Risk Management
A Necessary Digital Odyssey of RPA and AI/ML at HUD
Explore two RPA and AI/ML use cases at HUD during the operational challenges of the longest US Government shutdown, a rigid legacy IT environment, and complex federal regulations.
The U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) faced immense operational challenges, compounded by the rigidity of its legacy systems. Navigating through a mainframe-driven environment and the unforeseen hurdles of the 2018 and 2019 US Federal government shutdowns, which lasted 35 days — the longest in US history — HUD embarked on a transformative journey with Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning (AI/ML).
Challenge 1: Major Citizen Impacts from US Government Shutdown + Legacy Technology
Section 202 and Section 811 are HUD programs providing affordable housing to elderly and disabled individuals, respectively. Contracts like Project Rental Assistance Contracts (PRACs) are integral to these programs, offering government funding and operational subsidies to housing providers.
Due to the mainframe legacy environment of housing systems associated with these government funding programs, human monitoring and manual notifications have been the operating routines since the systems were built decades ago.
During government shutdowns, Federal employees are prohibited from working, and the inability to notify providers of their expiring contracts and renew these contracts disrupts the flow of funds, jeopardizing housing stability for elderly and disabled residents.
RPA in Impact for Automated Monitoring and Notification
The government shutdown revealed the fragility in HUD's contract management processes. In response, we innovatively deployed RPA to automate the monitoring of housing contract expirations, overcoming the constraints of its outdated systems.
It is expensive and time-consuming to complete mainframe migration. Before a full modernization effort can occur, for repetitive monitoring/alerting/notification of funding contracts, we built and prototyped a UiPath bot within a few weeks, spending a few more weeks to validate with stakeholders, capability documentation, and cybersecurity assessment and approval.
We deployed the bot in less than 90 days. The most time-consuming task was completing the government procurement process to acquire licenses and support. This swift implementation of RPA showcased a significant leap towards operational resilience and efficiency.
Challenge 2: Federal Regulation Creates Significant Challenges to Digital
Transformation Federal CIOs face significant challenges in procurement and HR, particularly in the context of transforming legacy IT environments:
Procurement: Navigating complex federal acquisition regulations often leads to lengthy procurement cycles, limiting the ability to quickly adopt new technologies. This can hinder efforts to modernize legacy systems, which often include outdated mainframes, and can delay the implementation of essential cybersecurity measures and data protection protocols.
HR: Recruiting individuals with the right technical expertise and management skills is challenging due to stringent federal hiring practices and competition with the private sector. The lack of skilled personnel can impede the progress of IT transformations, including securing sensitive data, ensuring transparency in government spending, and enhancing citizen services.
AI/ML and Big Data Impact for Process Re-engineering of HR and Procurement
These challenges were no different at HUD. To understand operating constraints, federal regulation impacts, timelines, workflows, and bottlenecks of acquisition and hiring, we turned to AI/ML and big data analysis.
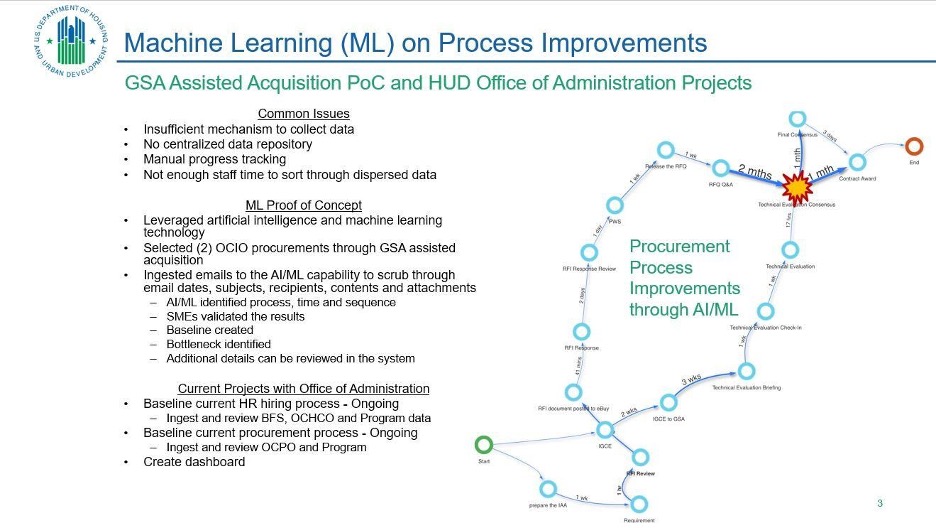
We leveraged this artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) capability called LiveObjects, which allows HUD to ingest an enormous amount of structured and unstructured agency procurement and HR data; the system is also designed to learn the intricacies of US Federal Government hiring and procurement regulations and processes through orchestrating the acquisition and hiring workflow; additionally, we spent time ensuring proper cybersecurity measures were in place for sensitive data; and developed data visualization capabilities mapping out processes, time taken, and identification of bottlenecks.
We were able to demonstrate performance gaps in these functions by tapping into the power of AI/ML, with learned scenario recommendations on improving isolated bottlenecks or greatest time or resource saving flows.
It started out as a proof of concept of (2) GSA-assisted acquisitions, analyzing procurement steps, timeframes, and identifying bottlenecks. With the demonstrated success, we partnered with our HR and Procurement counterparts to complete analysis of all the recruitments and procurement actions taken from 2018 to 2020 and subsequently took corrective action steps. Having the right technology and skilled personnel is crucial for modernizing IT infrastructure, securing data, ensuring accountability, executing government programs efficiently, and improving stakeholder experiences with government services.
In the next article, we will examine the ultra-complex case of leveraging AI, ML, RPA to expedite successful digital transformation in the $1.3 Trillion FinTech Platform in FHA Catalyst.

