Virtual Patching: Patch Those Vulnerabilities before They Can Be Exploited
 View Infographic: Minding Security Gaps: How Virtual Patching can Protect Businesses
View Infographic: Minding Security Gaps: How Virtual Patching can Protect Businesses
Vulnerabilities can adversely affect an organization beyond its bottom line. They can also risk the privacy of personally identifiable information (PII) that, when compromised, can have real-life consequences. They undermine not only a company’s reputation — they also undermine the integrity of the infrastructures that store and manage this sensitive data.
The Equifax data breach is a case in point. By exploiting a vulnerability (CVE-2017-5638) in their application framework, attackers gained unauthorized access to its network and systems. The attack exposed PII of 145.5 million U.S. citizens and 15.2 million U.K. customers, and resulted in financial losses expected to reach US$439 million.
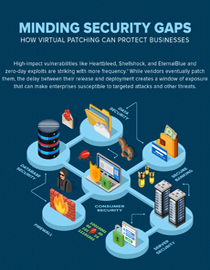
Indeed, a single, vulnerable endpoint, network, server, or application is sometimes all it takes to affect millions. Shellshock, Heartbleed, Poodle, and EternalBlue are just some of the notorious security flaws that leave doors open to data-stealing malware and other attacks. There are countless more — in fact, there were 1,522 publicly reported vulnerabilities reported in 2017. And 929 of these vulnerabilities, which were disclosed through Trend Micro’s Zero Day Initiative (ZDI), were rated to be “critical” or “high” in severity.
[Midyear Security Roundup: 202 Vulnerabilities in Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) Disclosed in 1H 2018]
Patching significantly reduces an enterprise’s exposure to these threats. However, it continues to be a perennial challenge for many organizations. In fact, surveyed organizations took an average of 197 days just to identify a data breach. Preventing data breaches is exacerbated by the added task of monitoring internet-of-things (IoT) devices and industrial-internet-of-things (IIoT) systems. IT and security teams may also find it arduous, if not virtually impossible, to download, test, and deploy patches for all vulnerabilities before they’re exploited — while also keeping gateways, endpoints, networks, and servers up and running.
Zero-day attacks are increasingly striking businesses. But urgent countermeasures like emergency/out-of-band patching and virtualization can cause operational downtime and additional overhead. There’s also compliance issues like the hefty fines that EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) can impose or the stringent patching requirements of the Payment Card Industry (PCI).
[Read: 2017’s Notable Vulnerabilities and Exploits]
Why enterprises take longer to apply patches
Vendors usually patch vulnerabilities, especially when they're considered critical. However, not all organizations and users apply them, or apply them immediately, and IT personnel are often left in a state of flux. The average organization takes over 30 days to patch standard operating systems and applications, and months or years to patch more complex business applications and systems.
- Uptime preservation. IT personnel might be hesitant to patch as it could involve downtime while critical business servers are offline.
- Cost reduction. Migrating from and replacing legacy systems or upgrading applications developed in-house could be costly and time consuming. In effect, IT groups become hesitant to fix or replace something that still functions regardless of its version.
These challenges can expose enterprises to risks such as network, system, endpoint, and security policy compromise, exposure of personal and mission-critical data, and ultimately, reputation damage and financial losses. Addressing these require the right tools. Technologies like virtual patching can help complement existing patch management processes by shielding known and unknown vulnerabilities. Virtual patching acts as an agentless emergency security tool that enterprises can use to quickly remedy vulnerabilities on affected servers and endpoints.
[Read: Patching Problems and How to Solve Them]
How organizations can benefit from virtual patching
- Higher consolidation by offloading virtual patching from individual virtual machines (VMs) to a single security virtual appliance.
- Faster performance by neutralizing security storms and resource contention from simultaneous patching.
- Better manageability by eliminating agents for virtual patching and the need to configure and update each one.
- Stronger security by providing instant-on protection for new VMs coordinated by the dedicated security appliance.
Learn how virtual patching can help provide immediate protection against vulnerabilities and exploits without the costs and downtime in our infographic: Minding Security Gaps: How Virtual Patching can Protect Businesses.
The Trend Micro™ Deep Security™ solution provides virtual patching that protects servers and endpoints from threats that abuse vulnerabilities in critical applications. The Trend Micro™ TippingPoint® system provides virtual patching and extensive zero-day protection against network-exploitable vulnerabilities via DigitalVaccine™ filters. The Trend Micro™ Deep Discovery™ solution provides detection, in-depth analysis, and proactive response to attacks using exploits and other similar threats through specialized engines, custom sandboxing, and seamless correlation across the entire attack lifecycle, allowing it to detect threats even without any engine or pattern update.
Like it? Add this infographic to your site:
1. Click on the box below. 2. Press Ctrl+A to select all. 3. Press Ctrl+C to copy. 4. Paste the code into your page (Ctrl+V).
Image will appear the same size as you see above.
Recent Posts
- The Industrialization of Botnets: Automation and Scale as a New Threat Infrastructure
- From Holiday Snap to Custom Scam in 30 Minutes: How AI Turns Public Photos Into Targeted Attacks
- From LinkedIn to Tailored Attack in 30 Minutes: How AI Accelerates Target Profiling for Cybercrime
- Threat Attribution Framework: How TrendAI™ Applies Structure Over Speculation
- AI Skills as an Emerging Attack Surface in Critical Sectors: Enhanced Capabilities, New Risks
 The Industrialization of Botnets: Automation and Scale as a New Threat Infrastructure
The Industrialization of Botnets: Automation and Scale as a New Threat Infrastructure AI Security Starts Here: The Essentials for Every Organization
AI Security Starts Here: The Essentials for Every Organization The AI-fication of Cyberthreats: Trend Micro Security Predictions for 2026
The AI-fication of Cyberthreats: Trend Micro Security Predictions for 2026 Stay Ahead of AI Threats: Secure LLM Applications With Trend Vision One
Stay Ahead of AI Threats: Secure LLM Applications With Trend Vision One