
Implementing AI technologies introduces new vulnerability points that didn't exist in traditional computing environments. These include malicious cyberattacks initiated by threat actors and vulnerabilities stemming from platform and user behavior.
Table of Contents
AI security vulnerabilities
The Open Worldwide Application Security Project (OWASP) identified a series of vulnerabilities pertaining to artificial intelligence (AI) built on learning language models (LLMs) and GenAI. These include the following:
- Prompt injection
- Insecure output handling
- Training data poisoning
- Model denial of service
- Supply chain vulnerabilities
- Sensitive information disclosure
- Insecure plugin design
- Excessive agency
- Overreliance
- Model theft
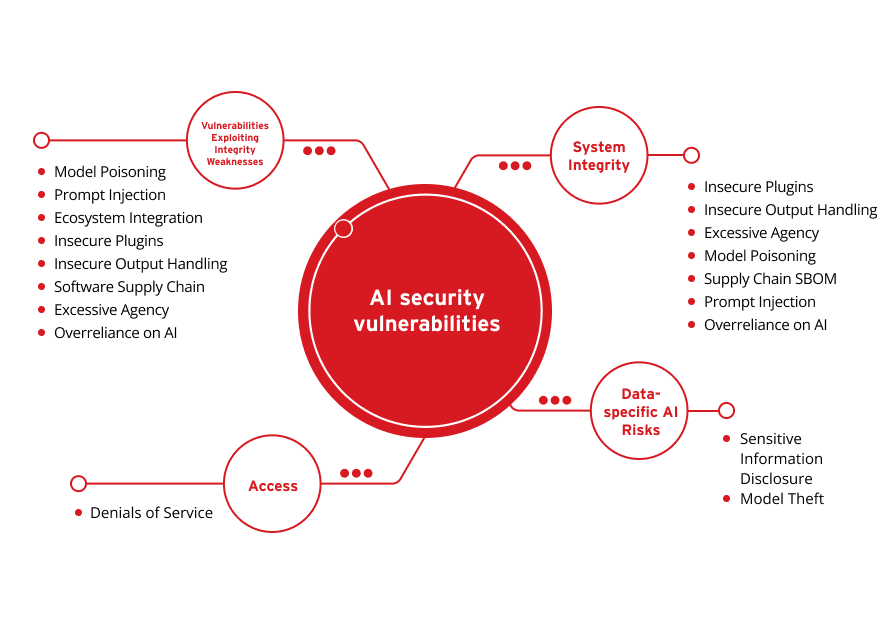
These vulnerabilities can be condensed and simplified further into the following core categories:
Data-specific AI Risks
System Integrity
Access
Vulnerabilities Exploiting Integrity Weaknesses
Sensitive Information Disclosure
Model Theft
Insecure Plugins
Insecure Output Handling
Excessive Agency
Model Poisoning
Supply Chain SBOM
Prompt Injection
Overreliance on AI
Denials of Service
Model Poisoning
Prompt Injection
Ecosystem Integration
Insecure Plugins
Insecure Output Handling
Software Supply Chain
Excessive Agency
Overreliance on AI
Being largely dependent on available data and user input, AI is increasingly targeted by threat actors to breach digital defenses and siphon sensitive information. In a recent Gartner® survey, the five most cited emerging risks of Q1 2024 were revealed. AI-related risks took the top two spots in the form of AI-enhanced malicious attacks and AI-assisted misinformation. As Gartner notes, AI enhancement can “facilitate phishing and social engineering, which enables better intrusion, increased credibility and more damaging attacks.”
Rogue AI
Rogue AI is when AI is misaligned with the goal of the user. This misalignment can be accidental, such as a failure of appropriate guardrails. It can also be intentional, in which case threat actors may seek to subvert a target's AI system or use, or they may attempt to install maliciously aligned AI models within an environment.
Fraud automation
Fraud automation is the synthetic content creation of text, audio, and/or video that exploits business process whether through phishing, business email compromise (BEC) or deepfake videos or audio. Fraud automation can easily scale with AI.
Data governance
AI systems are data reliant. Therefore, the data used in the AI systems—and the live data they touch—must comply with all privacy and fair use regulations, hence the need for proactive and effective data governance that helps to minimize risk.
Learning language model (LLM) security risks
LLMs face critical vulnerabilities including prompt injection that manipulates model behavior, sensitive information disclosure that exposes confidential data, and improper output handling that enables attacks on downstream systems. Other major risks include supply chain vulnerabilities from third-party dependencies, excessive agency granting unnecessary permissions, data poisoning that compromises model integrity, and system prompt leakage exposing confidential instructions. Additionally, vector embedding weaknesses, misinformation generation, and unbounded consumption attacks threaten the security, reliability, and availability of LLM applications.
Generative AI security risks involving user prompts
Generative AI (GenAI) makes use of available past and present data to assist users. Therefore, for tools that require prompting, it’s best to be mindful and proactive about what you put into the prompt field. Some tools allow for users to opt out of data collection, such as ChatGPT’s option to turn off chat history. Depending on the AI governance and usage policies enforced by the industry regulator in question, preventative measures and/or behaviors like these may be a requirement for maintaining compliance.
Inserting financial information, confidential specifics on yet-to-be-released software, personal identifying information (PII) such as personal addresses and contact details, and/or other sensitive data means that information it is freely accessible by the AI application. This data is at risk of being manipulated, shared with others in recommendations from the tool in response to similar queries, and/or stolen by threat actors if the AI’s protection measures are breached. This is particularly a risk when using generative AI tools to assist with ideation or quickly compile large quantities of data, especially if insufficient encryption and security measures aren’t in place.
ChatGPT security risks
As a form of generative AI that delivers text-based responses to user prompts, ChatGPT can be manipulated by threat actors to help disguise and/or strengthen their phishing attempts. Alternatively, the platform itself may be targeted to gain access to—and potentially misuse—user data. This may include drafting phishing emails by leveraging writing samples from the targeted organization or individual, as well as correcting typos, grammar, and language to appear more convincing. There is also a risk of user data theft and/or breaches via prompt injection or jailbreaking.
There are also security risks stemming from use that don’t directly involve threat actors. For example, the information ChatGPT receives from you may be leveraged to train LLMs. There is also the risk of insufficient data encryption, as demonstrated by the ChatGPT MacOS app initially launching with user chats stored as plaintext.
OpenAI security risks
The OpenAI API itself has potential to be targeted by cybercriminals. Although it is SOC 2 compliant and undergoes regular penetration testing, your risk is never entirely eradicated since cyber threats are constantly evolving. A recent Soft Kraft article explores OpenAI data security risks in comprehensive detail, revealing those of particular interest to enterprise users:
- ChatGPT conversation data could be used for model retraining purposes
- Data sent via the API could be exposed internally and externally
- It may be a challenge to ensure General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) compliance
- The use of third-party sub-processors complicate location and data handling
Microsoft Copilot AI security risks
With support for Microsoft 365 applications, Microsoft Copilot AI is readily available to users. Moreover, at the hardware level, the latest Copilot+ branded PCs ship with dedicated physical Copilot keys to encourage even quicker user input. These streamlined access measures may introduce security risks if sensitive information is made available to Copilot, just as with other generative AI tools. Should permissions not be correctly set, or if AI-generated documents don’t have the proper privacy settings enabled, you may also find yourself facing confidential data leaks and/or breaches. The same applies to user access management. Lastly, attacks on the platform itself could enable threat actors to modify how it accesses and shares your data.
Who can help us manage our AI security risks?
The continuous evolution of AI innovation requires security that is proactive and backed by 35 years of industry-leading threat intelligence, 20 years of pioneering AI development, and unmatched vulnerability protection—that is Trend Vision One™ AI Security.
With our AI Security solution, we protect your critical business workloads, including your entire AI stack, while enhancing your overall security posture. Powered by Trend Cybertron, our AI Security predicts attack paths and detects anomalies while defending against deepfakes and AI-generated attacks to eliminate security blind spots and transform AI security into a catalyst for innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the security risks of AI?
AI security risks include data breaches, adversarial attacks, model manipulation, privacy violations, and misuse in cybercrime or surveillance.
Who is the real father of AI?
John McCarthy is widely recognized as the father of AI for coining the term and pioneering artificial intelligence research.
What are the 4 risk categories of the AI Act?
The AI Act defines four categories: unacceptable risk, high risk, limited risk, and minimal risk for AI systems.
What is the 30% rule for AI?
The 30% rule limits AI automation to 30% of tasks, ensuring human oversight and accountability in decision-making processes.
How is AI impacting security?
AI improves threat detection and cybersecurity but also introduces vulnerabilities like deepfakes, automated attacks, and data exploitation risks.
Is my AI system high risk?
Your AI system is high risk if it affects safety, fundamental rights, critical infrastructure, or involves sensitive personal data.