Modern Ransomware Shakes Up Banking, Government, Transportation Sectors in 1H 2021
Top three industries observed with the most ransomware attack attempts:
- Banking
- Government
- Transportation
Total ransomware attack attempts across enterprise customer base:
3,600,439
Average ransom payment for organizations in Q2:
$136,576 (Source: Coveware)
The prevalence and impact of modern ransomware attacks presented new challenges for decision makers in the first half of the year. This report collates detections from Trend Micro static and dynamic security layers from over 20 industries, some of which came from ransomware families reportedly used by big game hunters. The report also breaks down the potential financial, operational, and reputational impact of modern ransomware if they fall victim to an attack. From January to June 2021, ransomware operators have turned their attention to critical industries — namely banking, government, and transportation — which, when incapacitated, could affect national security, economic stability, public health or safety, or any of its combinations.
In this report, you will find:
- Ransomware insights for the banking industry in 1H
- Ransomware insights for the government sector in 1H
- Ransomware insights for the transportation industry in 1H
- Typical initial access points for REvil, a common threat to BGT
- The real costs of a ransomware attack
- An overview of ransomware in 1H 2021
- How to deter ransomware and minimize its impact
Banking, government, and transportation industries as big game targets
Our sensors showed that the banking, government, and transportation (BGT) sectors ranked as ransomware operators’ most targeted industries in the first half of 2021. While premodern ransomware such as dormant WannaCry variants were still highly tracked by our sensors, modern ransomware has made its way into this report's list of ransomware families with most detections. REvil (also known as Sodinokibi) has been consistently detected in BGT. Threat actors have been known to use this ransomware in modern ransomware attacks, which are targeted or advanced persistent threat (APT)-like in nature. These attacks also often use double extortion techniques that threaten victims with publicizing stolen sensitive data if they don’t pay the ransom.
Even prior to the drastic business shifts caused by the pandemic, these groups inherently have unique business characteristics that make for a wide attack surface: the number of offices in different parts locally, the number of partners and suppliers globally, dispersed locations of remote workers, restrictions that inhibit cybersecurity measures’ implementation, the layers of services they offer the public, and the likelihood of these industries paying the ransom to protect their customers’ data and restore systems at the soonest.
Banking
Banks are attractive targets for ransomware operators because apart from offering various financial services, the types of information that can be stolen from the banking industry (such as credit card and bank account details) are highly sensitive and profitable. Trend Micro sensors detected over 130,000 ransomware attack attempts in the sector, with banks in the Americas as having the highest number of ransomware counts recorded in the first half of the year.
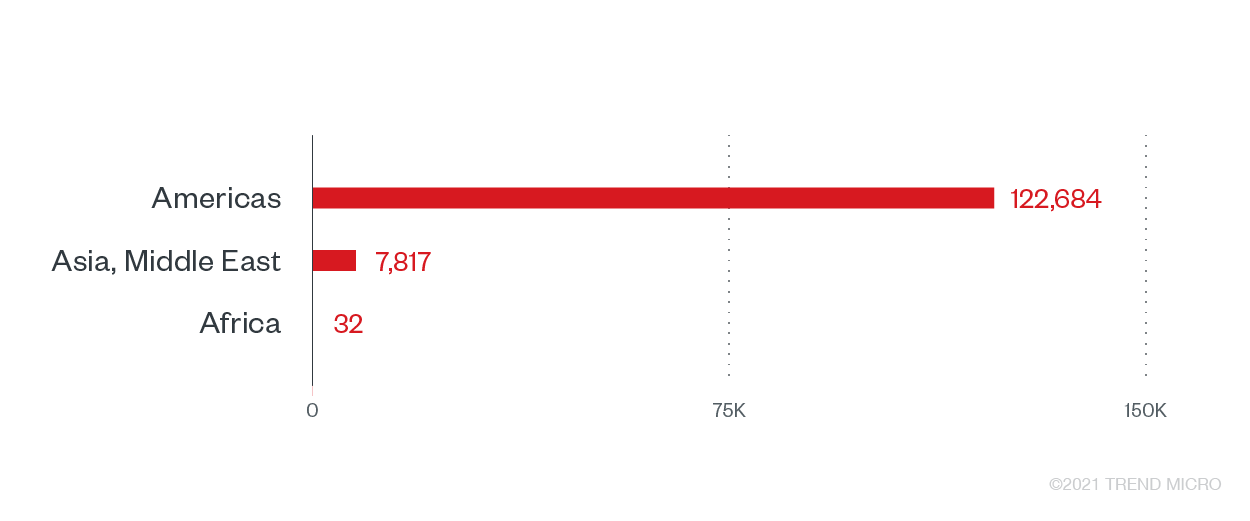
Ransomware attack attempts in the banking industry by region
The lucrative business of banks makes it a prized target for sophisticated attackers who have been known for profiling and conducting financial health studies of organizations to determine the next potential targets. The most recent attack against the industry was reported in June, where a New Jersey bank was allegedly hit by Avaddon, another modern ransomware family. The active modern ransomware families we found in this sector for the first half of the year are REvil and Crysis (aka Dharma).
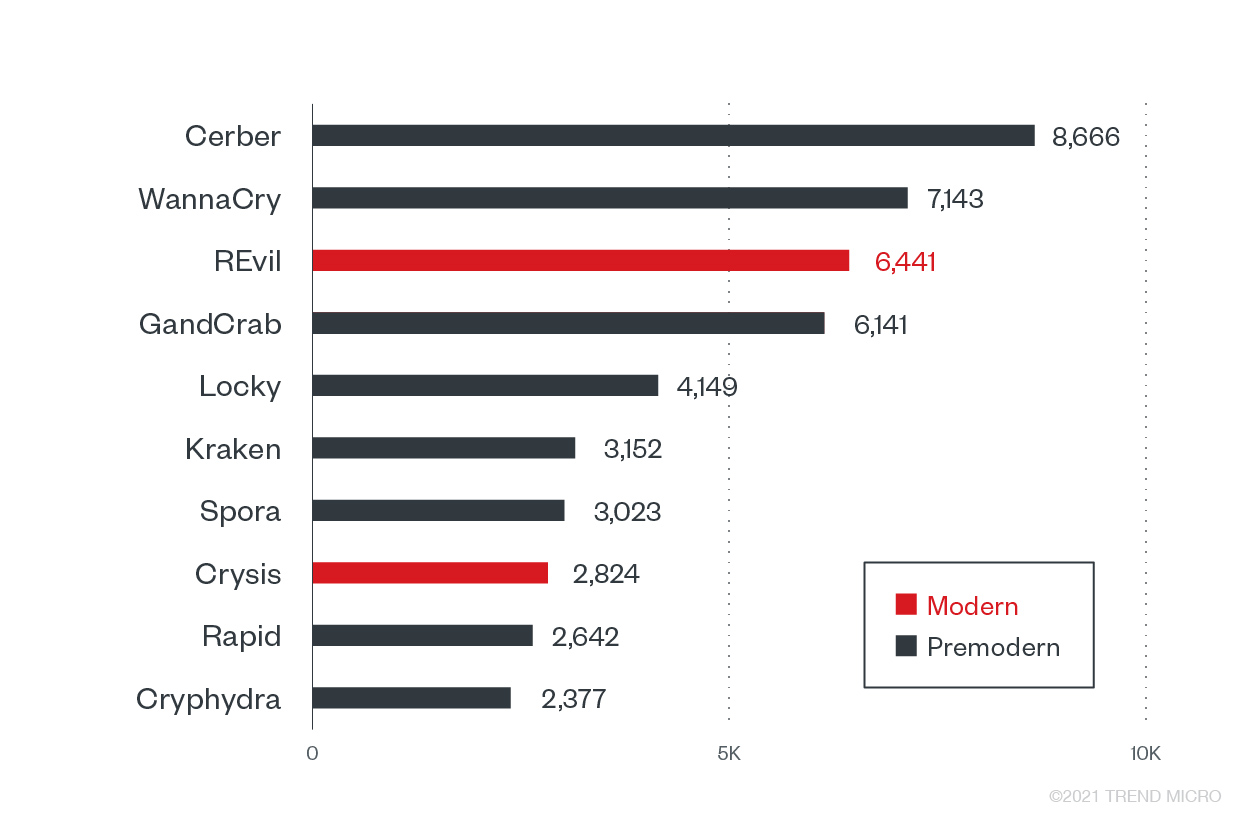
Top 10 ransomware families with the most detected attack attempts against the banking industry
Potential impact of attacks on the banking sector:
- On average, a consumer is estimated to own five accounts; an attack on one branch’s employee or infrastructure could affect at least 9,090 adults and more than 45,000 accounts.
- Small- and mid-sized banks can be used to attack more organizations within and outside the financial industry via different service platforms. Stoppage or closure of these local branches can affect communities and other critical sectors significantly.
- Attacks and ransom payments could potentially violate other legal mandates such as Know Your Customer (KYC), Anti-Money Laundering (AML), and Combatting Financing of Terrorism (CFT) laws in the US.
Government
The Center for Internet Security’s (CIS) Multi-State Information Sharing & Analysis Center (MS-ISAC) cited that its 11,000 members reported 75 ransomware attacks across the US between January to June. Meanwhile, a global survey conducted in early 2021 showed that entities in the central government and non-departmental public body (NDPB) are more likely to experience ransomware double extortion attacks.
Government agencies make attractive ransomware targets for various reasons. Stored data of citizens, such as social security numbers and voters’ information, serve as low-hanging fruit for data theft and abuse. Modern ransomware operators capable of stealing information prior to ransomware implementation could make additional profit by selling the stolen data somewhere else. Trend Micro recorded more than 82,000 ransomware attack attempts, with the most counts in the African region’s government systems, followed by those in Asia and the Middle East.
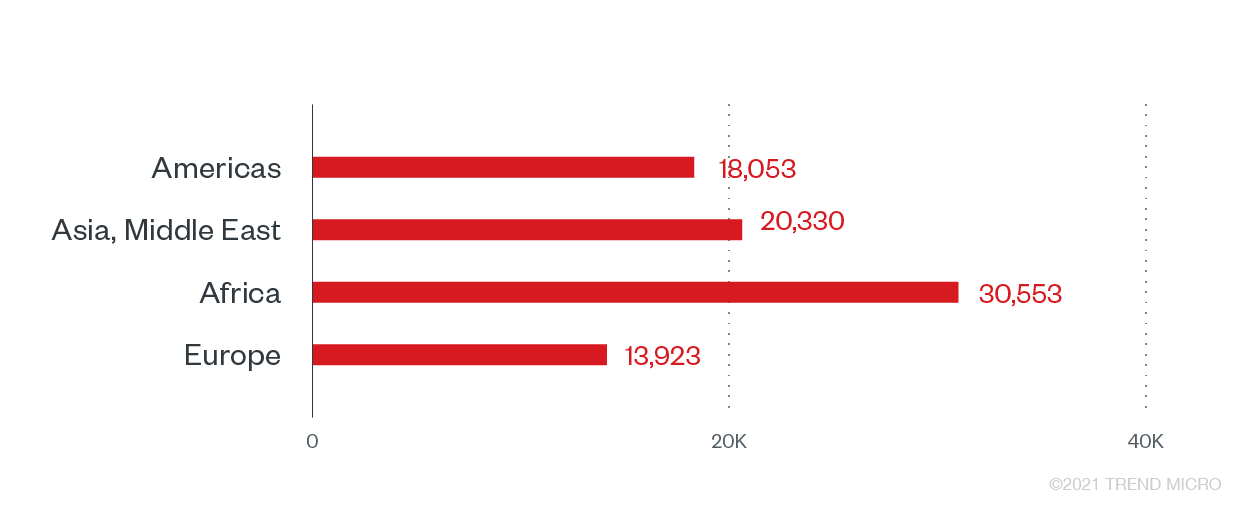
Ransomware attack attempts against the government sector, by region
Premodern ransomware made up the bulk of ransomware triggers from the government sector, but modern ransomware families, particularly REvil and Crysis, were also prominent in this sector in the first half of 2021.
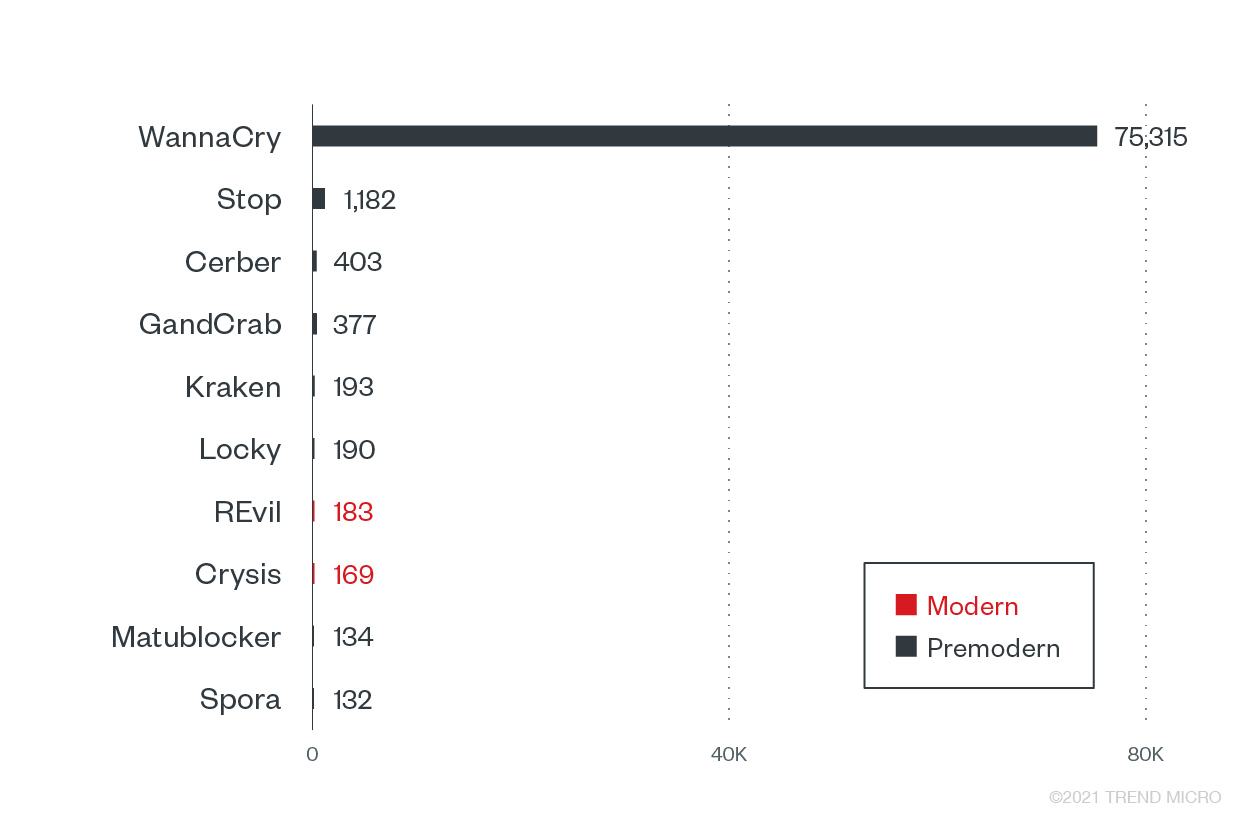
Top 10 ransomware families with the most attack attempts against the government sector
Potential impact of attacks on the government sector:
- Largest paid ransom: $592,000 (2019, Florida) (Source: Sungard Availability Services)
- Largest amount paid for recovery post-ransomware attack: $18 million (2019, Baltimore) (Source: Sungard Availability Services)
- Local governments serve as an intersection and reflection of a wider national security posture. An attack on a local government office’s infrastructure or individual affects local, national, and digital security such as taxes, financials, identification, investments, and public services, among others.
- Fiscal and audit mandates restrict the potential development of resources and capabilities of agencies to prepare, respond, and recover from ransomware attacks on their own. This can prolong service downtimes, affecting residents without local or municipal functions such as traffic, sanitation, and healthcare.
Transportation
Weekly ransomware attacks in the transportation industry have increased by 186% from 2019 to 2020. Given the interconnected nature of aviation, maritime, logistics, and ground shipping and transport, an abrupt disruption of normal functions ensures extensive impact on businesses, people’s welfare, and national security, and a potentially hefty payday for attackers. While vehicles’ own IT systems can be infected and attacked, it is their land/shore-based systems that remain vulnerable: systems and devices in data centers and offices used to manage details for operations are viable targets. Trend Micro sensors detected over 32,000 ransomware attack attempts in this sector, with the most counts observed in Asia and the Middle East.
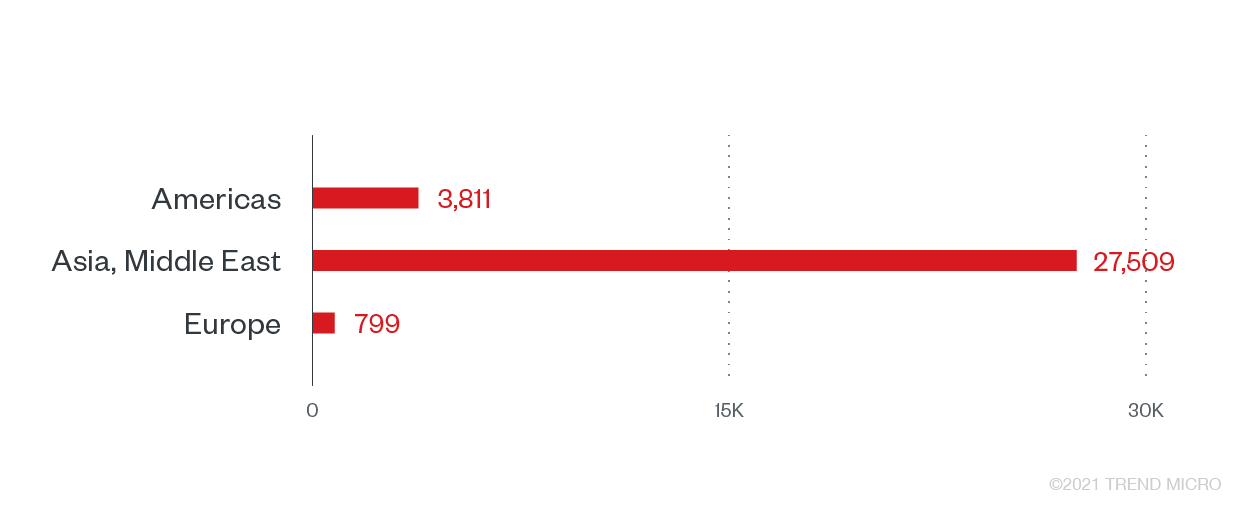
Ransomware attack attempts against the transportation industry by region
The first publicly known ransomware attack in the US freight rail sector was reported in January 2021. OmniTRAX, a US-based railroad transportation company, confirmed that it was hit by the Conti ransomware gang. The attackers reportedly published stolen data on a leak site – a common double extortion tactic used by modern ransomware operators. Meanwhile, one of the most recent attacks against the transportation industry involved Death Kitty ransomware, nearly causing the operations of South African ports to a complete halt.
With the high number of modern ransomware families targeting the transportation sector, it is highly likely that threat actors banked on organizations becoming desperate for operations to resume in the event of a disruption. As the priority is on minimizing potential downtime during incidents, transportation companies are more likely to pay the ransom to resume operations as soon as possible. The modern ransomware families highly observed in this sector are REvil, Ryuk, Conti, and DarkSide.
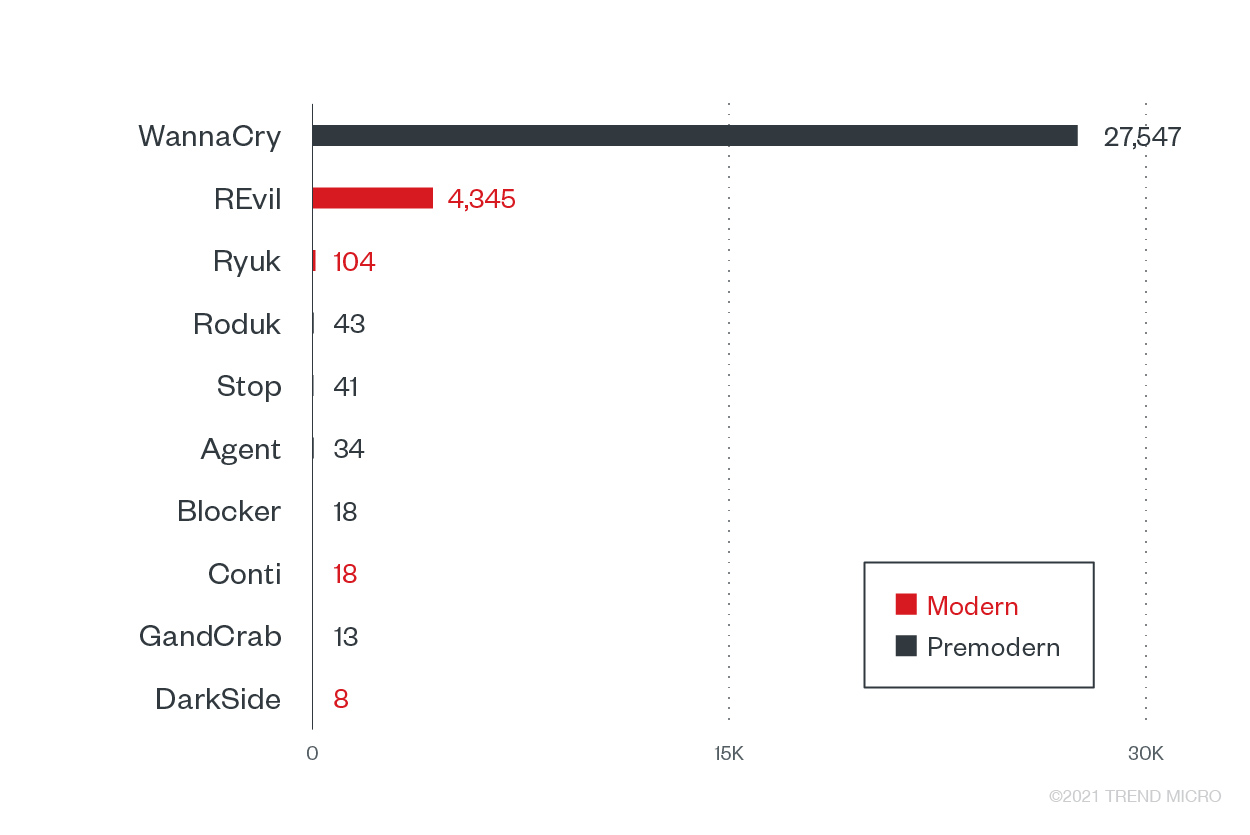
Top 10 ransomware families with the most attack attempts against the transportation industry
Potential impact of attacks on the transportation sector:
- The transportation sector ties together all supply chains worldwide, making it a tempting target for all kinds of malicious profiteering activities. A ransomware attack on one of the major transit systems could give attackers valuable information encompassing the Eastern and Western hemispheres, potentially crippling economies and supply chains.
- The sector lies at the heart of businesses’ and economies’ supplier-consumer delivery interdependence, making it a significant point of infection after infiltration.
- The sudden interruption of public transportation and its related services can cause real threats to life such as those for emergency services, road accidents, and infrastructure damage (e.g., trains’ schedules and direction mishaps).
Typical initial access points for REvil, a common threat to BGT
REvil is one of the modern ransomware families that have been detected consistently in BGT. The decentralized tasks of the group and affiliates allow simultaneous infiltrations and deployments using multiple techniques and tools. REvil operators typically gain initial access to organizations' IT environment through spear-phishing emails, remote desktop protocol (RDP) or valid accounts, compromised websites, and unpatched vulnerabilities. REvil's complete attack tactics and techniques can be found in this article.
Organizations need to ensure that the abovementioned entry points are properly secured and monitored to mitigate modern ransomware techniques, such as those employed by the REvil group, and prevent malicious components from spreading within the network.
The REvil group has been behind massive ransomware attacks in 2021. Meat supplier JBS and IT management and software provider Kaseya were among the group's high-profile victims in recent months. JBS' production operations were reportedly disrupted in the US, the UK, Canada, and Australia, and the company paid US$11 million to resolve the ransomware attack. Meanwhile, REvil infected almost 1,500 of Kaseya’s customers and demanded US$70 million from the company for a decryption key. However, the company confirmed later on that they were able to obtain the key from a trusted third party.
REvil’s documented entry vectors
- Spear-phishing emails
- Remote desktop protocol (RDP) access or valid accounts
- Compromised websites
- Unpatched vulnerabilities
The real costs of a ransomware attack
Apart from the running costs of downtime and ransom paid, recovery via decryption keys do not guarantee a return to normal operations. However, the true cost of a ransomware attack becomes apparent during recovery.
Financial: Operations downtime, fines, and recovery
Considering that not all companies report attacks, the number of victims and accumulated amounts of ransom paid may be higher than what official reports show. But according to Coveware, the average ransomware payments for organizations reached US$136,576 in Q2 2021. While large enterprises can afford cyber insurance, a single attack on an SMB may be enough to put them out of business altogether. Reports show that the average ransom demanded from modern ransomware attacks reached over $5 million. In addition, potential regulatory fines and litigation settlements also add up to the costs of payments and recovery. The average downtime for every ransomware attack has increased to 23 days compared to 16 days in 2020, compared to 12 days in 2019, and initial system, file, and (in some instances) infrastructure recovery adds to downtime expenses.
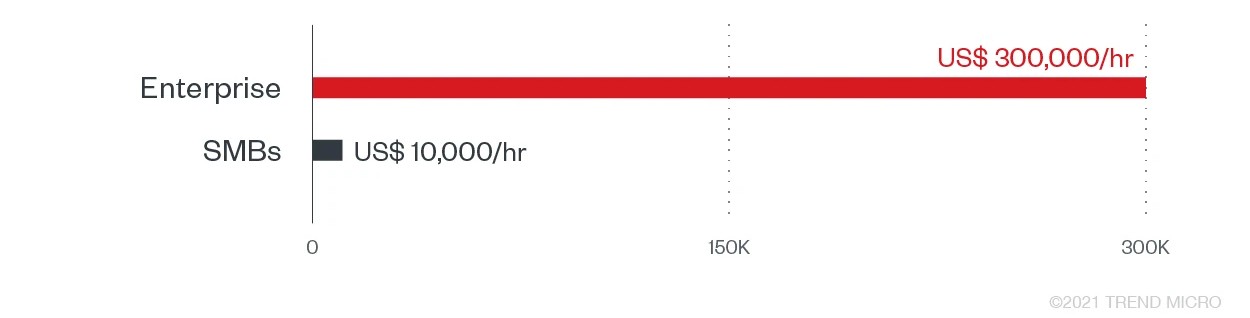
Estimated downtime cost per hour during and after a ransomware attack according to a 2021 Webroot report
Reputation damage
In a study of ransomware attack impact on businesses, 53% of the companies who participated in the study said ransomware attacks not only included losses in revenue, but also unplanned employee layoffs and damage to the brand due to the diversion of allocations for recovery. From a consumer perspective, loyal subscribers can also redirect their attention to the competition when cyber incidents arise. In a study analyzing customers’ loyalty to brands, 77% of respondents are able to retract their loyalty to brands compared to prior years, and 61% are able to switch some or all of their business to another provider within a year.
Modern ransomware’s extortion methods come in different phases and has progressed over time. Aside from locking systems and files, these are some of the other techniques ransomware operators employ to threaten victims and inflict reputational damage on organizations:
- Posting data in leak sites
- Posting data in underground forums and blogs
- Distributed denial of service (DDoS)
- Direct contact of customers, victim’s business partners, and the media
- Auction of stolen data
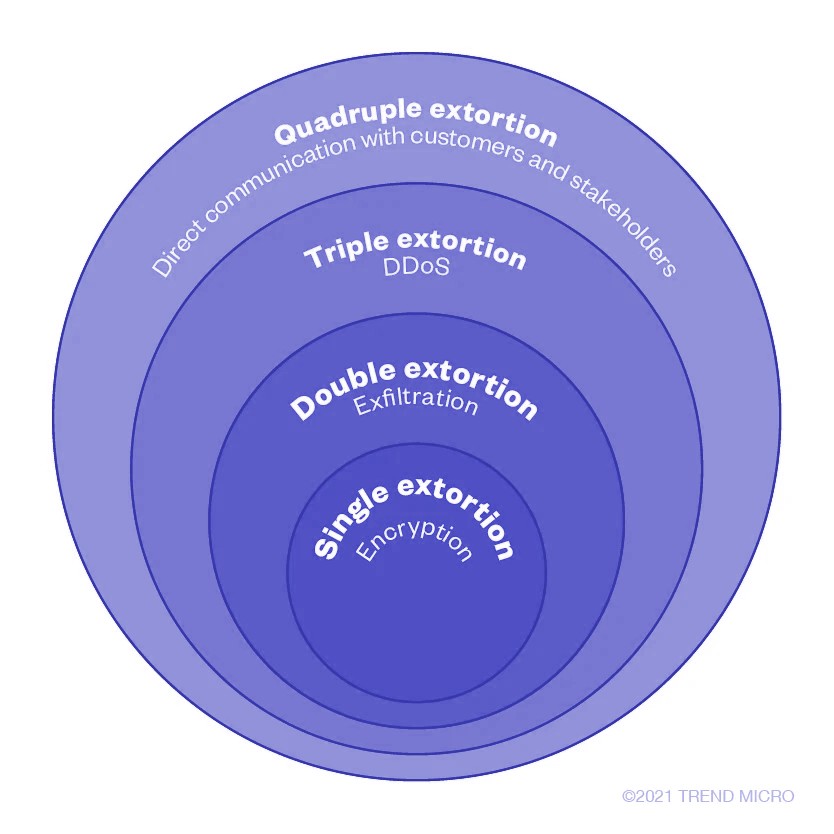
The four phases of ransomware extortion
Cyber insurance sector’s maturity
Cyber insurance companies are also noting that premiums have gone up and requirements for coverage should have a security baseline. Facing scrutiny that cyber insurers’ presence for payments are causing more ransomware attacks, an adapting industry is beginning to agree that companies should comply with security prerequisites before giving ransomware coverage claims. Certain security technologies, practices, and precautionary measures have to be in place, acknowledging that investments in prevention and recovery is still cheaper and better than dealing with attack costs and the aftermath.
Overview of 2021 1H Ransomware Detections Across Industries
Other critical sectors did not go unscathed. We observed the total ransomware attack attempts against enterprises were at 3,600,439, with BGT closely followed by other critical sectors that experienced major adjustments in the past months for business continuity. Moreover, Trend Micro observed the addition of 49 new ransomware families during the first half of the year.
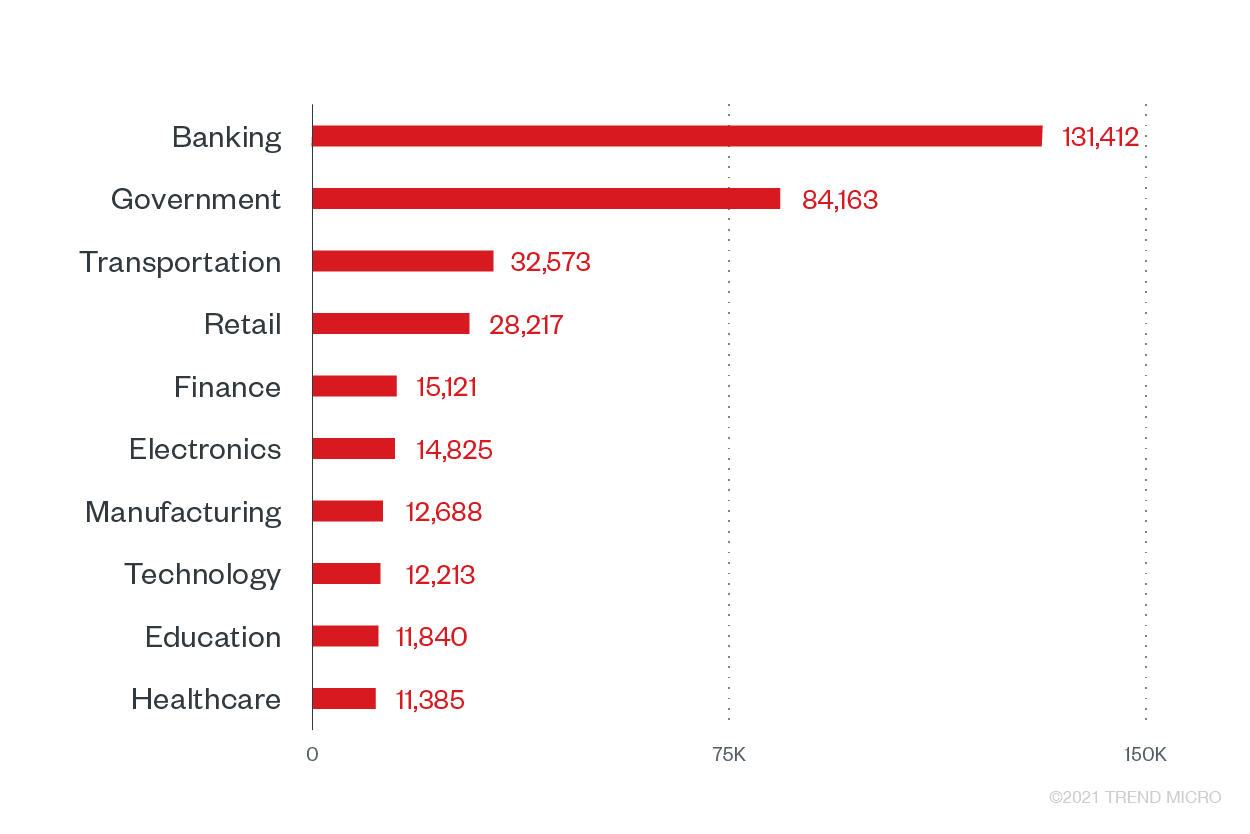
Top 10 industries with the highest ransomware attack attempts in 1H 2021
The industries following the BGT sectors are also considered critical, especially given their respective participation in serving the public during the pandemic and inoculation procedures.
We also noted the countries with the highest counts of ransomware attack attempts during the first six months of the year, with majority of the attempts observed in the Americas.
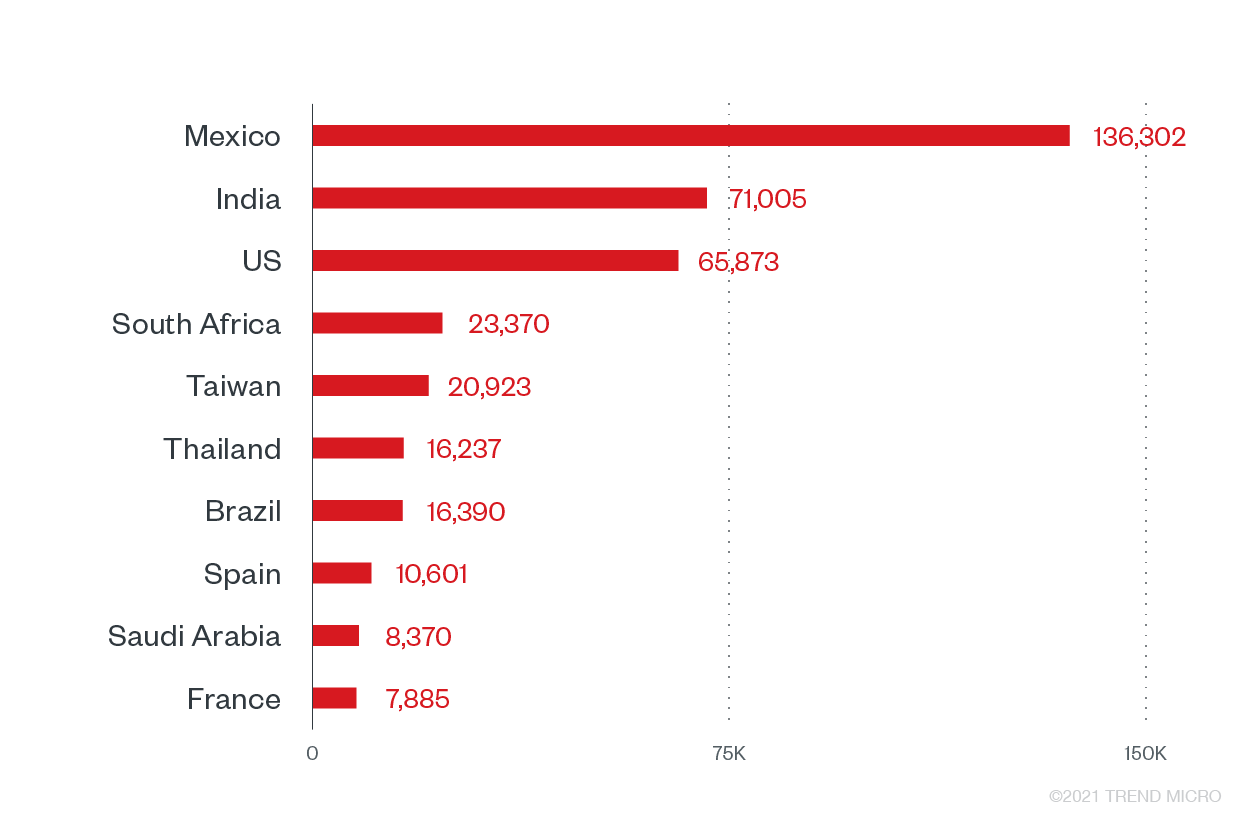
Top 10 countries with the most ransomware attack attempts
As ransomware operates on a global scale, the inclusion of these countries as the most targeted countries in 1H can be attributed to the number of multinational companies and business interests stationed in them.

Top ransomware families in 1H 2021
The dominant presence of premodern ransomware families such as WannaCry point to the latency of its components in systems, implicating the longevity and persistence of worm-based network variants due to unpatched devices. While this is expected to continue decreasing as more systems are replaced with better technologies and solutions, industries are strongly advised to pay attention to detecting and blocking the growing numbers of modern ransomware deployed.
How to deter ransomware and minimize its impact
Persistent ransomware groups will find ways to attack organizations and industries, and a ransomware compromise is no longer a matter of “if” but “when.” Organizations can mitigate the risks of ransomware with these best practices:
- Continuous education and awareness programs. Implement a consistent learning and awareness program for all the employees and partners of the organization. Get IT, development, security, and incident response (IR) teams to spearhead security programs so everyone recognizes their roles in maintaining the systems’ security.
- Invest in cross-layered detection and response solutions. Enable technical improvement and technological solutions that can anticipate and respond to ransomware activities, techniques, and movements before it can launch an attack. An integrated and cohesive solution enables simultaneous monitoring and tracking of all the potential entry points. Emails, servers, networks, endpoints, mobile, cloud storage, and workloads should have multilayered protection systems that can keep and prevent ransomware from running. A cybersecurity platform that provides visibility into the early activities of modern ransomware attacks, such as Trend Micro Vision One™️ with Managed XDR, helps detect and block ransomware components to stop attacks before threat actors are able to exfiltrate sensitive data.
- Create an incident response (IR) team and playbook for prevention and recovery. Invest in IR teams, as well as a playbook applicable to the company’s make-up and covers a broad base. IR playbook frameworks allow an organization to plan and prepare for attacks such as ransomware and breaches. Constantly update the security and incident playbook as a guide that everyone can follow when the need arises.
A cyber incident implies that all preventive measures and enabled defenses have been exhausted and have failed. If properly structured and implemented, an IR plan included in the playbook activates the team to prioritize, contain, and stop a cyberattack even without identifying the actors behind the compromise. By qualifying and identifying the gap or threats that breached the defenses, an IR team and playbook can ensure that:- Procedures are in place to enable a business to run again after an attack.
- Forensics can look into the incident in-depth after the threat has been terminated.
- The same incident or threat will not happen again.
- Practice attack simulations. Include a realistic simulation for cyberattacks that everyone in the workplace can use. A swift response strategy from everyone can minimize the impact and damage at crucial points. These simulations can give decision-makers, security, and IR teams an idea of what to anticipate and prepare for, such as the potential gaps for abuse and pressure points in systems and with people.
Download the executive summary. To find more insights on ransomware, visit Trend Micro Research, News, and Perspectives.
Like it? Add this infographic to your site:
1. Click on the box below. 2. Press Ctrl+A to select all. 3. Press Ctrl+C to copy. 4. Paste the code into your page (Ctrl+V).
Image will appear the same size as you see above.
Ultime notizie
- The State of Criminal AI: Market Consolidation and Operational Reality
- How Unmanaged AI Adoption Puts Your Enterprise at Risk
- Estimating Future Risk Outbreaks at Scale in Real-World Deployments
- The Next Phase of Cybercrime: Agentic AI and the Shift to Autonomous Criminal Operations
- Reimagining Fraud Operations: The Rise of AI-Powered Scam Assembly Lines
 Complexity and Visibility Gaps in Power Automate
Complexity and Visibility Gaps in Power Automate AI Security Starts Here: The Essentials for Every Organization
AI Security Starts Here: The Essentials for Every Organization The AI-fication of Cyberthreats: Trend Micro Security Predictions for 2026
The AI-fication of Cyberthreats: Trend Micro Security Predictions for 2026 Stay Ahead of AI Threats: Secure LLM Applications With Trend Vision One
Stay Ahead of AI Threats: Secure LLM Applications With Trend Vision One