, Exfiltration
- As of now, there are no data exfiltration and leaks being done by Magniber.
Impact
- The final ransomware binary would then be deployed, thereby ensuring that files are encrypted in the machine. It also ensures that shadow copies are deleted to inhibit system recovery.
- It initially encrypts target files via symmetric AES, then encrypts the AES symmetric key and IV via RSA using CryptoAPIs. It encrypts equal-size data blocks (1,048,576 bytes) per iteration until the final block is encrypted.
- It appends the mutex name as its appended extension.
- It can also delete shadow copies in the infected machine.
Other technical details
- Magniber encrypts files with the following extensions:
- .abm
- .abs
- .abw
- .accdb
- .act
- .adn
- .adp
- .aes
- .aft
- .afx
- .agif
- .agp
- .ahd
- .ai
- .aic
- .aim
- .albm
- .alf
- .ans
- .apd
- .apm
- .apng
- .aps
- .apt
- .apx
- .arc
- .art
- .arw
- .asc
- .ase
- .asf
- .ask
- .asm
- .asp
- .asw
- .asy
- .aty
- .avi
- .awdb
- .awp
- .awt
- .aww
- .azz
- .bad
- .bak
- .bay
- .bbs
- .bdb
- .bdp
- .bdr
- .bean
- .bib
- .bmp
- .bmx
- .bna
- .bnd
- .boc
- .bok
- .brd
- .brk
- .brn
- .brt
- .bss
- .btd
- .bti
- .btr
- .c
- .ca
- .cals
- .can
- .cd
- .cdb
- .cdc
- .cdg
- .cdmm
- .cdmt
- .cdmz
- .cdr
- .cdt
- .cf
- .cfu
- .cgm
- .cimg
- .cin
- .cit
- .ckp
- .class
- .clkw
- .cma
- .cmx
- .cnm
- .cnv
- .colz
- .cpc
- .cpd
- .cpg
- .cpp
- .cps
- .cpx
- .crd
- .crt
- .crw
- .cs
- .csr
- .csv
- .csy
- .ct
- .cvg
- .cvi
- .cvs
- .cvx
- .cwt
- .cxf
- .cyi
- .dad
- .daf
- .db
- .dbc
- .dbf
- .dbk
- .dbs
- .dbt
- .dbv
- .dbx
- .dca
- .dcb
- .dch
- .dcr
- .dcs
- .dct
- .dcx
- .dd
- .dds
- .ded
- .der
- .dgn
- .dgs
- .dgt
- .dhs
- .dib
- .dif
- .dip
- .diz
- .djv
- .djvu
- .dmi
- .dmo
- .dnc
- .dne
- .doc
- .docb
- .docm
- .docx
- .docz
- .dot
- .dotm
- .dotx
- .dpp
- .dpx
- .dqy
- .drw
- .drz
- .dsk
- .dsn
- .dsv
- .dt
- .dta
- .dtsx
- .dtw
- .dv
- .dvi
- .dwg
- .dx
- .dxb
- .dxf
- .eco
- .ecw
- .ecx
- .edb
- .efd
- .egc
- .eio
- .eip
- .eit
- .em
- .emd
- .emf
- .emlx
- .ep
- .epf
- .epp
- .eps
- .epsf
- .eq
- .erf
- .err
- .etf
- .etx
- .euc
- .exr
- .fa
- .faq
- .fax
- .fb
- .fbx
- .fcd
- .fcf
- .fdf
- .fdr
- .fds
- .fdt
- .fdx
- .fdxt
- .fes
- .fft
- .fi
- .fic
- .fid
- .fif
- .fig
- .fla
- .flr
- .flv
- .fmv
- .fo
- .fodt
- .fpos
- .fpt
- .fpx
- .frm
- .frt
- .frx
- .ftn
- .fwdn
- .fxc
- .fxg
- .fzb
- .fzv
- .gcdp
- .gdb
- .gdoc
- .gem
- .geo
- .gfb
- .gfie
- .ggr
- .gif
- .gih
- .gim
- .gio
- .glox
- .gpd
- .gpg
- .gpn
- .gro
- .grob
- .grs
- .gsd
- .gthr
- .gtp
- .gv
- .gwi
- .gz
- .h
- .hbk
- .hdb
- .hdp
- .hdr
- .hht
- .his
- .hp
- .hpg
- .hpi
- .hs
- .htc
- .hwp
- .hz
- .ib
- .ibd
- .icn
- .icon
- .icpr
- .idc
- .idea
- .idx
- .igt
- .igx
- .ihx
- .ii
- .iiq
- .imd
- .info
- .ink
- .ipf
- .ipx
- .iso
- .itdb
- .itw
- .iwi
- .j
- .jar
- .jas
- .java
- .jbig
- .jbmp
- .jbr
- .jfif
- .jia
- .jis
- .jng
- .joe
- .jpe
- .jpeg
- .jpg
- .jps
- .jpx
- .jrtf
- .js
- .jsp
- .jtf
- .jtx
- .jw
- .jxr
- .kdb
- .kdbx
- .kdc
- .kdi
- .kdk
- .kes
- .ke
- .kic
- .klg
- .knt
- .kon
- .kpg
- .kwd
- .lay
- .lbm
- .lbt
- .ldf
- .lgc
- .lis
- .lit
- .ljp
- .lmk
- .lnt
- .lrc
- .lst
- .ltr
- .ltx
- .lue
- .luf
- .lwo
- .lwp
- .lws
- .lyt
- .lyx
- .ma
- .mac
- .man
- .map
- .maq
- .mat
- .max
- .mb
- .mbm
- .mbox
- .mdb
- .mdf
- .mdn
- .mdt
- .me
- .mef
- .mel
- .mft
- .mgcb
- .mgmf
- .mgmt
- .mgmx
- .mgtx
- .mid
- .min
- .mkv
- .mm
- .mmat
- .mnr
- .mnt
- .mos
- .mov
- .mpeg
- .mpf
- .mpg
- .mpo
- .mrg
- .mrxs
- .msg
- .mud
- .mwb
- .mwp
- .mx
- .my
- .myd
- .myi
- .ncr
- .nct
- .ndf
- .nef
- .nfo
- .njx
- .nlm
- .now
- .nrw
- .nsf
- .nyf
- .nzb
- .obj
- .oce
- .oci
- .ocr
- .odb
- .odg
- .odm
- .odo
- .odp
- .ods
- .odt
- .of
- .oft
- .omf
- .oplc
- .oqy
- .ora
- .orf
- .ort
- .orx
- .ost
- .ota
- .otg
- .oti
- .otp
- .ots
- .ott
- .ovp
- .ovr
- .owc
- .owg
- .oyx
- .ozb
- .ozj
- .ozt
- .p
- .pa
- .pan
- .pano
- .pap
- .paq
- .pas
- .pbm
- .pcd
- .pcs
- .pdb
- .pdd
- .pdm
- .pds
- .pdt
- .pef
- .pem
- .pff
- .pfi
- .pfs
- .pfv
- .pfx
- .pgf
- .pgm
- .phm
- .php
- .pic
- .pict
- .pix
- .pjpg
- .pjt
- .plt
- .pm
- .pmg
- .png
- .pni
- .pnm
- .pntg
- .pnz
- .pobj
- .pop
- .pot
- .potm
- .potx
- .ppam
- .ppm
- .pps
- .ppsm
- .ppsx
- .ppt
- .pptm
- .pptx
- .prt
- .prw
- .psd
- .psdx
- .pse
- .psid
- .psp
- .pst
- .psw
- .ptg
- .pth
- .ptx
- .pu
- .pvj
- .pvm
- .pvr
- .pwa
- .pwi
- .pwr
- .px
- .pxr
- .pza
- .pzp
- .pzs
- .qd
- .qmg
- .qpx
- .qry
- .qvd
- .rad
- .rar
- .ras
- .raw
- .rb
- .rctd
- .rcu
- .rd
- .rdb
- .rft
- .rgb
- .rgf
- .rib
- .ric
- .riff
- .ris
- .rix
- .rle
- .rli
- .rng
- .rpd
- .rpf
- .rpt
- .rri
- .rs
- .rsb
- .rsd
- .rsr
- .rst
- .rt
- .rtd
- .rtf
- .rtx
- .run
- .rw
- .rzk
- .rzn
- .saf
- .sam
- .sbf
- .scad
- .scc
- .sch
- .sci
- .scm
- .sct
- .scv
- .scw
- .sdb
- .sdf
- .sdm
- .sdoc
- .sdw
- .sep
- .sfc
- .sfw
- .sgm
- .sh
- .sig
- .skm
- .sla
- .sld
- .sldm
- .sldx
- .slk
- .sln
- .sls
- .smf
- .sms
- .snt
- .sob
- .spa
- .spe
- .sph
- .spj
- .spp
- .spq
- .spr
- .sq
- .sqb
- .srw
- .ssa
- .ssk
- .st
- .stc
- .std
- .sti
- .stm
- .stn
- .stp
- .str
- .stw
- .sty
- .sub
- .suo
- .svf
- .svg
- .svgz
- .swf
- .sxc
- .sxd
- .sxg
- .sxi
- .sxm
- .sxw
- .tab
- .tar
- .tbk
- .tcx
- .tdf
- .tdt
- .te
- .tex
- .text
- .tgz
- .thp
- .tif
- .tiff
- .tlb
- .tlc
- .tm
- .tmd
- .tmv
- .tmx
- .tne
- .tpc
- .trm
- .tvj
- .udb
- .ufr
- .unx
- .uof
- .uop
- .uot
- .upd
- .usr
- .utxt
- .vb
- .vbr
- .vbs
- .vcd
- .vct
- .vdb
- .vdi
- .vec
- .vm
- .vmdk
- .vmx
- .vnt
- .vob
- .vpd
- .vrm
- .vrp
- .vsd
- .vsdm
- .vsdx
- .vsm
- .vstm
- .vstx
- .vue
- .vw
- .wav
- .wbk
- .wcf
- .wdb
- .wgz
- .wire
- .wks
- .wma
- .wmdb
- .wmv
- .wn
- .wp
- .wpa
- .wpd
- .wpg
- .wps
- .wpt
- .wpw
- .wri
- .wsc
- .wsd
- .wsh
- .wtx
- .x
- .xar
- .xd
- .xdb
- .xlc
- .xld
- .xlf
- .xlgc
- .xlm
- .xls
- .xlsb
- .xlsm
- .xlsx
- .xlt
- .xltm
- .xltx
- .xlw
- .xps
- .xwp
- .xyp
- .xyw
- .ya
- .ybk
- .ym
- .zabw
- .zdb
- .zdc
- .zip
- .zw
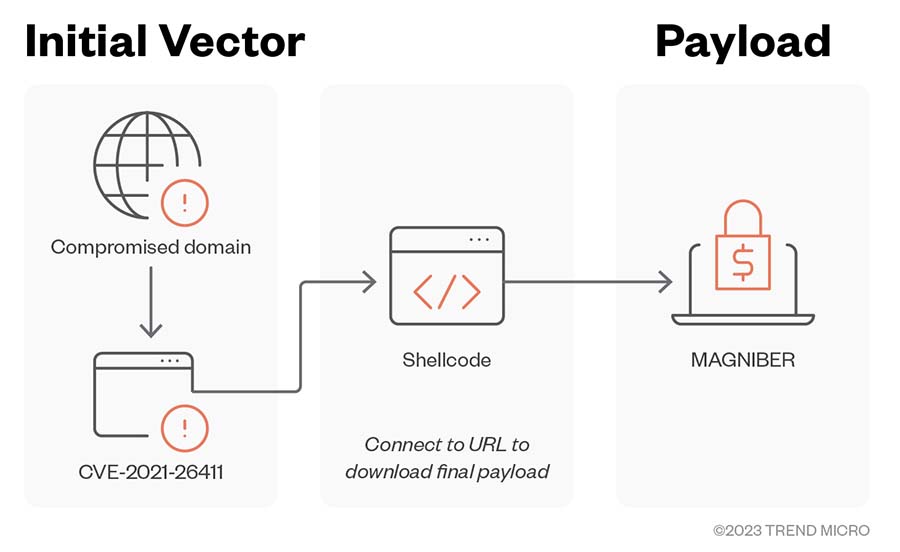
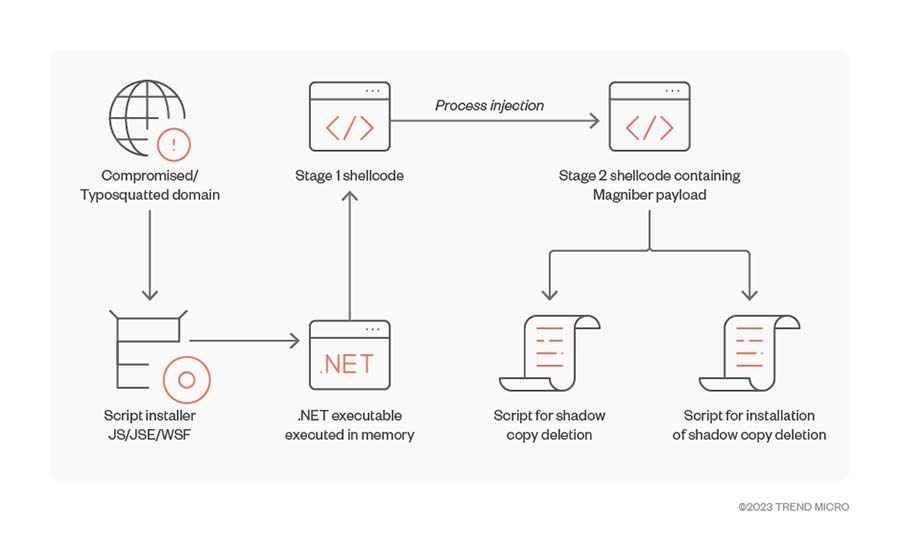
The following diagrams detail the Magniber ransomware infection chains we observed when malicious attackers exploit Internet Explorer, MSI installer, and JS, JSE, and WSF installer vulnerabilities.
Figure 5. Magniber ransomware infection chain involving the Internet Explorer Memory Corruption Vulnerability
MITRE tactics and techniques
| Initial Access | Execution | Defense Evasion | Discovery | Command and Control | Impact | Resource Development |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
T1190 - Exploit Public-Facing Application | T1059.003 - Command and Scripting Interpreter: Windows Command Shell T1047 - Windows Management Instrumentation T1059.007 - Command and Scripting Interpreter: JavaScript T1204 - User Execution T1203 - Exploitation for Client Execution | T1218.010 - Signed Binary Proxy Execution: Regsvr32 T1055.003 - Process Injection: Thread Execution Hijacking T1140 - Deobfuscate/Decode Files or Information T1112 - Modify Registry T1218.007 - System Binary Proxy Execution: Msiexec T1218.002 - System Binary Proxy Execution: Control Panel T1036.005 - Masquerading: Match Legitimate Name or Location T1620 - Reflective Code Loading T1553.005 - Subvert Trust Controls: Mark-of-the-Web Bypass | T1083 - File and Directory Discovery T1135 - Network Share Discovery T1057 - Process Discovery T1082 - System Information Discover | T1071.001 - Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols | T1490 - Inhibit System Recovery T1486 - Data Encrypted for Impact | T1608.005 - Stage Capabilities: Link Target |
Summary of malware, tools, and exploits used
Security teams must take not of and be on the lookout for the following tools and exploits typically used in Magniber ransomware attacks:
Exploits
- CVE-2016-0189
- CVE-2018-8174
- CVE-2019-1367
- CVE-2020-0968
- CVE-2021-26411
- CVE-2021-40444
- CVE-2021-34527
- CVE-2022-44698
Tools
- WMI
Malware
- Fodscript
| Initial Access | Execution | Defense Evasion | Privilege Escalation | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| ||||
| ||||
| ||||
| ||||
|
Recommendations
Given its continued activity in 2022, we can expect to see more of the Magniber ransomware in the future. As attackers continue to find ways to distribute its payloads and circumvent security warnings, organizations and their members must remain vigilant to prevent being compromised. We encourage organizations to remain on the lookout for the Magniber ransomware and continue monitoring its evolution to minimize the possibility of a successful attack.
To protect systems against the Magniber ransomware and other similar threats, organizations can implement security frameworks that allocate resources systematically to establish a strong defense strategy.
Here are some best practices that organizations can consider to help protect themselves from the Magniber ransomware infection:
Audit and inventory
- Take an inventory of assets and data.
- Identify authorized and unauthorized devices and software.
- Audit event and incident logs.
Configure and monitor
- Manage hardware and software configurations.
- Grant admin privileges and access only when necessary to an employee’s role.
- Monitor network ports, protocols, and services.
- Activate security configurations on network infrastructure devices such as firewalls and routers.
- Establish a software allowlist that only executes legitimate applications.
Patch and update
- Conduct regular vulnerability assessments.
- Perform patching or virtual patching for operating systems and applications.
- Update software and applications to their latest versions.
Protect and recover
- Implement data protection, back up, and recovery measures.
- Enable multifactor authentication (MFA).
Secure and defend
- Employ sandbox analysis to block malicious emails.
- Deploy the latest versions of security solutions to all layers of the system, including email, endpoint, web, and network.
- Discover early signs of an attack, such as the presence of suspicious tools in the system.
- Use advanced detection technologies such as those powered by AI and machine learning.
Train and test
- Regularly train and assess employees on security skills.
- Conduct red-team exercises and penetration tests.
A multilayered approach can help organizations guard possible entry points into the system (endpoint, email, web, and network). Security solutions that can detect malicious components and suspicious behavior can also help protect enterprises.
- Trend Micro Vision One™ provides multilayered protection and behavior detection, which helps block questionable behavior and tools early on before the ransomware can do irreversible damage to the system.
- Trend Micro Cloud One™ - Workload Security protects systems against both known and unknown threats that exploit vulnerabilities. This protection is made possible through techniques such as virtual patching and machine learning.
- Trend Micro™ Deep Discovery™ Email Inspector employs custom sandboxing and advanced analysis techniques to effectively block malicious emails, including phishing emails that can serve as entry points for ransomware.
- Trend Micro Apex One™ offers next-level automated threat detection and response against advanced concerns such as fileless threats and ransomware, ensuring the protection of endpoints.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
The IOCs for this article can be found here. Actual indicators might vary per attack.
Like it? Add this infographic to your site:
1. Click on the box below. 2. Press Ctrl+A to select all. 3. Press Ctrl+C to copy. 4. Paste the code into your page (Ctrl+V).
Image will appear the same size as you see above.
последний
- They Don’t Build the Gun, They Sell the Bullets: An Update on the State of Criminal AI
- How Unmanaged AI Adoption Puts Your Enterprise at Risk
- Estimating Future Risk Outbreaks at Scale in Real-World Deployments
- The Next Phase of Cybercrime: Agentic AI and the Shift to Autonomous Criminal Operations
- Reimagining Fraud Operations: The Rise of AI-Powered Scam Assembly Lines

 Complexity and Visibility Gaps in Power Automate
Complexity and Visibility Gaps in Power Automate AI Security Starts Here: The Essentials for Every Organization
AI Security Starts Here: The Essentials for Every Organization The AI-fication of Cyberthreats: Trend Micro Security Predictions for 2026
The AI-fication of Cyberthreats: Trend Micro Security Predictions for 2026 Stay Ahead of AI Threats: Secure LLM Applications With Trend Vision One
Stay Ahead of AI Threats: Secure LLM Applications With Trend Vision One